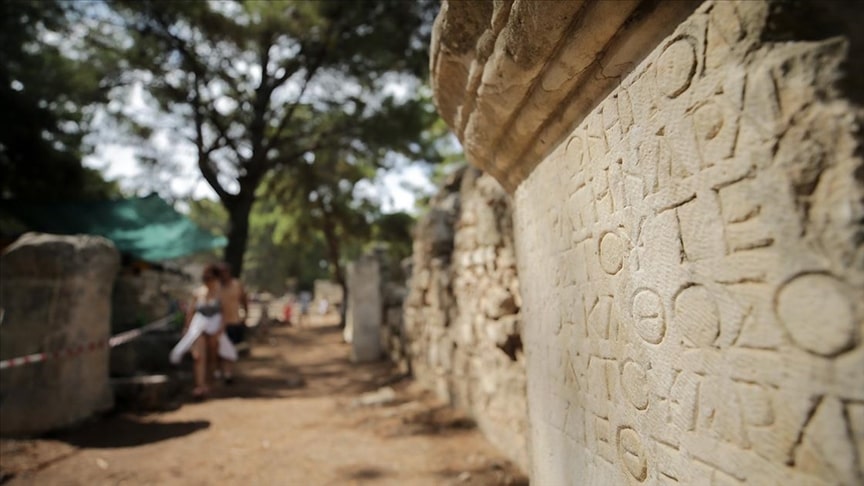
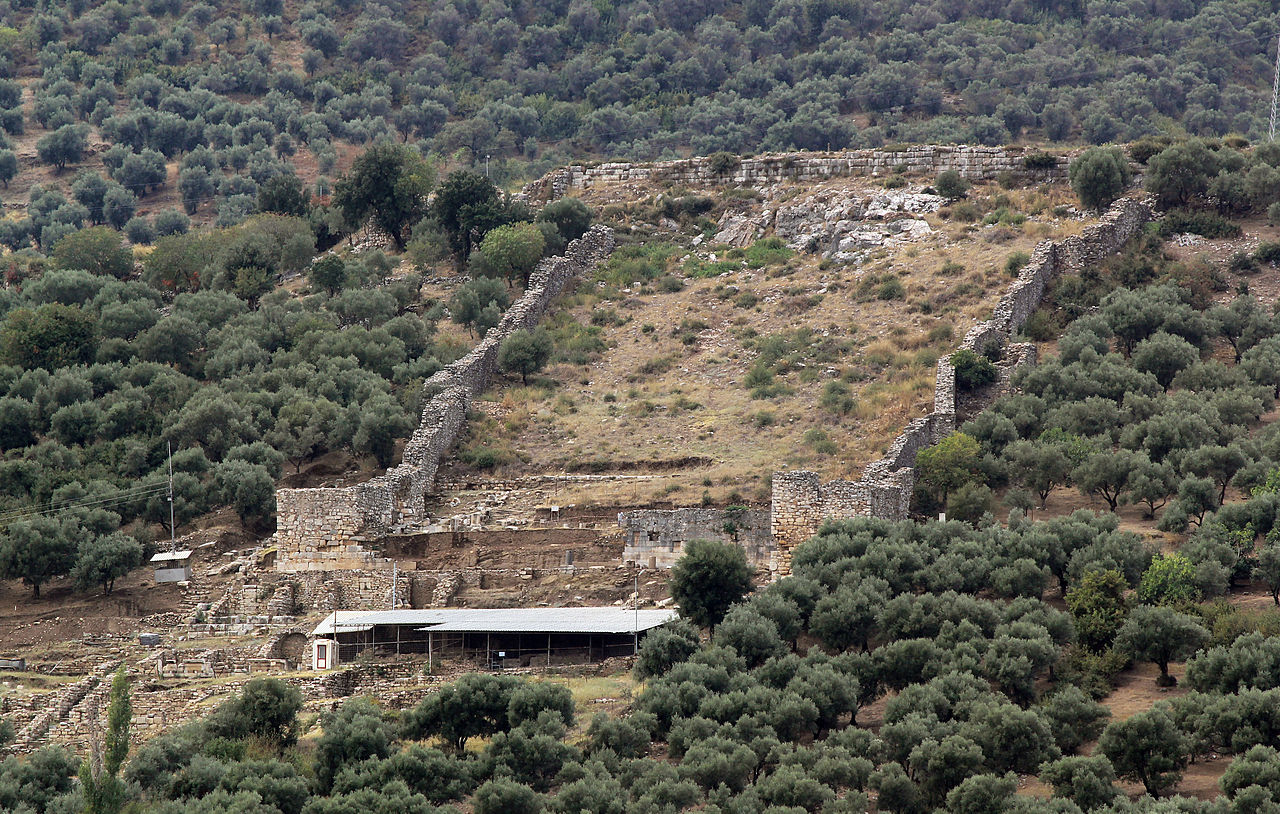
Efforts are ongoing to uncover the entire main street of Phaselis Ancient City, which has a 2,000-year-old history and was once walked upon by important figures like Roman Emperor Caesar and Macedonian King Alexander the Great.
Phaselis Ancient City is located in the district of Kemer in Antalya, Türkiye.
An archaeological team, led by Prof. Dr. Murat Arslan, the Chair of the Department of Ancient History at Akdeniz University, is continuing the excavation work in the ancient city, which was the region’s most important trade center during the Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine periods.
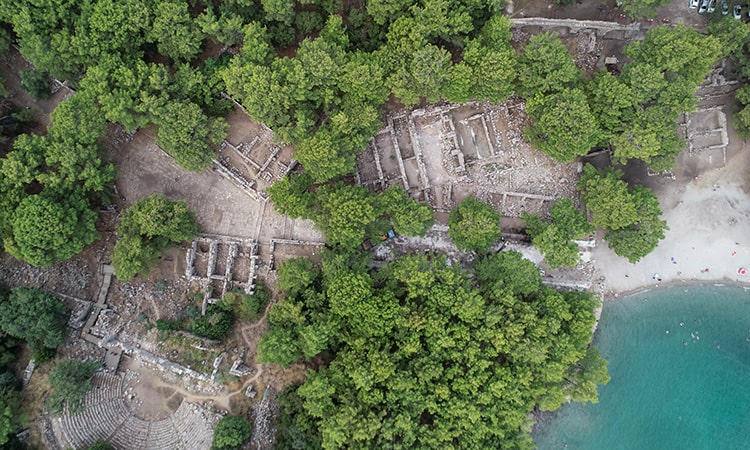

