
Traces of the mega-drought that is thought to have caused the fall of the Akkadian Empire will be investigated in Kültepe
In Kültepe, traces of a mega-drought, thought to have played a role in the collapse of the Akkadians, the first ancient empire founded in Mesopotamia after the fall of the Sumerian civilization, will be investigated.
Kültepe/Kanesh is known as the place where written history began in Anatolia. It is one of the most important karums of the Assyrian trade colonies era. Thousands of clay tablets have been found so far during excavations. The tablets provide unique information about the culture, political and economic life of Anatolia and Mesopotamia of that period.
Archaeological excavations in Kültepe continue under the direction of Prof. Dr. Fikri Kulakoğlu, a faculty member at Ankara University, Faculty of Language, History and Geography, Department of Archaeology.
The Akkadian Empire, founded by Sargon around 2330 BC, was also influential in the Levant and Anatolia. The Akkadians, who established a culturally and scientifically important civilization, were destroyed by the Gutids in 2150 BC.
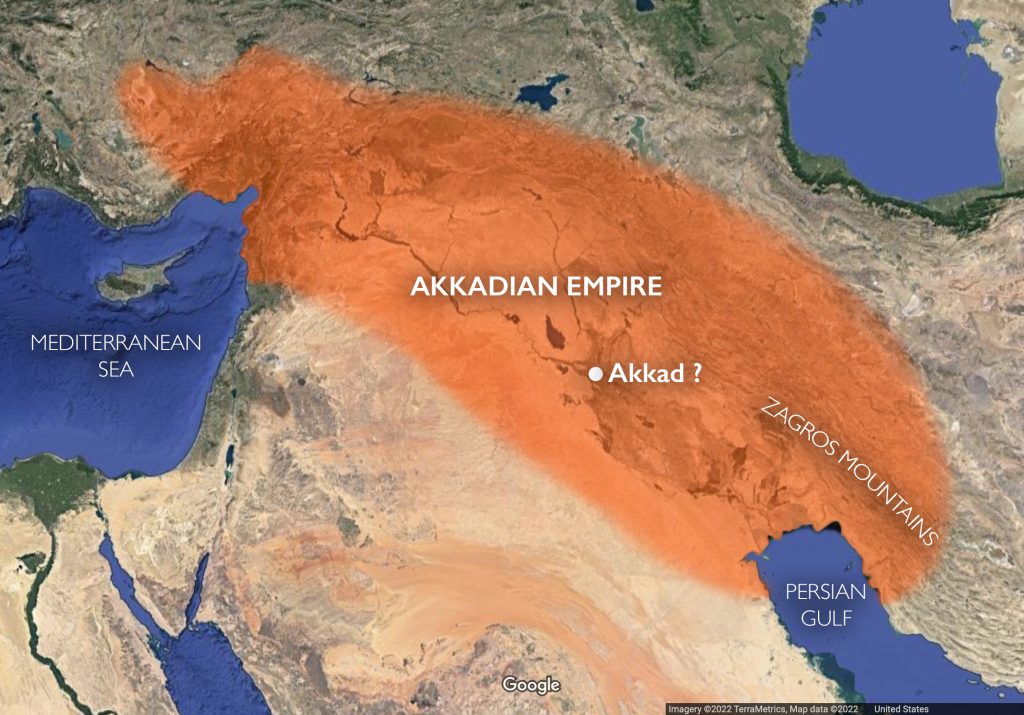
The prevailing view of the fall of the Akkadian empire was that it was weakened by internal strife and attacks by neighboring tribes.
Prof. Dr. Harvey Weiss from Yale University, who thinks that drought played a role in the Akkadians’ withdrawal from the stage of history, will participate in the Kültepe excavations this year.
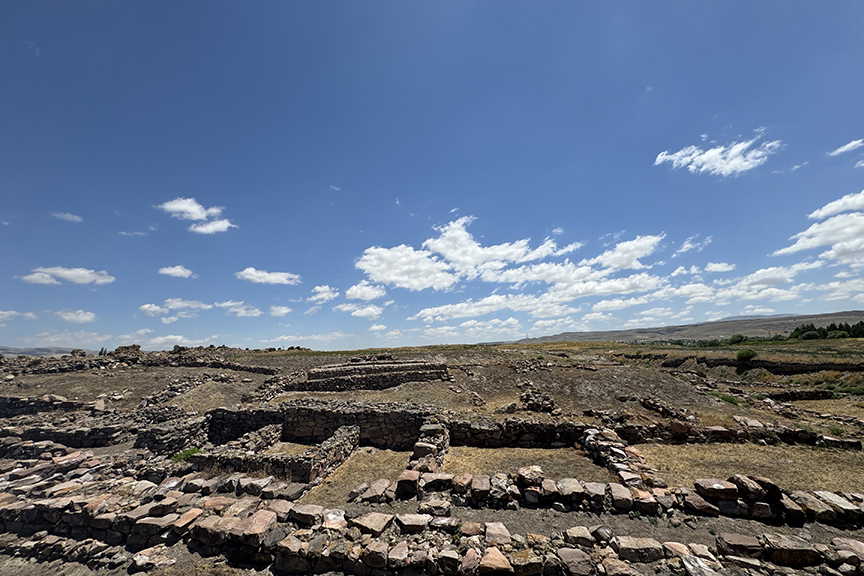

Stating that Harvey Weiss attributes the fall of the Akkadians to a “mega drought” and that they will investigate the traces of this drought together at Kültepe this year, Head of Excavation Fikri Kulakoğlu said: “Weiss says that a severe drought in this region, especially in the east of the Mediterranean, in the south of Anatolia, from the Taurus Mountains southward to Iraq, caused the collapse of this empire and led to great migrations. This year, we will investigate whether this drought in southern Anatolia, south of the Taurus Mountains, 4,200 years ago, could have happened in the north. This is a very important question. In our studies, the destruction of large monumental structures from the Early Bronze Age period in Kültepe coincides with this period.”

Kulakoğlu said, “An empire that ruled all these regions is collapsing. There are no signs of war, we see no signs of destruction. Climate changes begin, the clouds coming from the Mediterranean Sea change direction, water becomes scarce, people have to leave the cities and retreat to the mountains, and as a result, that great empire collapses. This is a cycle, and we can follow it at certain periods in the ancient world.”

We attribute the collapse of the Akkadians to climate change.
“Harvey Weiss’ theory has been confirmed not only by archaeological excavations but also by paleogeographical research in the region from Syria to Anatolia.”
“In the archaeological literature, we attribute the collapse of the Akkadians to climate change. Just as the Akkadians collapsed in the south, we want to determine why such a situation is not possible if there is drought in the north, north of the Taurus Mountains.”
Cover Photo: Esma Küçükşahin/AA
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply