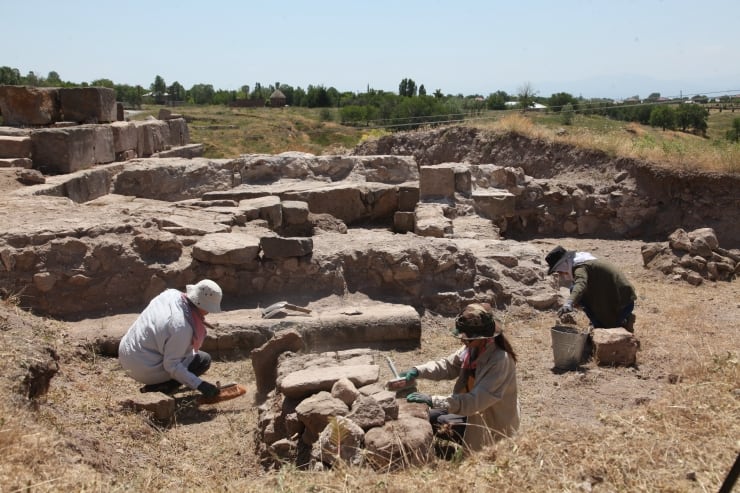
In the easternmost part of Türkiye, in the İpekyolu district of Van, archaeological excavations at the castle ruins on the foothills of Mount Erek have uncovered cuneiform inscribed pithoi used for storing oil, grain, and beverages during the Urartian period.
The castle ruins, which are considered one of the important settlement sites of the Urartians on the foothills of Mount Erek, have seen the start of archaeological excavations.
The work is being conducted under the permission of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, led by the Van Museum, with scientific consultancy from Assoc. Prof. Dr. Rıfat Kuvanç, a faculty member of the Department of Art History at Iğdır University.
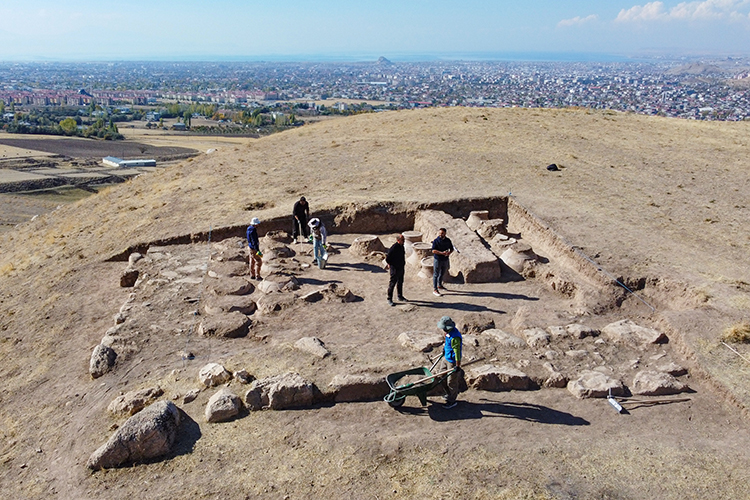

