A new discovery has been made about how the 5,300-year-old mummy known as Ötzi the Iceman, found frozen in the Alps, was tattooed. Scientists have found evidence that Ötzi’s 61 tattoos were made using a single-ended tool.
The results of the study, conducted by an international team of archaeologists, historians and tattoo artists, were published in the European Journal of Archaeology.
Previous research had suggested that Ötzi’s tattoos were made with more than one tool. But new analysis shows that the tattoos were made with a single tool, possibly a metal needle or thorn.
When the Iceman was found, he had numerous tattoos on his body, lower back, abdomen, lower legs and left wrist.
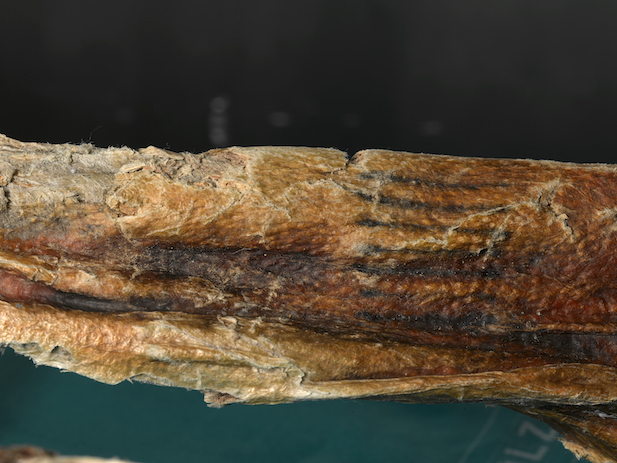

Previous research has suggested four possibilities: hand poking, subcutaneous tattooing, hand touching and incision. Because most of the tattoos contained short, straight lines, many have suggested that the tattoos were likely done using the incision method, in which an incision is made in the skin using a sharpened object, such as a stone, and a coloring material, such as ash, is inserted into the incision.
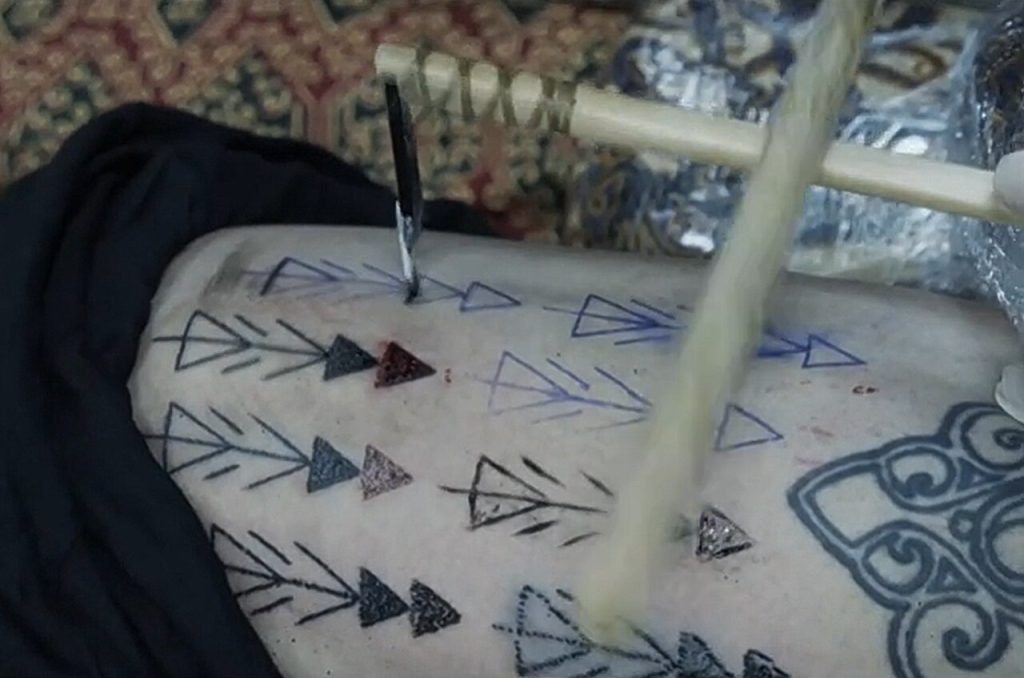

By examining Ötzi’s tattoos under a microscope and comparing them with modern tattooing techniques, scientists have found evidence of single-ended tool use.
To find out the technique used in Ötzi’s tattoos, the researchers recruited a tattoo expert as a volunteer subject. The expert tattooed his leg with four different techniques similar to Ötzi’s. After the tattoos healed, the researchers took close-up photos of the new tattoos and compared them with Ötzi’s. In the end, the tattoos made by hand, dot by dot, were the most similar to Ötzi’s. This suggests that the Iceman’s tattoos were most likely made using this technique.
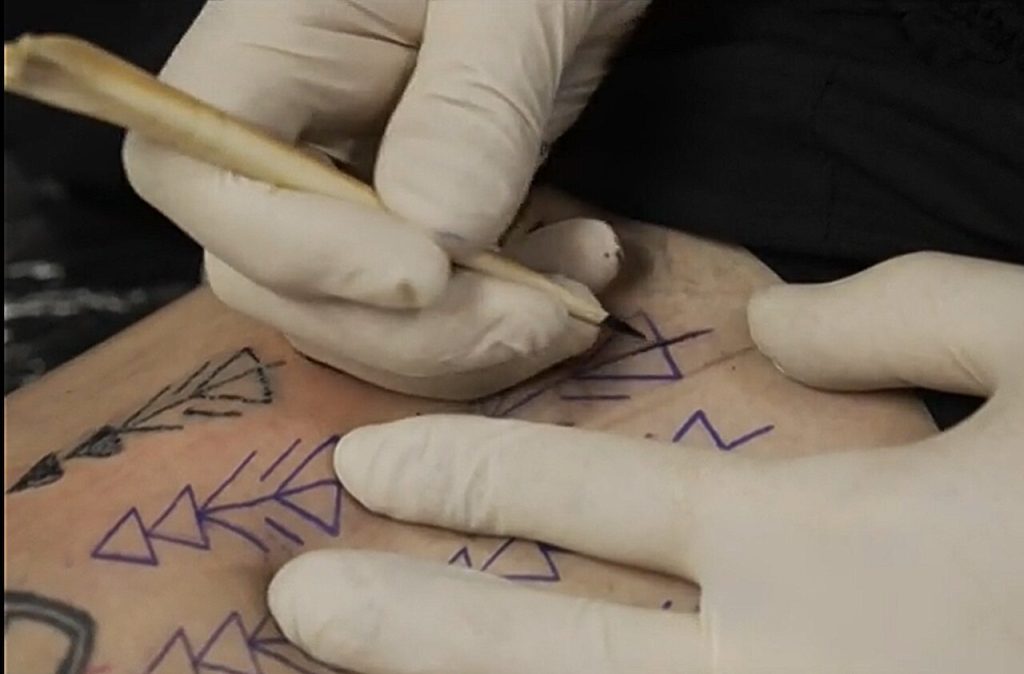
Hand Tattoo Technique
The hand tattoo technique is a traditional tattoo method used before the advent of modern tattoo machines. In this method, the ink is manually placed under the skin using a sterile needle or thorn. The needle is repeatedly inserted into the skin, allowing the ink to penetrate under the skin.
















