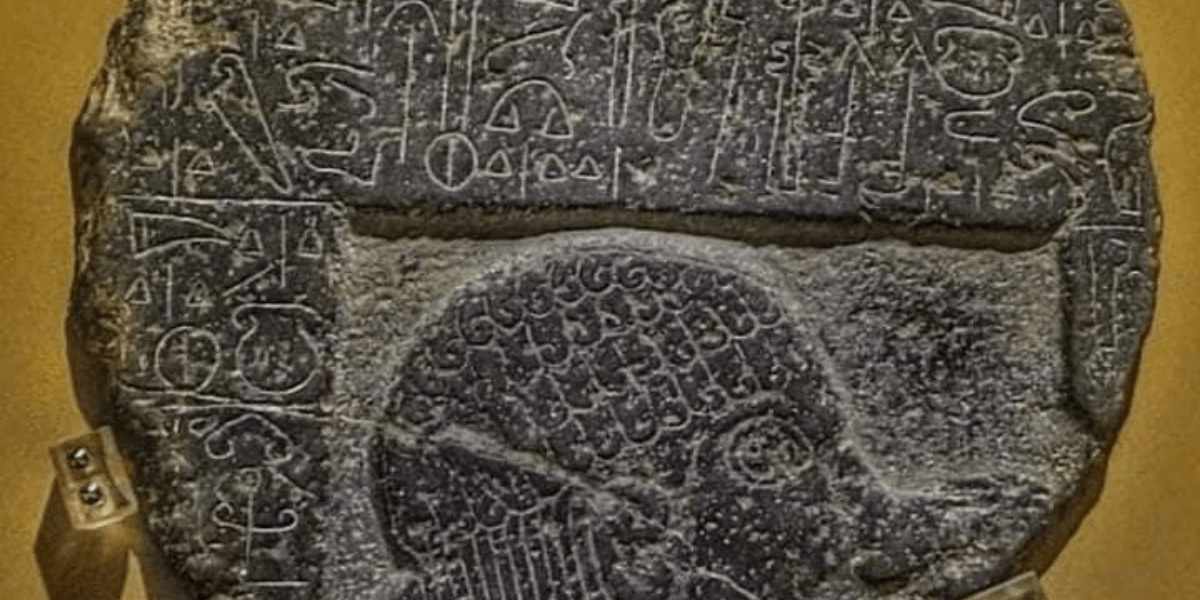
The Andaval Relief is an important historical artifact located near the village of Aktaş in Niğde Province, in the Central Anatolia region of Türkiye. It was first discovered in 1890 by W. M. Ramsey in the floor of a church approximately 9 km northeast of Niğde.
The stele piece has a circular shape with a diameter of about 50 cm and features a relief along with a four-line inscription.
The inscription includes the phrase, “King Saruwani, lord of the city of Nahitiya.” This indicates that Saruwani was the king of Tuwana and ruled before Warpalawa. Nahitiya is the name of the city during the Hittite period that corresponds to present-day Niğde, highlighting the historical significance of the region. Saruwani’s name also appears on another stele found in Niğde, further reinforcing his influence and presence in the area.
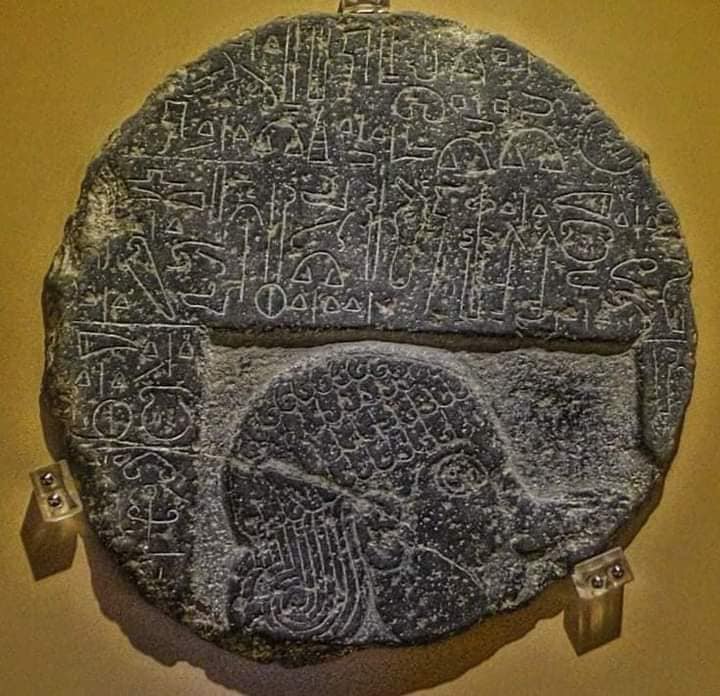

The Andaval Relief is dated to the late 9th century to the early 8th century BC. This period is significant as it marks an important time in shaping the political and cultural structure of Anatolia. The location where the relief was found contains the remnants of Nahitiya, an important settlement in ancient times. This indicates that the Andaval Relief serves not only as an artistic piece but also as a document shedding light on the region’s history.
Today, the Andaval Relief is exhibited in the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations in Ankara. Additionally, a replica of this artifact is available for visitors at the Niğde Museum.
The Andaval Relief is a significant artifact that carries traces of ancient Anatolian civilizations and holds great historical and cultural importance.
As a legacy that has reached us from the depths of the past, the Andaval Relief reflects the rich history and cultural diversity of Anatolia. This artifact is a treasure waiting to be discovered by both archaeologists and history enthusiasts.