
Çemka Höyük, which represents an important turning point in human history
Çemka Höyük is an important settlement that provides important clues about the transition from hunter-gatherer life to agriculture and settled life.
Çemka Höyük, also known as Water’s Edge Höyük, is located within the borders of Ilısu village in Dargeçit district of Mardin province in southeastern Türkiye.
Çemka is located about 1,100 m southwest of the Ilisu Dam dam gate on the Tigris River and the dam road works have severely damaged the site in many places.
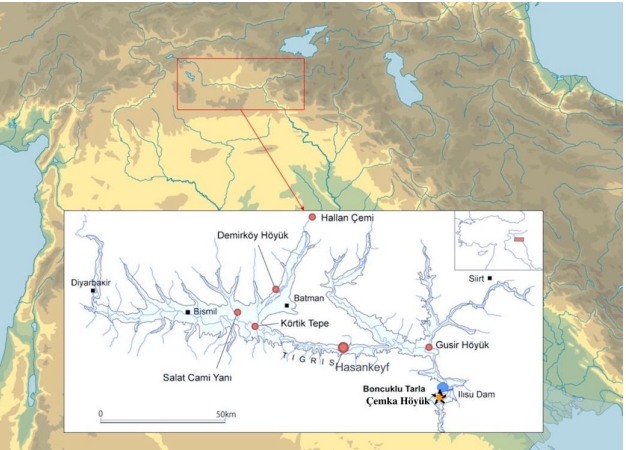
Çemka Höyük is adjacent to the Boncuk Tarla mound, which bears traces of a settled agricultural society.
In 2008, architectural remains, skeletal remains, chipped stone and other finds found during the surveys conducted by the archaeologists of the Mardin Museum showed that Çemka Höyük can be dated to the PPNA and Late Epipaleolithic Period.
In 3 sections opened during the surveys, round-plan houses dating to the PPNA Period and Late Epipaleolithic Period were found.
The remains of floors and walls belonging to simple shelter type structures were discovered.
The structures dated to the PPNA Period have round plans, floors and walls. It was also observed that it was plastered with a light brown clay-soil mixture.
The finds from the rescue excavations carried out in Çemka at a later date provide information about the development of the Zarzian culture in the north.
The Zarzian culture of Zagros origin is one of the most important cultures of the Neolithic Period.
The radial-planned structures found at Çemka Höyük, which provide important new information about the Neolithization process of the Upper Tigris Basin, also point to an architectural feature that has not been seen before in Southeastern Anatolia. These structures provide important information about the cultural structure of the region and its relationship with the surrounding regions.
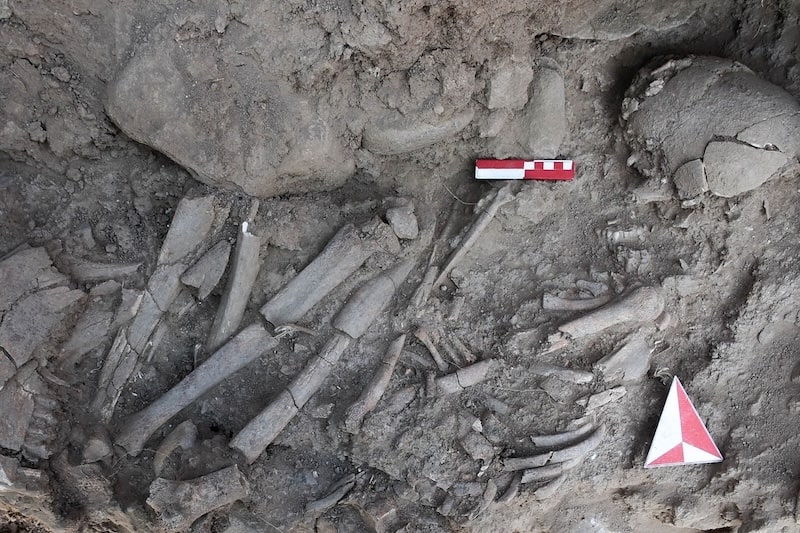

In addition to the radial-planned structures, remains of floors and walls belonging to temporary shelter-type structures made of a mixture of soil and pebble, which are thought to date to the Late Epipaleolithic Period, were also found.
A skeleton was unearthed as a whole under the floor of a house during the cleaning of a section in the mound. The skeleton belonging to a 2-3 years old child was found in full hocker (fetus) position, head facing south, face and the grave was exhumed while he was buried facing east.
No grave goods were found inside the grave.
During the documentation and registration works, a large number of close chipped stone among the artifacts collected were flint and obsidian microblades, blades, microlith tools, flake tools with one or two striking planes flint cores with flint cores were found.
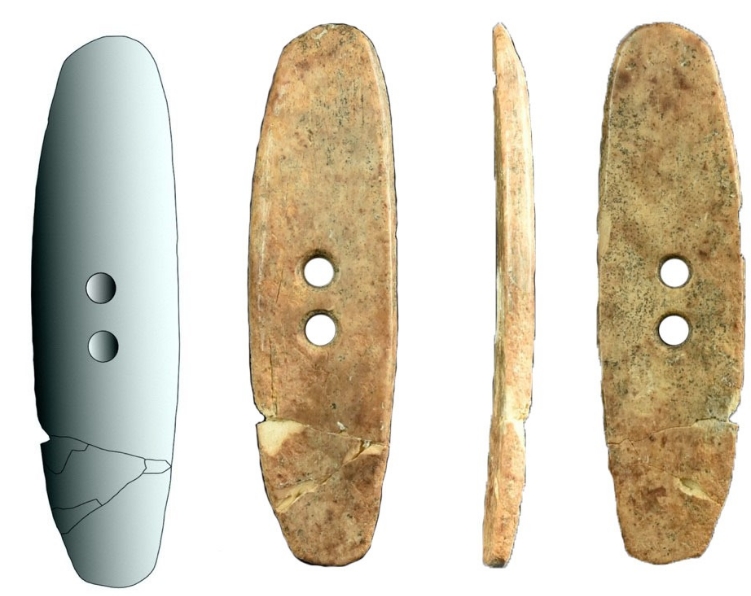

Grinding stones made of basalt dated to the PPNA Period were found during the Pottery-Free Neolithic Period A. The bone tools recovered from the plates indicate that Çemka Höyük is similar to settlements such as Körtik Tepe, Hasankeyf and Gusir Höyük.
With the ongoing archaeological excavations at Çemka Höyük, which is under threat from the Ilısu Dam, it is expected to be possible to obtain more detailed information about the first settlements in the Upper Tigris Basin, the beginning of agriculture and social structures.
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply