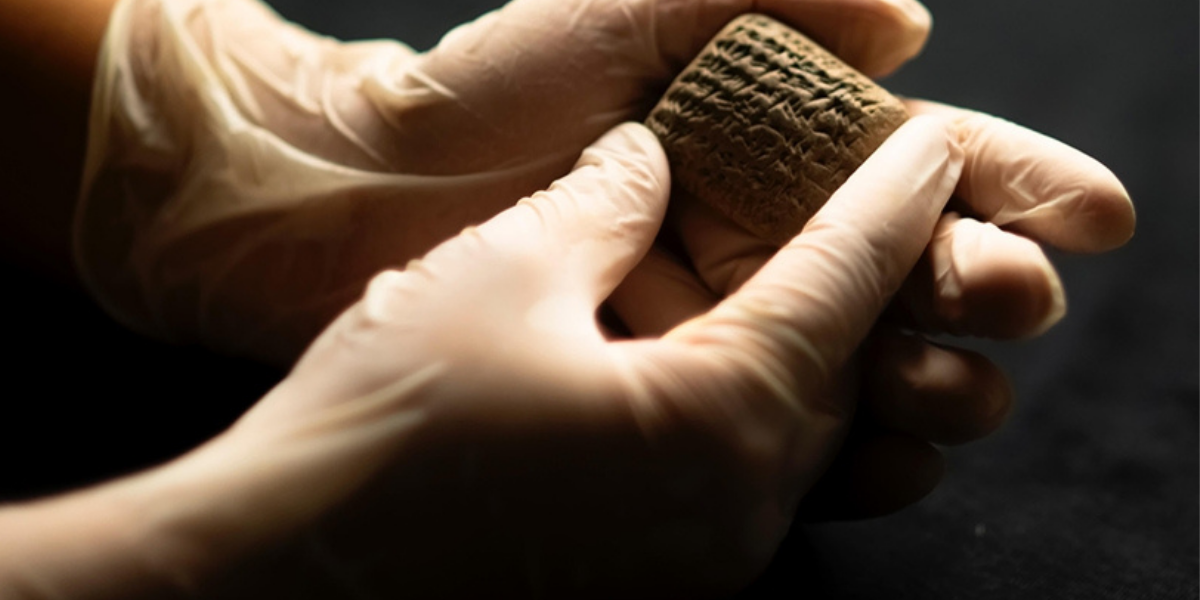

3500-year-old clay tablet written in Akkadian discovered at Aççana mound
Archaeological excavations at Aççana mound in Reyhanlı district of Hatay province in southern Türkiye have unearthed a 3500-year-old clay tablet written in Akkadian. The Aççana mound contains the remains of Alalah, an important city in ancient times. The mound dates back to 4000 BC and is known to have been inhabited continuously for 4000 years.
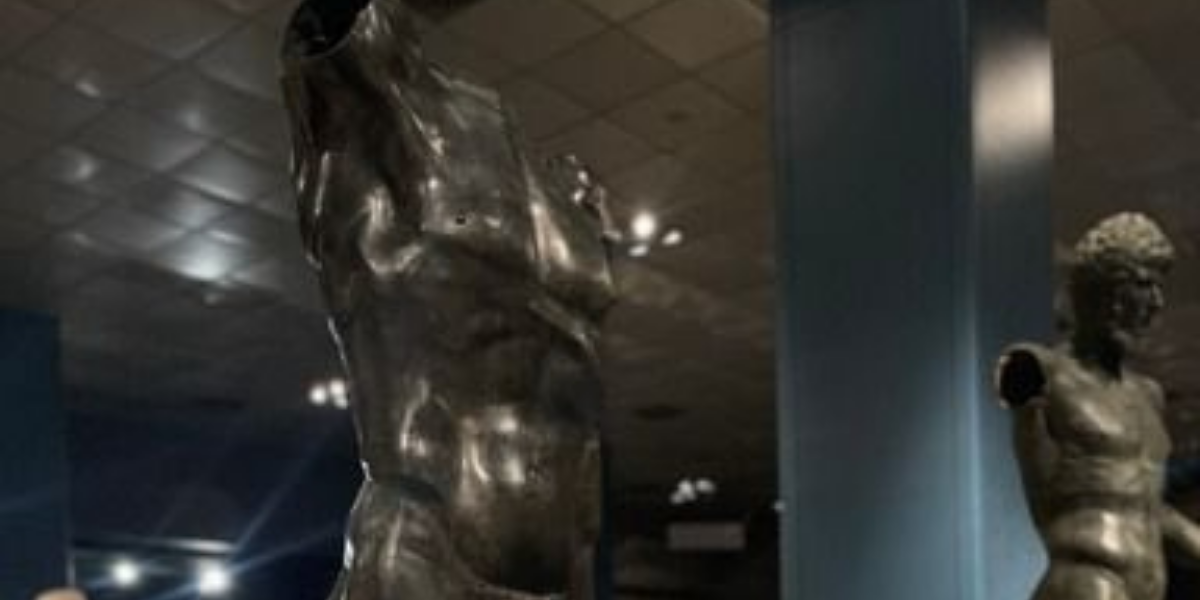

19 historical artifacts smuggled abroad brought to Türkiye
Thousands of artifacts illegally smuggled out of Türkiye have been brought back thanks to the successful efforts of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism. The number of artifacts returned to Türkiye has reached 12,139 since 2002 and 7,823 since 2018. Finally, the Ministry of Culture and Tourism announced that 19 artifacts returned from the UK,
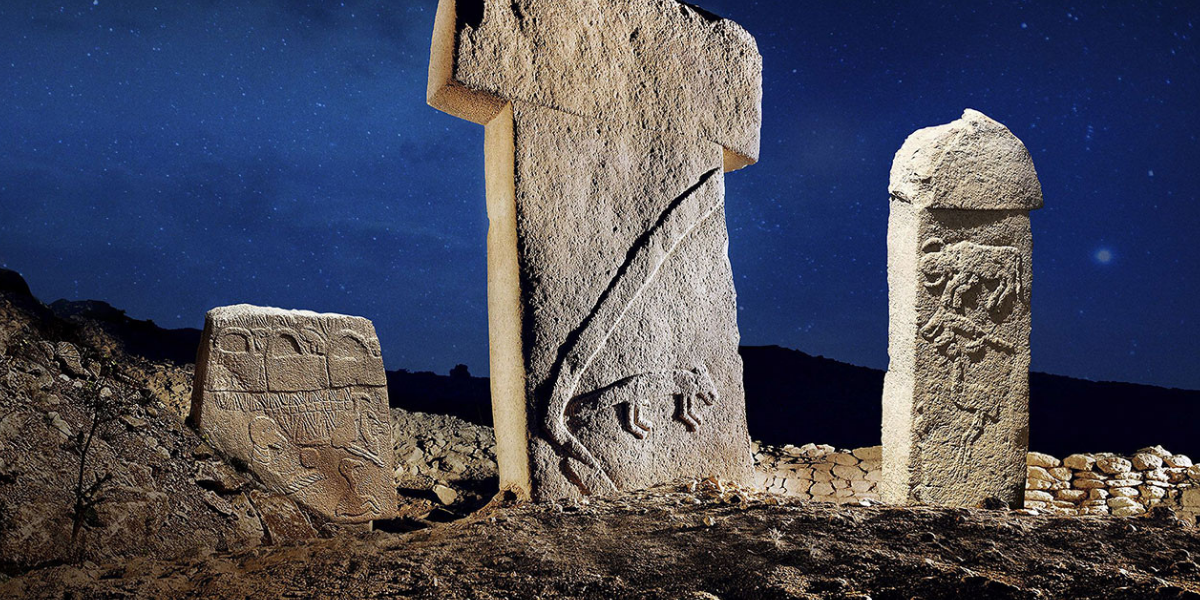

Did aliens build Göbekli Tepe? The head of the excavation answers
Göbekli Tepe is the most exciting archaeological discovery that has profoundly influenced human history. Klaus Schmidt, who discovered Göbekli Tepe dating back to 12,000 BC and headed excavations until 2014, described it as a shelter used by nomadic hunter-gatherer groups over a large area, with few or no permanent residents. In recent days, especially on

Underwater work at Parion reveals 2,700-year-old Roman military harbor
Underwater work in the ancient city of Parion in the Biga district of Çanakkale in northwestern Türkiye has uncovered a 2,700-year-old military harbor dating back to the Roman Empire. The military harbor is the second harbor found in the ancient city. Excavations in the ancient city of Parion, which was an important trade center of
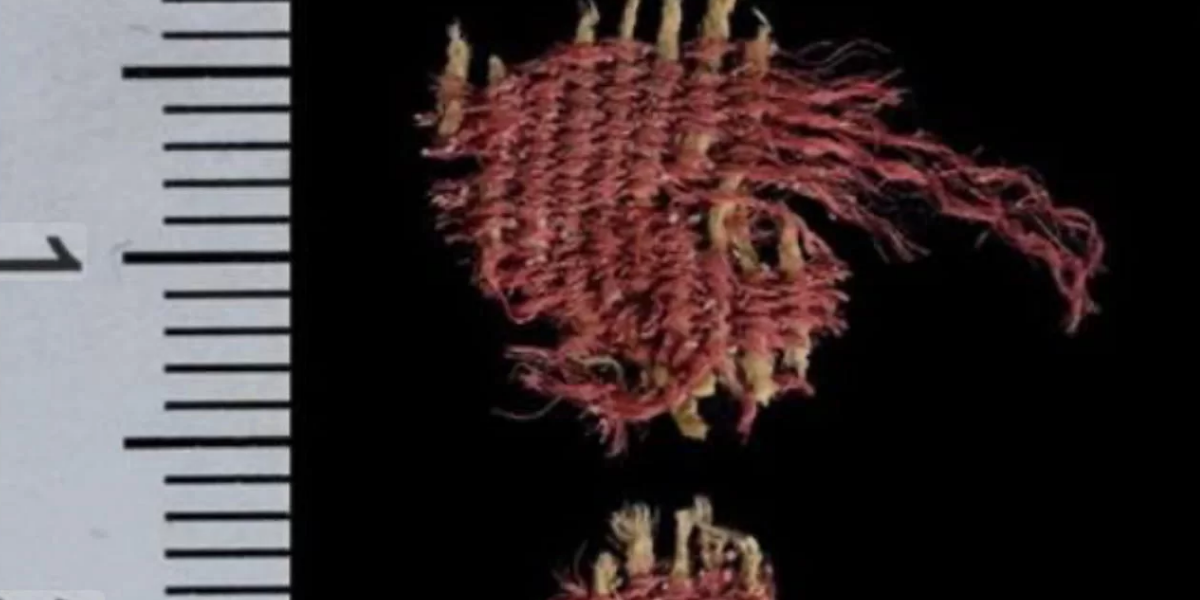
4000-year-old fabric dyed with insect dye discovered in a cave in the Judean Desert
Researchers have discovered fabric dyed with kermes (Kermes vermilio) in the Cave of the Skulls, which bears traces of the Middle Bronze Age. The piece of red fabric found in the Cave of the Skulls in the Judean Desert was made of linen and wool. Radiocarbon dating dated the fabric to the Middle Bronze Age,
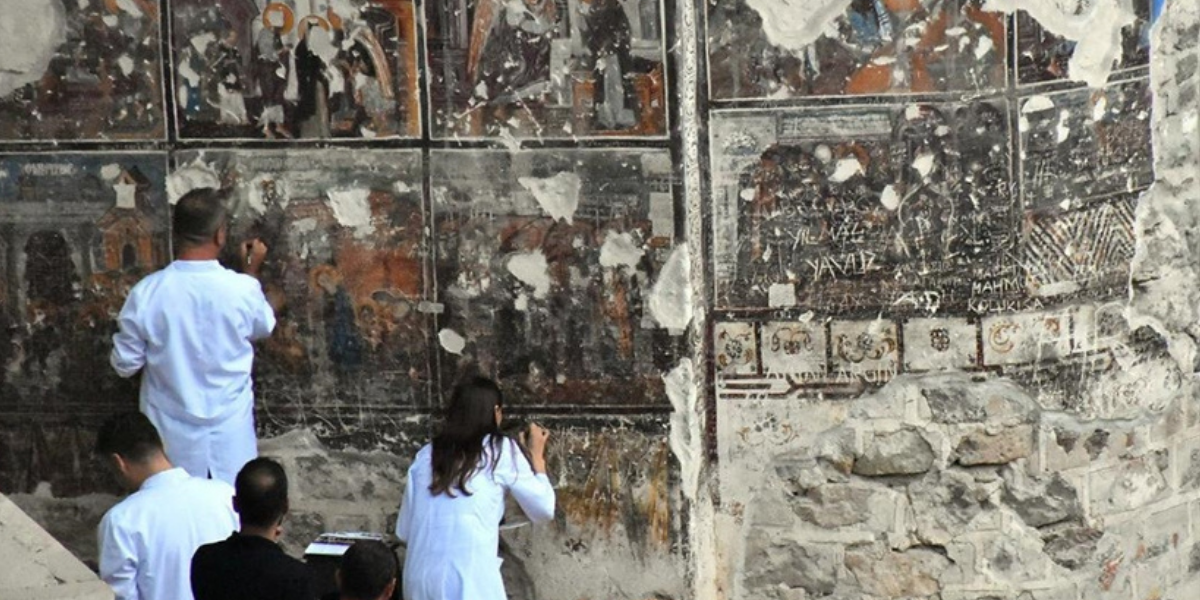

