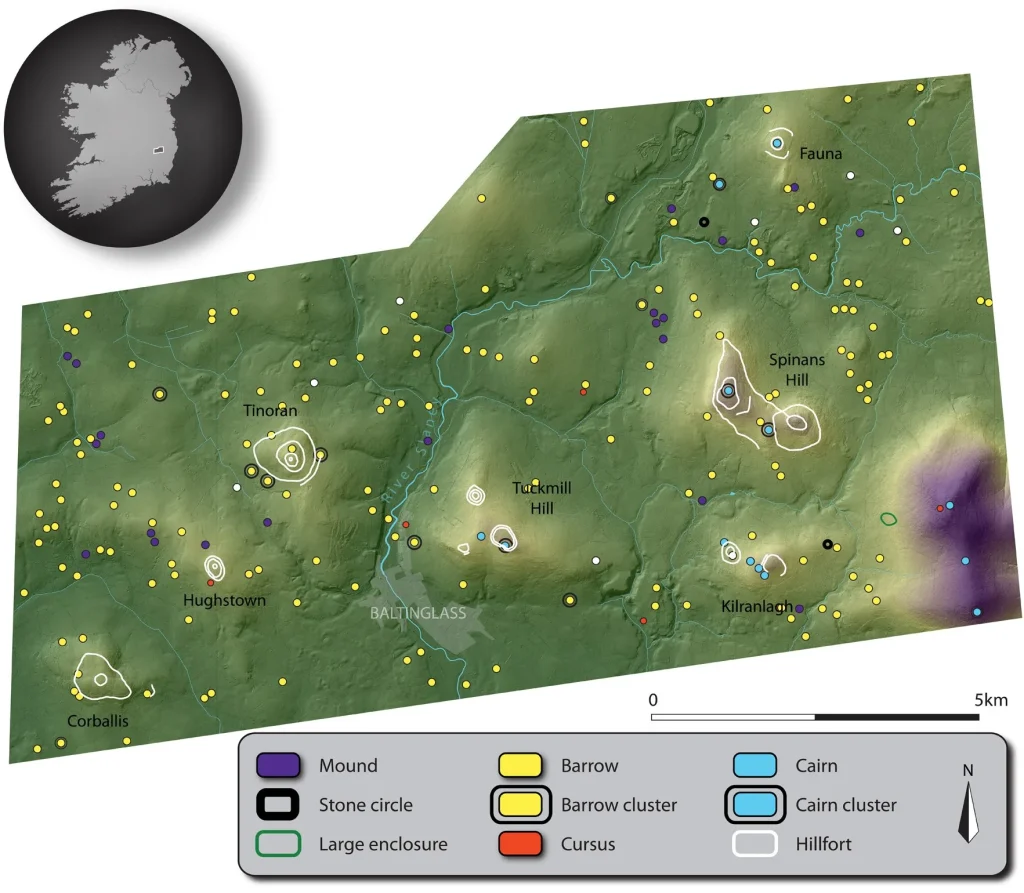
James O’Driscoll from the Department of Archaeology at the University of Aberdeen used LIDAR technology to survey the Baltinglass site in County Wicklow, Ireland.
The results of the study were published in the journal Antiquity.
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing method that measures the distance and shape of an object or surface using laser beams. It is similar to radar technology, but uses light instead of radio waves.
O’Driscoll’s detailed topographic survey using LiDAR revealed previously unknown monuments such as a “massive” Bronze Age hill fort, early medieval ring forts and numerous burial structures from various prehistoric periods.
“I have been working on the Baltinglass landscape for over a decade. It formed the core component of my PhD,” O’Driscoll told Newsweek.
The crucial finding of the study was a cluster of five previously unknown “cursus” monuments.
These prehistoric monuments, found on the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, are typically long and relatively narrow earthwork enclosures. Although these monuments are relatively well known in Britain, they are poorly documented in Ireland.
It showed that at least four of the five cursus monuments were aligned with important solar events. These events were linked to death and rebirth, as well as annual agricultural cycles, shedding light on the purpose of these mysterious monuments.
“These examples may have symbolized the ascension of the dead to heaven and their perceived rebirth,” O’Driscoll said.
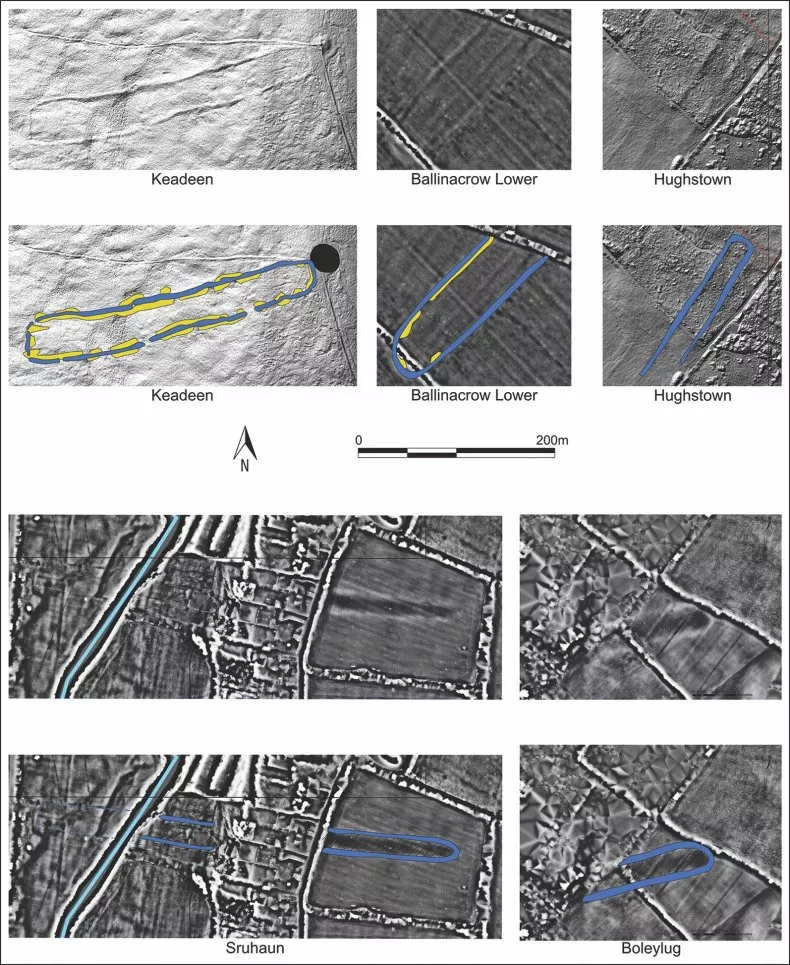
“The function of such monuments has always been a thorny issue because we don’t know enough about them. But given that some Baltinglass sites may also be linked to funerary monuments, this suggests to me that they may have been ceremonial monuments used in funerary practices, with the cursus marking the physical route by which the dead passed from the living to the afterlife,” O’Driscoll said.
The new monuments show that the Baltinglass landscape continued to be an important region for developing farming communities in the region during the Neolithic period in Ireland, which lasted from roughly 4000-2400 BC.
According to O’Driscoll, the results of the study are important because they allow us to understand the ritual and ceremonial practices of our ancestors who lived more than 5,000 years ago.
Cover photo: James O’Driscoll/Antiquity




