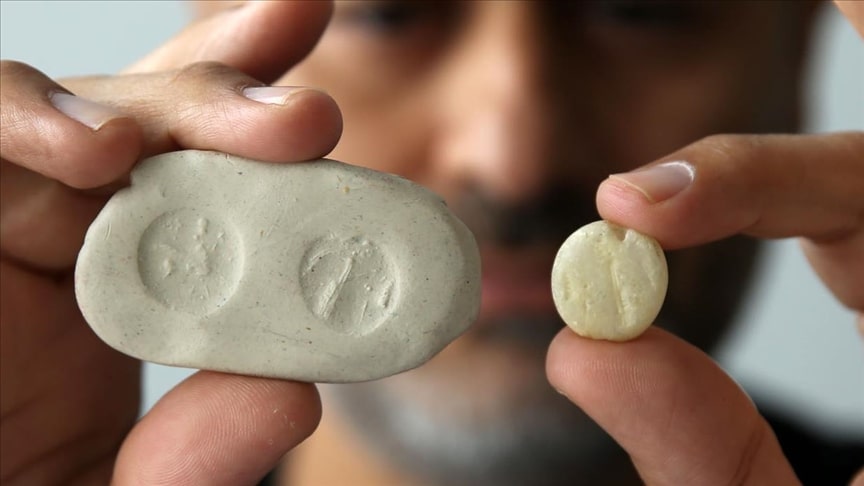
A seal belonging to an Assyrian noble was found at Kef Castle, which was built by the Urartians
During ongoing excavations at the ancient Kef Castle, built at an altitude of 2,300 meters by Urartian King II. Rusa, a seal belonging to an Assyrian noble was found.
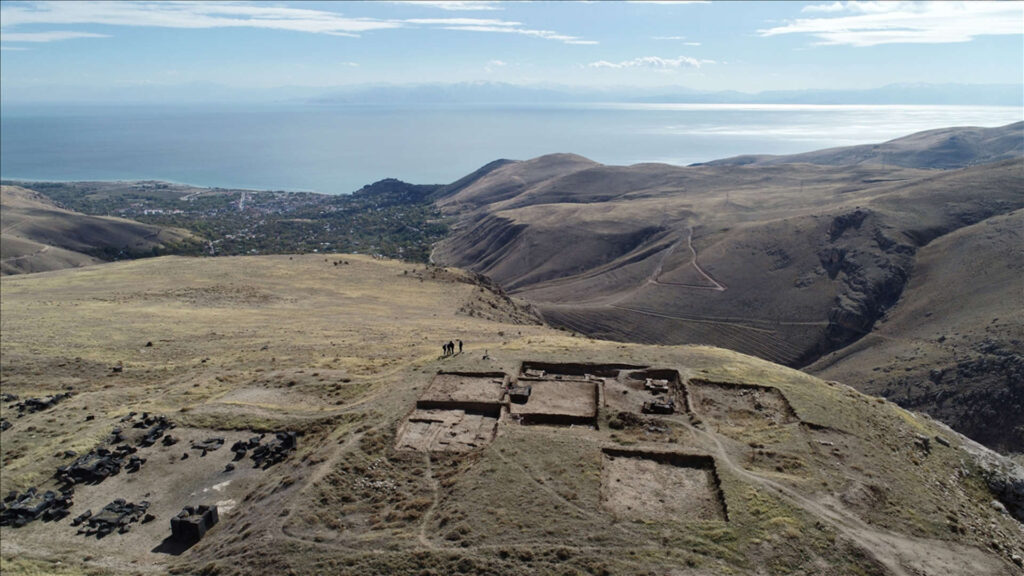
Kef Castle is located in Bitlis province in eastern Türkiye. It was built by King II. Rusa, who reigned between 685 and 645 BC. During his reign, four major iconic cities were constructed, and Kef Castle is one of the remaining parts of these cities. The castle holds a strategic position as it was able to control trade routes and oversee the region.

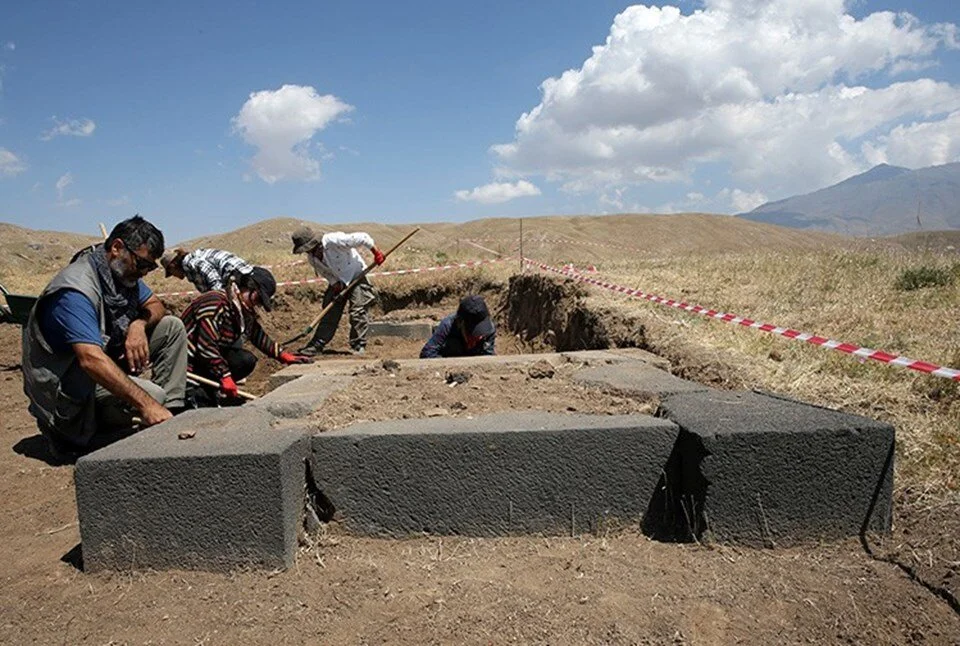
The excavation work led by Assoc. Professor İsmail Coşkun from Van Yüzüncü Yıl University (YYÜ) Department of Archaeology is being conducted with the permission of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism.
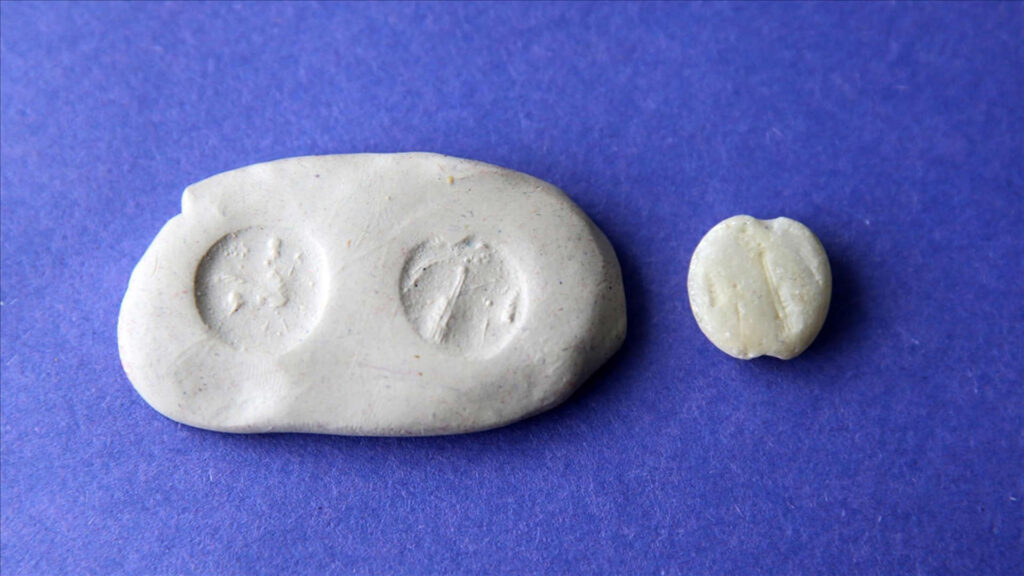
In previous years’ excavations, arrowheads, seven column bases, textile needles, and a button-shaped seal made of alabaster, believed to originate from the Assyrian Empire and featuring figures on both sides, were discovered in architectural structures associated with the hall.

Coşkun stated that this year they have conducted work at six different locations on the side of the upper hall, and in addition to the three column bases identified last year, they have uncovered seven new column bases.
The use of basalt stones in the construction of Kef Castle distinguishes it as a unique Urartian structure. It is thought that these stones likely came from Mount Süphan, which rises above the site.

Coşkun also mentioned that they have opened side rooms connected to the hall, where they found arrowheads, textile needles, and an alabaster seal. This button-shaped seal features figures on both sides. Based on the content of the figures, it is believed that the seal is not local but imported, likely from the Assyrian Empire. Given the rarity of alabaster in the region and its significance as a material, it is thought that this seal belonged to a noble.
These discoveries are significant for a better understanding of Urartian history and contribute to the cultural heritage of the region.
Cover Photo: Harun Nacar/AA
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply