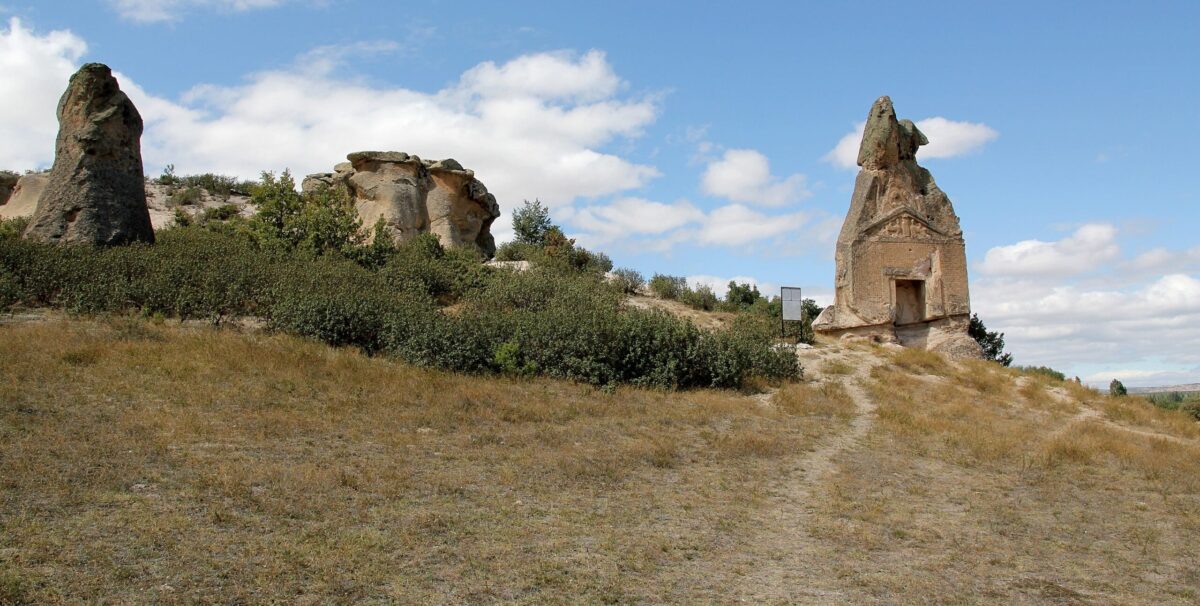

Lost Phrygian Inscription on Arslan Kaya Monument waiting to be deciphered for centuries Deciphered
Professor Mark Munn of Pennsylvania State University has deciphered part of the heavily damaged inscription on the legendary Arslan Kaya Monument (also known as “Lion Kaya”), which has been difficult to decipher for centuries. The Arslan Kaya Monument is carved into a volcanic rock formation about 15 meters high near Lake Emre in the Phrygian
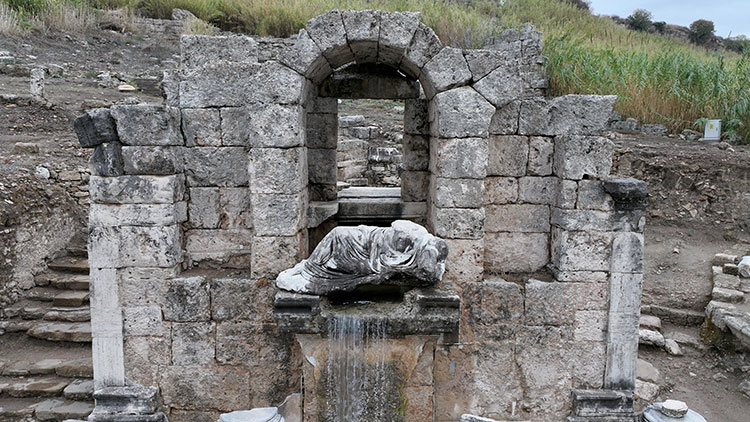

The Kestros Fountain, built by Emperor Hadrian, has started to flow with water again after 1800 years
The ancient “Kestros Fountain,” known to have been built by Emperor Hadrian in the 2nd century AD, has started to flow with water again following restoration efforts in the ancient city of Perge. The ancient city of Perge is located within the borders of Aksu district in the center of Antalya. The first traces of
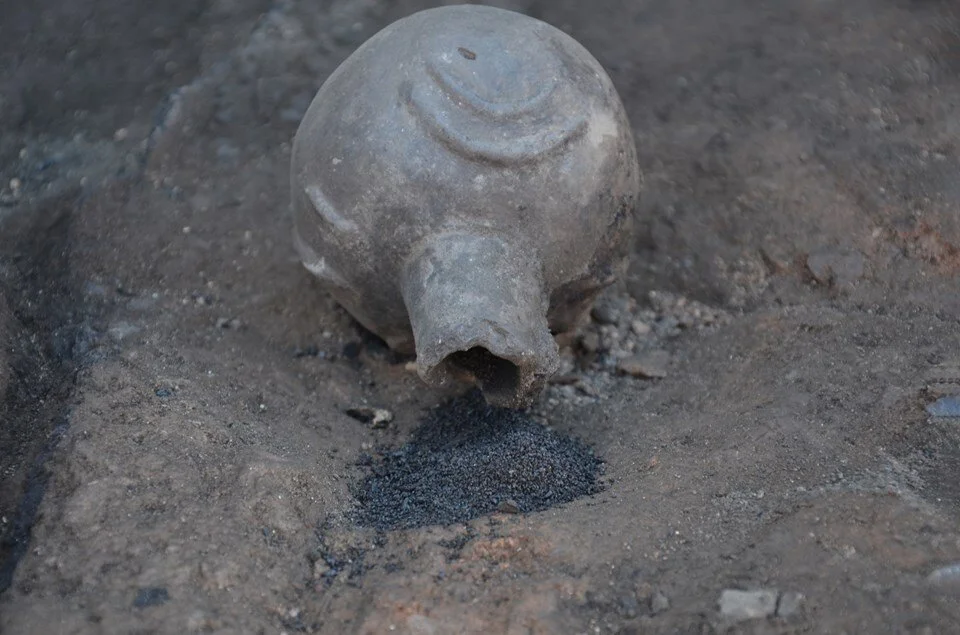

Archaeologists find 5,000-year-old poppy and chickpea grains at thermal power plant site
Turkish archaeologists discovered 5,000-year-old chickpeas and opium poppy seeds in a structure from the Early Bronze Age during rescue excavations at the Seyitömer Mound, located at the thermal power plant site. Beneath Seyitömer Mound, there are 12 million tons of lignite reserves. Rescue excavations were initiated before coal extraction began. The excavations, which started in

The markings on a 4,400-year-old clay cylinder found in a grave may represent an example of the world’s oldest alphabet
Humans discovered writing through the Sumerians in Mesopotamia. A series of symbols inscribed on clay tablets is considered the beginning of writing. Over time, these symbols evolved in the hands of scribes, transforming into a more easily writable form, which became the alphabet. The creators of the alphabet are believed to be ancient Egyptian scribes.
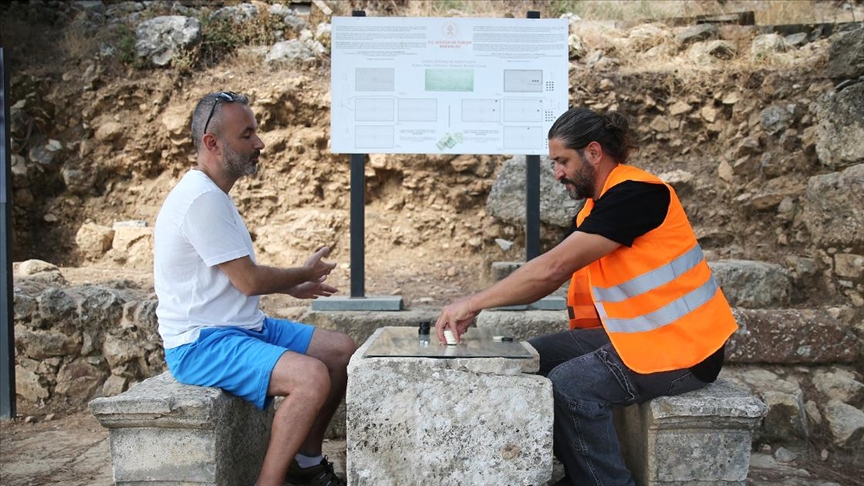

Visitors to the ancient city of Syedra are playing the popular Roman game “12 Signs”
The popular Roman game “12 Signs” (ludus duodecim scriptorum) is being introduced to visitors at the ancient city of Syedra, located in the Alanya district of Antalya. The game “12 Signs” is also known as “Roman Backgammon.” Pieces of the game were found during excavations on the Colonnaded Street of the 3,000-year-old ancient city. The
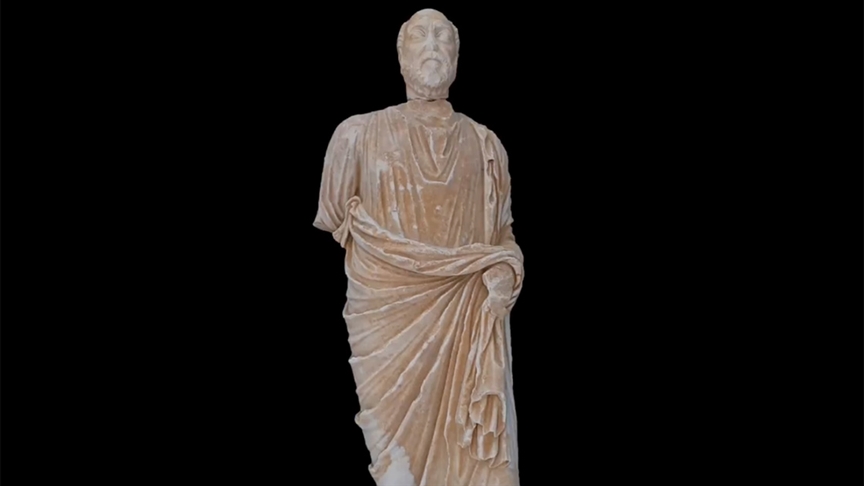

The head of the statue, whose body was found six years ago in the Tripolis excavations, has been unearthed
The body of a statue was found six years ago during excavations in the ancient city, which was founded under the name Apollonia in the Hellenistic period and later renamed Tripolis. This season, the excavation team discovered the head of the statue. The ancient city of Tripolis is located in Denizli province. It developed under

The hidden text beneath the intricate gold leaf decorations on a page of the Blue Quran has been revealed
Researchers from the Zayed National Museum have uncovered hidden text beneath a complex layer of gold leaf on a page of the Blue Quran, one of the world’s most renowned Quran manuscripts, using multispectral imaging techniques. The team discovered verses from the Surah An-Nisa hidden under an intricate decoration adorned with gold leaf on a
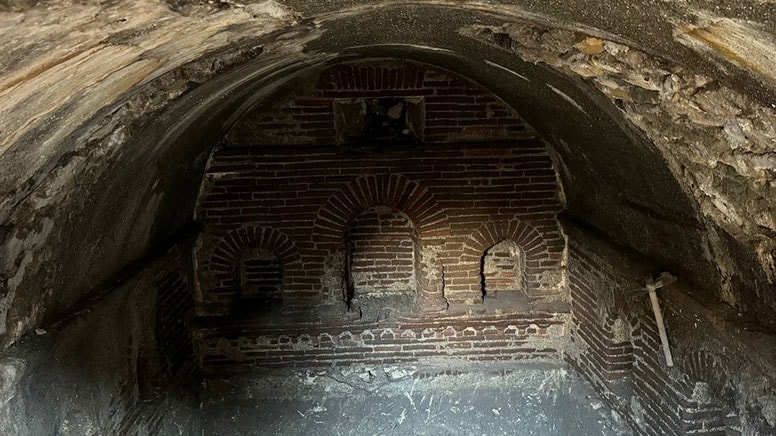

A 1500-year-old structure was discovered beneath the rubble of a building that collapsed in the earthquake
In Hatay, which was shaken by two severe earthquakes two years ago, a 1500-year-old structure has emerged beneath the rubble of a collapsed building. During the removal of the rubble from a detached house that was destroyed by a magnitude 7 earthquake on February 6, 2023, a structure believed to date back to the Late
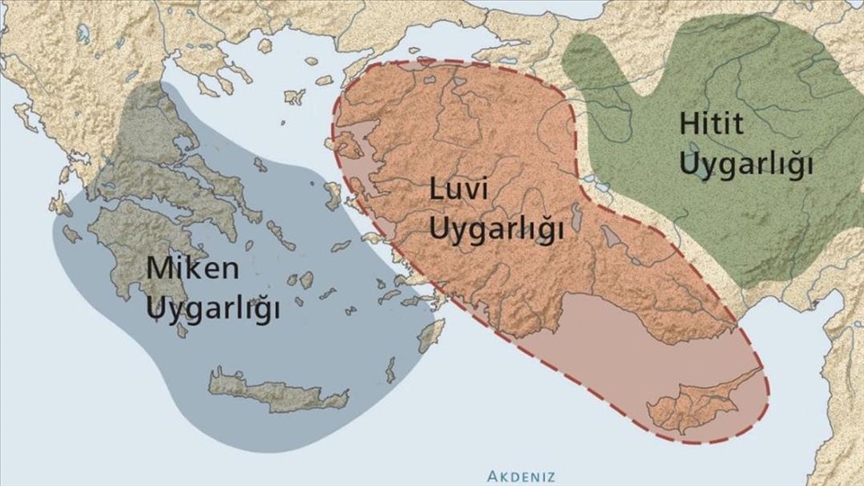
The Luvi Research Foundation has published data on 483 settlements from the Bronze Age in Western Anatolia
The Luvi Research Foundation, based in Switzerland, has released a new open-access database and interactive map providing comprehensive information on 483 significant settlements dating to the Middle and Late Bronze Age in Western Anatolia. The study titled “An Interactive Look at the Bronze Age” includes detailed information such as the names of archaeological sites and
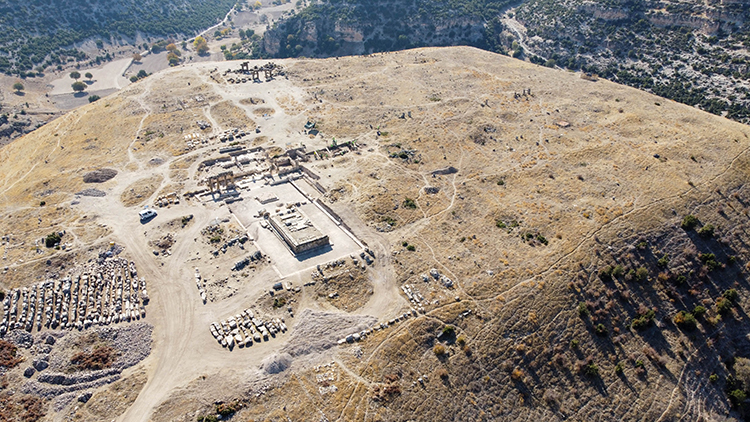

The ‘monumental tomb’ from the 2,000-year-old Roman period in Blaundos has been unearthed
Excavations in the ancient city of Blaundos, known as a garrison town, have uncovered a 2,000-year-old ‘monumental tomb’ from the Early Roman period. Blaundos is the place where soldiers who came from Macedonia settled during Alexander the Great’s campaign in Anatolia. The ancient city is located in the Ulubey district of Uşak, Türkiye. It draws
