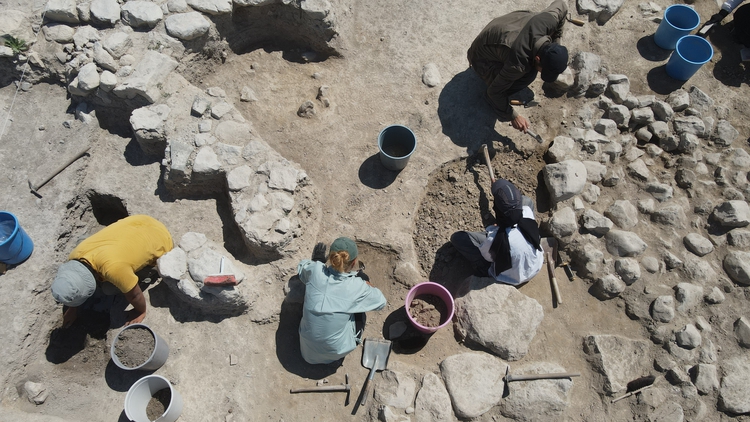
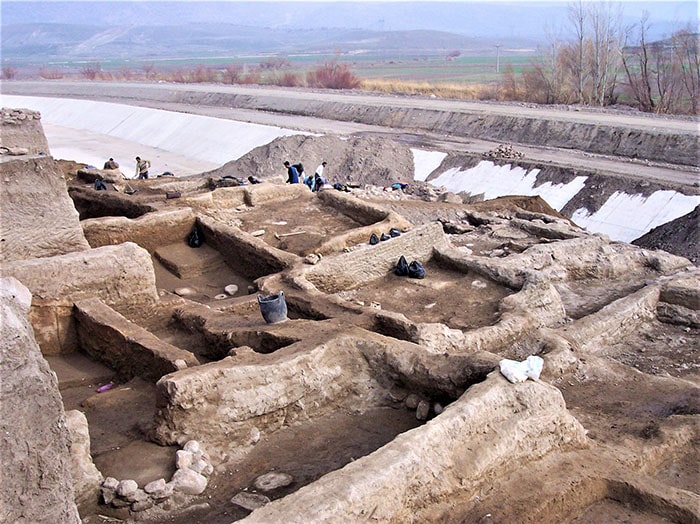
In Nerik, an important religious city of the Hittite Empire, remains from the Iron Age are being searched for.
Nerik is located at the Oymaağaç Mound, situated 7 kilometers northwest of the Vezirköprü district in Samsun province of present-day Turkey.
Established by the Hattians, one of the oldest civilizations of Anatolia, around 3500 years ago, Nerik maintained its significant status as a sacred city after falling into the hands of the Hittites.
The city of Nerik, dedicated to the Hittite Storm God Teshub, was known for this feature, where Hittite kings came to show respect to Teshub, perform ceremonies, and make offerings as an act of devotion.
Nerik continues to be excavated by Prof. Dr. Rainer Czichon, a faculty member of the Department of Archaeology at Uşak University and the Head of the Oymaağaç Excavation.
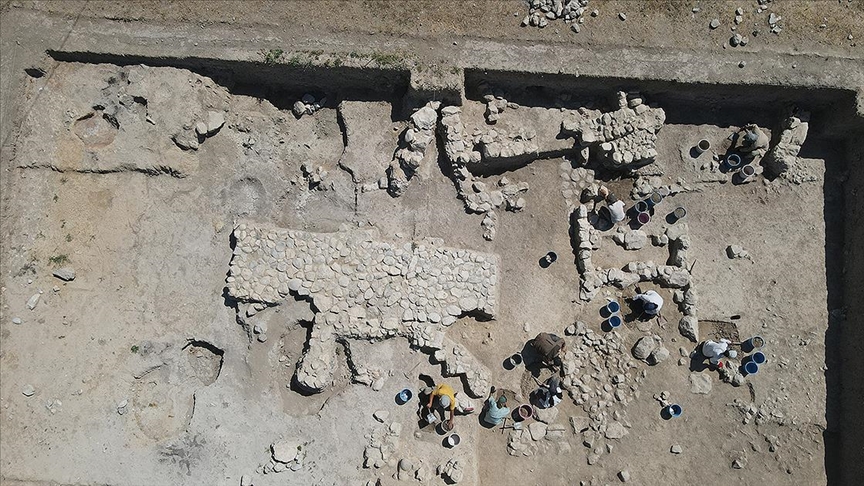

Prof. Dr. Rainer Czichon stated to an AA correspondent, “Together, we are working here to shed light on the Hittites’ sacred city Nerik, pre-Nerik settlements, post-Nerik settlements, and its history.”
Prof. Dr. Czichon further stated that in the excavations up to the present day, they have uncovered the temples of Nerik. He continued, “Additionally, there is a city gate, examples of which resemble the typical city gates of Hittite cities. Just like in Hattuşa, the capital of the Hittites, we have them here as well. Apart from that, there is a tunnel with 50 steps, leading to a pool at the end. We recognize this pool from Hittite sources; it’s the spring beloved by Nerik’s god of weather.”
“We discovered it here, and this is quite a rare find. This Nerik spring is a special case for us; it goes very deep, similar to a structure in Hattuşa, but not as large as the one here. The Nerik spring, located 8 meters underground, is currently considered the widest and largest underground spring in the Hittite world.”
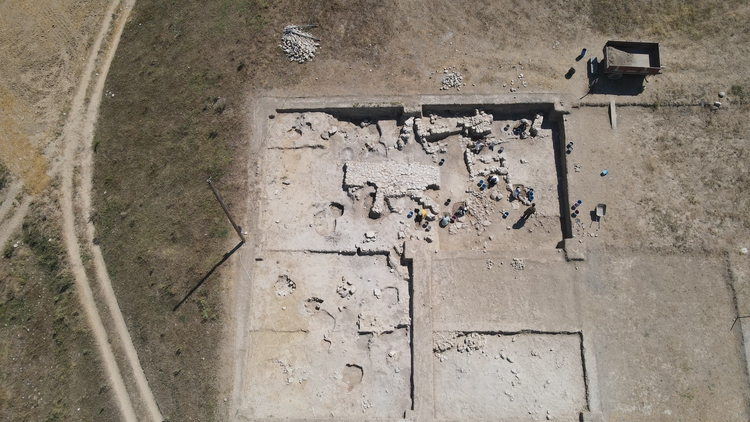

“We have been working in a new area at the northwestern corner of the mound for the past 3 years. We are researching the structures of people from the Hittite period and the Iron Age. We want to learn about the houses where ordinary people lived, their belongings, and their way of life. We want to know how people during that time ate, for example, did they use plates or eat sitting on the ground? Answers to such simple questions are quite challenging in archaeology. We are seeking these answers. In the new excavation area, we are uncovering artifacts from the Iron Age. This is a first for Nerik, because on the hilltop, there were only pits from the Iron Age, but no architecture. Now, we are observing Iron Age architecture here. We are in the initial stages right now, and it’s gradually coming to light. Soon, we will reveal the plan of Iron Age life in this area.”
Cover Photo İlyas Gün