The frescoes of the Mother Rock Church in Sumela Monastery are being restored
The damaged frescoes of the Mother Rock Church in Sumela Monastery, which is on the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List, are being restored in accordance with the original. The Sumela Monastery, carved into a steep cliff and therefore also known as the “Eagle’s Nest”, is located in Trabzon’s Maçka district, within the boundaries of the
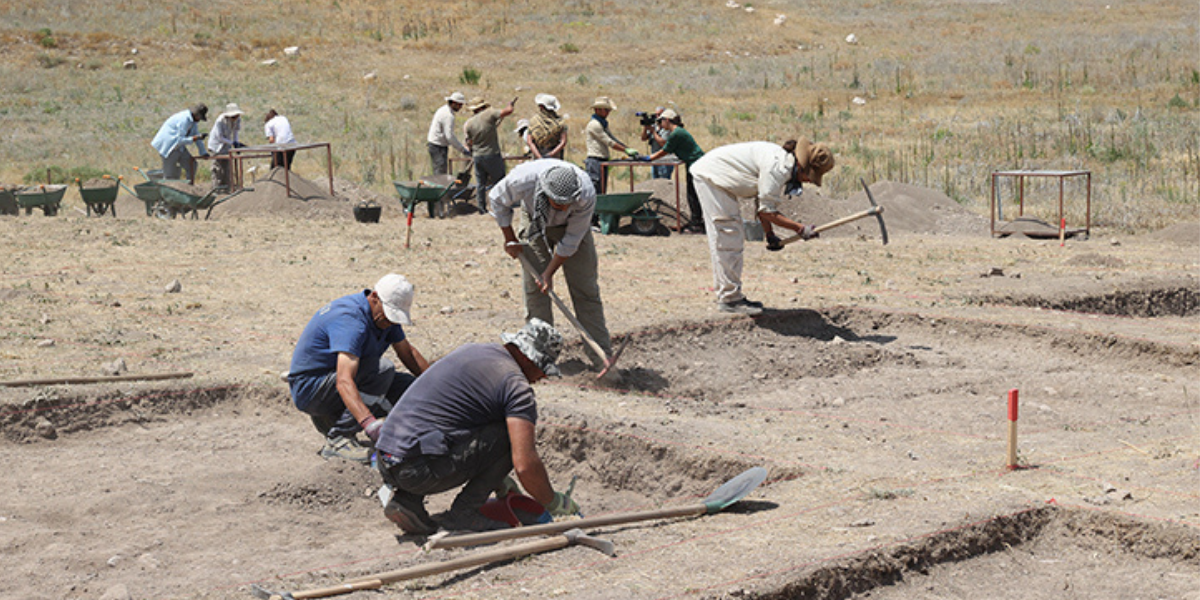

Archaeologists may have found the temple of Šauška, sister of the air god Teshup, in the Samuha
In Samuha, an important religious city for the Hittites, a structure thought to be the temple of Šauška, the sister of the weather god Teshup, was unearthed. Samuha is a Hittite city of religious significance that flourished between 1800-1600 BC. Samuha, now known as Kayalıpınar, is located in central Türkiye, about 40 kilometers west of
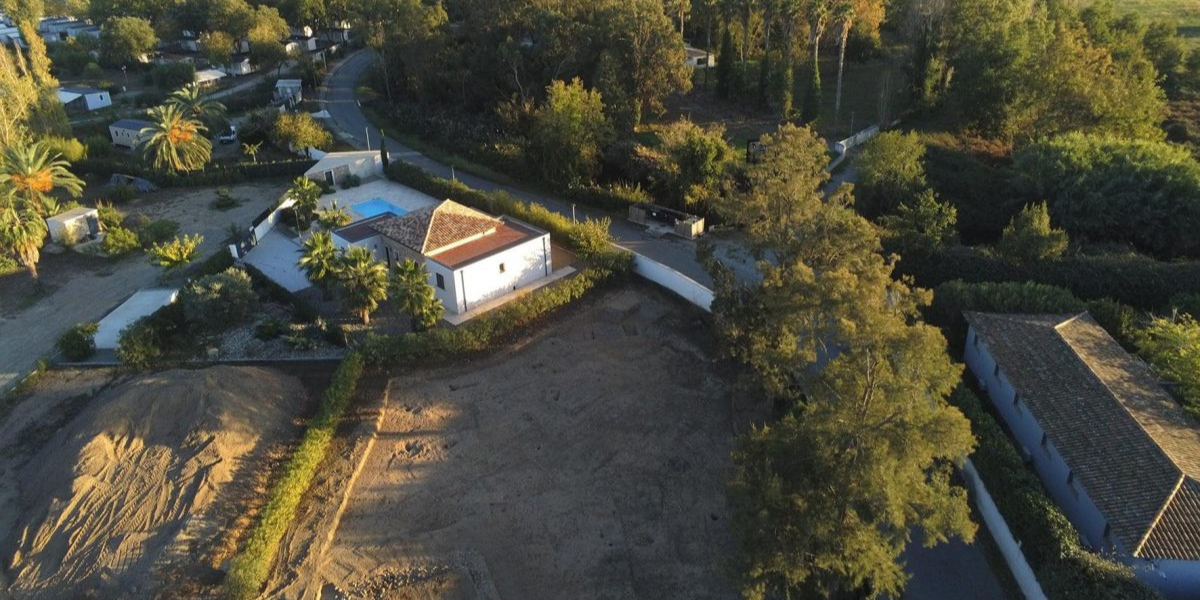