The excavation team found 42 pithoi in the southeastern part of the castle ruins, in an area believed to have been used as a storage facility during the Urartian period.
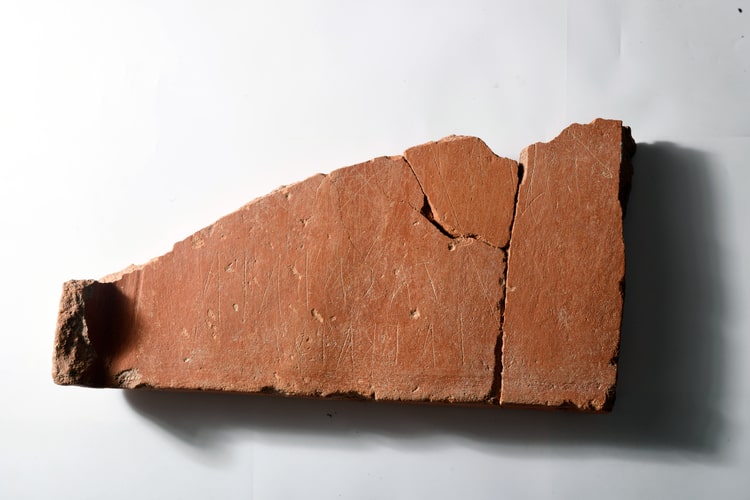
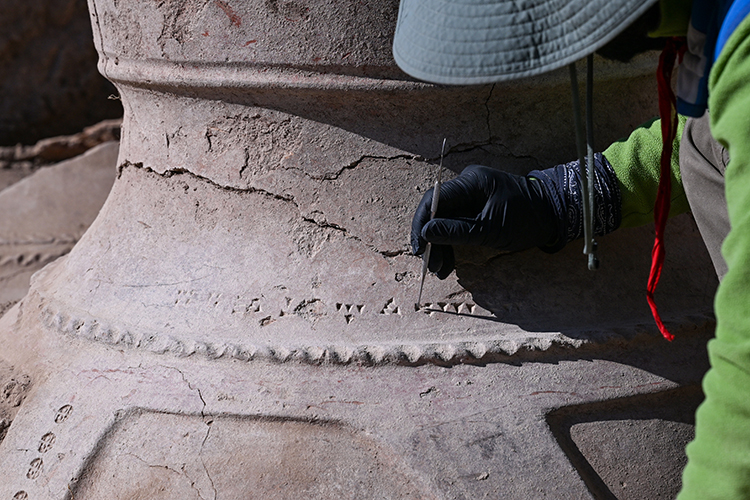
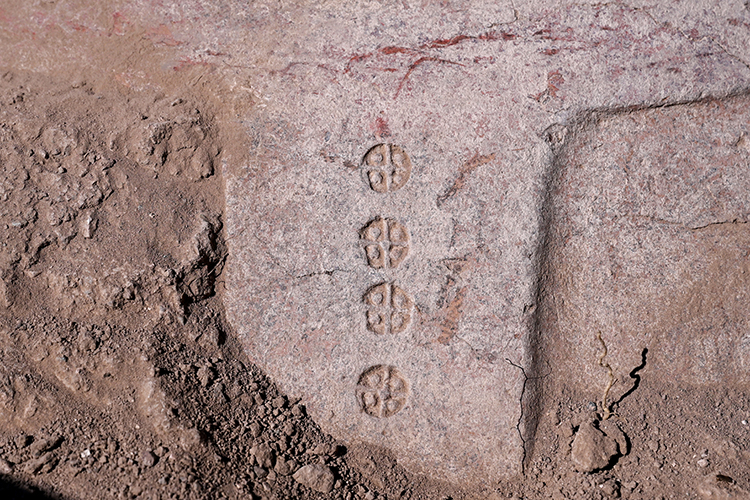
It was determined that the pithoi, which are scaled with cuneiform inscriptions on them, were used for the storage of oil, grain, and beverages during the Urartian period.

Excavation leader Assoc. Prof. Dr. Rıfat Kuvanç stated, “This is one of the places where Urartian research is conducted. It is a site we visit frequently. Our research and the data we have obtained indicate that this was a significant Urartian project. As a result of the 10-day excavation we conducted this year, we have uncovered an important facility. In this facility, we discovered 42 storage vessels known as pithoi. While there are similar storage areas in Urartian sites, we have found a storage facility of this large scale for the first time in a location that overlooks Van and the plain.”

He stated, “The Urartians were an agricultural society. The storage of agricultural products is involved here. These pithoi have cuneiform inscriptions and various groups of symbols. These symbols provide information about the stored products. It is particularly understood that sesame oil and wines were preserved in them. Additionally, the cuneiform inscriptions contain information about the measurement units of the pithoi. With this information, we can learn how much product was stored in the storage area. We can say that this is a large center for the storage of agricultural products in the Van Plain. This year, we are working in a limited area. Next year, we aim to uncover other architectural features of the castle.”

Cover Photo: Mesut Varol/AA