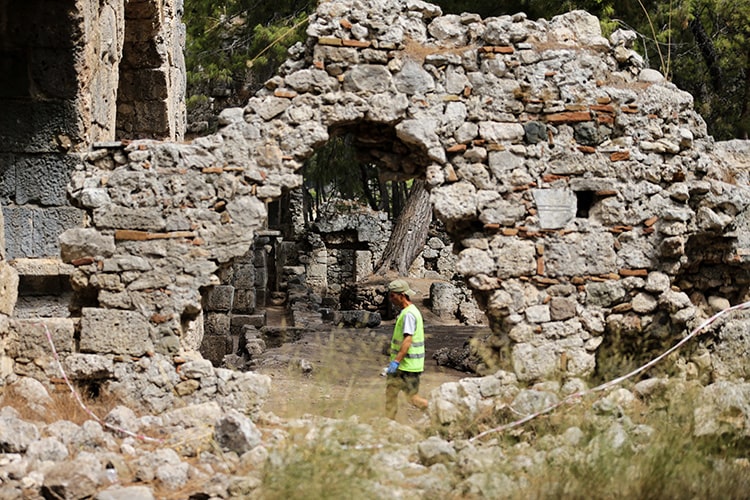
The team is working to uncover the part of the main street that extends to the harbor, which was buried underground due to major earthquakes and was once the route for processions.
Arslan, in an interview with AA, stated that Phaselis Ancient City was founded in the 7th century BC and became prominent in the Eastern Mediterranean in terms of trade volume from the early period.
He pointed out that the city maintained its significance during the Classical, Hellenistic, and Roman periods, saying, “We know that the most prominent figures of these periods, including emperors, kings, and generals, used Phaselis as a stopover. Famous historical figures such as Kimon, Pompeius, Caesar, Hadrian, Caracalla, and Alexander the Great also visited the city.”

Arslan mentioned that they are continuing their work on the main street, which is at the heart of the ancient city. He said, “The main street is approximately 225 meters long and 12 meters wide. It serves as a street connecting the central harbor of Phaselis with the southern harbor and the main trade axis. On both sides of the street, there are city agoras, shops where merchants and traders conducted their business, and public buildings. Our excavation goals for 2023 include restoring the main street that constitutes Phaselis’ central hub and primary trade route, making it accessible to both domestic and foreign visitors.”
He described how they carefully remove and repair the stones of the street, uncovering the city’s infrastructure system in the process.

Arslan pointed out that beneath the city lies an infrastructure and sewage system resembling a spider’s web. He said, “Both wastewater and freshwater infrastructure have been discovered. During these works, we determined that the street has been used without significant changes since the Classical period.”
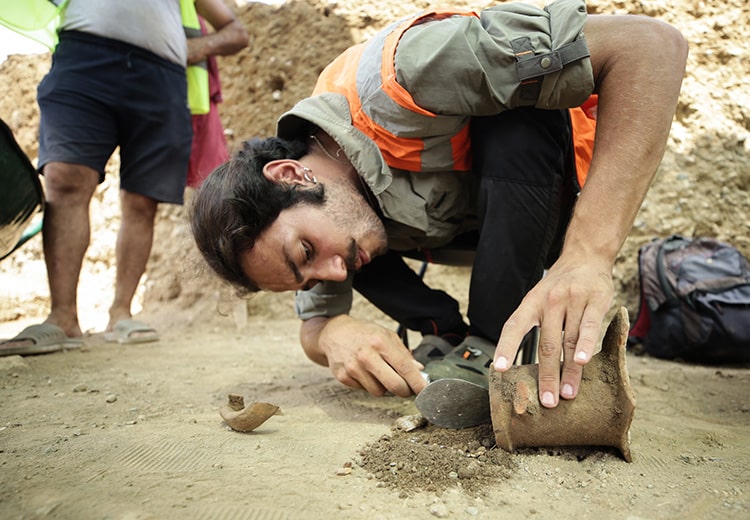
By restoring temples, aqueducts, and placing the stones back in their original positions, Arslan explained, “We don’t bring stones from outside; we repair the structure with its own stones and document it before placing them back. Each stone has its own identity. We uncover details such as who extracted a stone, when it was extracted, what treatments it underwent, and when it was placed back, creating a record and identity for each stone.”
Cover Photo AA