Archaeologists discover first Etruscan house structure in Corsica
Archaeologists have discovered on the east coast of Corsica the first Etruscan house structure dating from the 6th to 4th centuries BC. Archaeologists from Inrap, the French National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research, uncovered the Etruscan house structure as part of a project to build a detached house in the municipality of Ghisonaccia. Until today,

New season excavations in the ancient city of Satala begin
New season excavations begin in the ancient city of Satala, which dates back to the Bronze Age. Satala Ancient City is located in the Kelkit district of Gumushane in the Eastern Black Sea Region of Türkiye. Satala, which gathered Antioch, Cappadocia and Trabzon at a crossroads, was an important fortress in the defense of Rome,
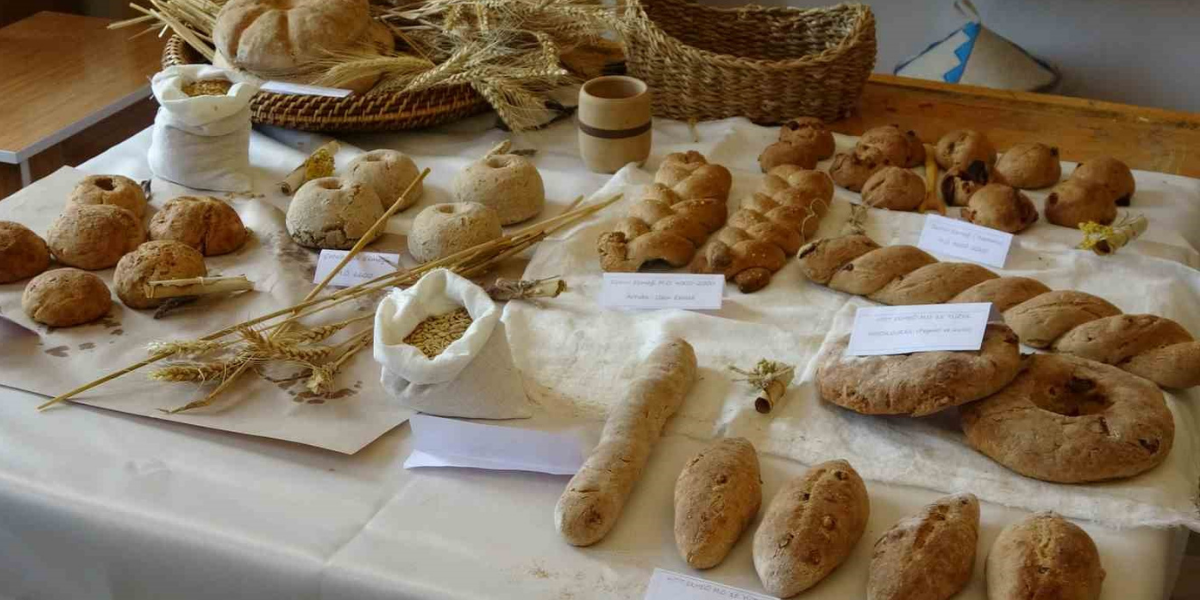

Using 3,500-year-old tablets, bread from the Hittite, Sumerian and Roman periods was baked
Bread is an indispensable food source in every period of history. In Anatolia, home to the transition to settled life, bread is considered both a foodstuff and a sacred food offered to the gods. The Hittites are a Bronze Age civilization that stands out with its bread making and diversity. Hundreds of tablets unearthed in
