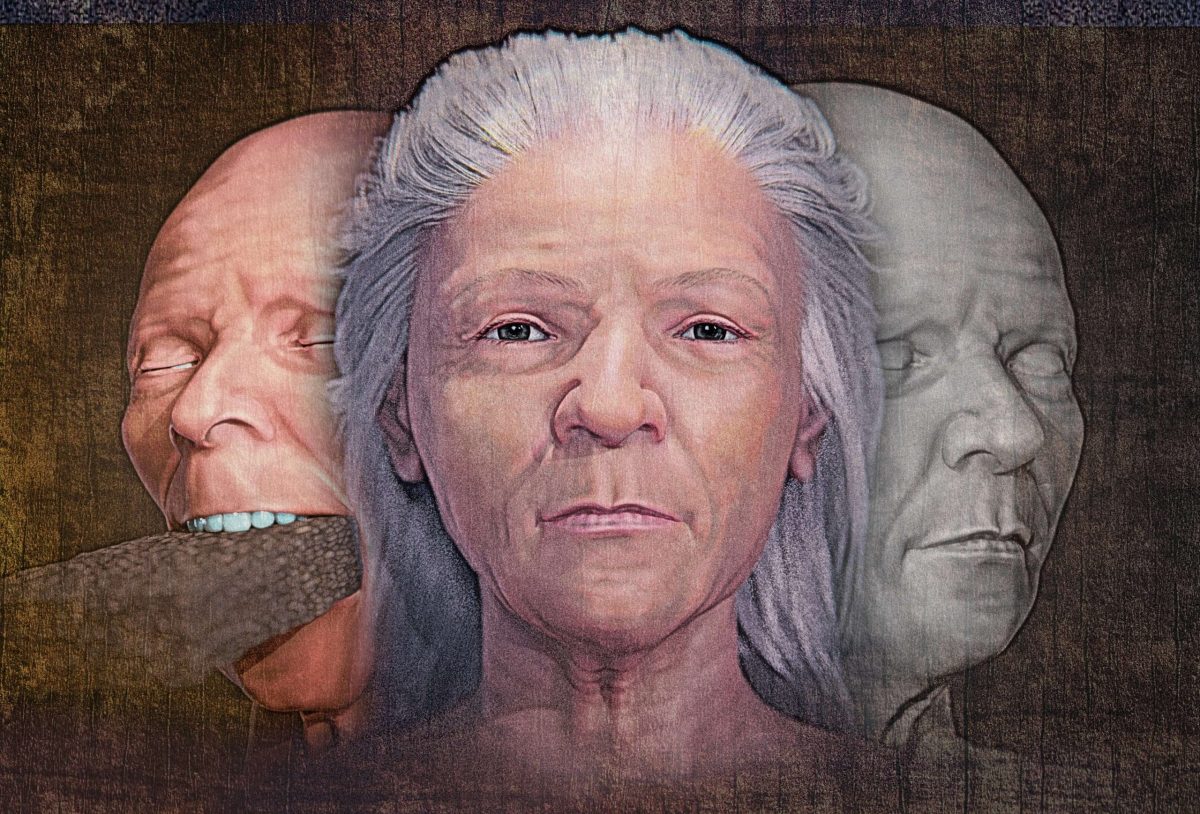

A 16th century Italian ‘vampire’ found buried with a brick in its mouth has had its face reconstructed
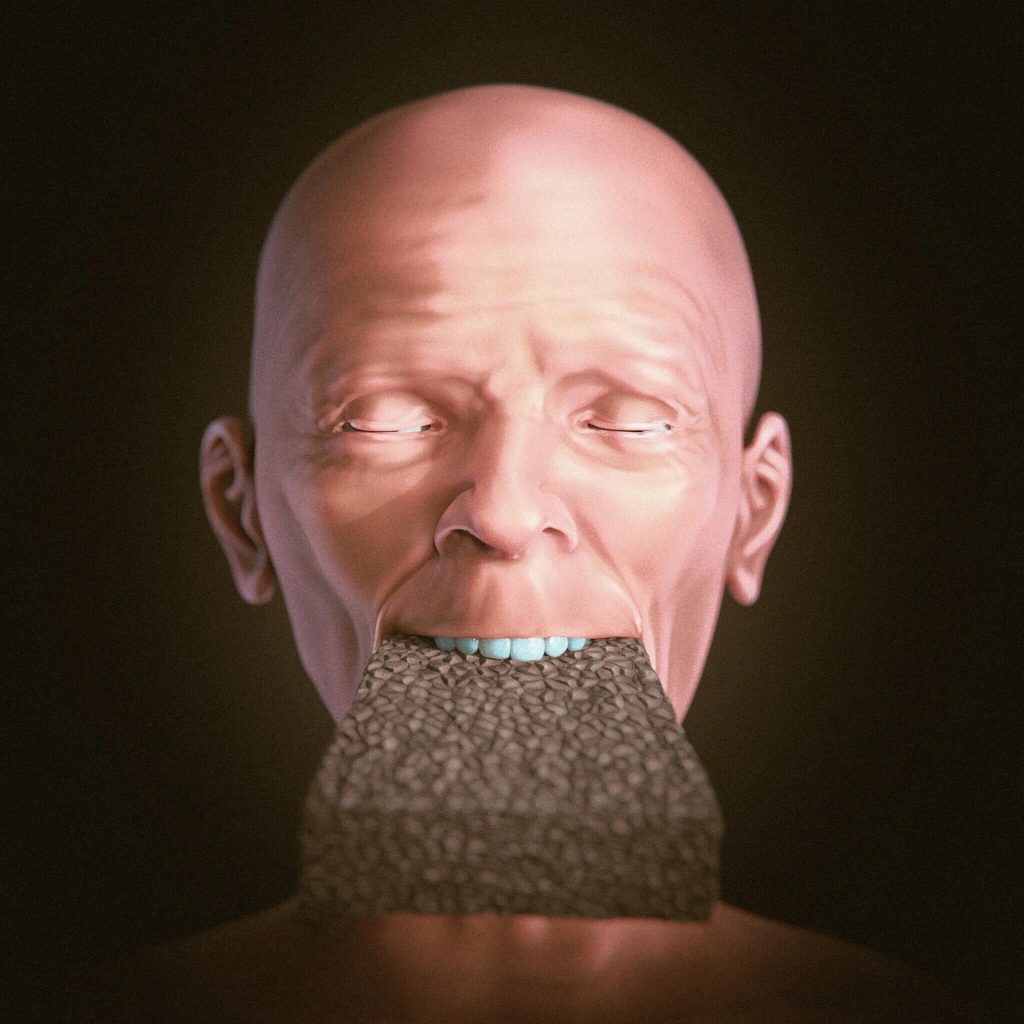
The face of a “vampire” whose grave was dug up in Venice in the 16th century and found with a brick in his mouth has been reconstructed.
Archaeologists made an interesting discovery while excavating mass graves on the island of Lazzaretto Nuovo in Venice in 2006.
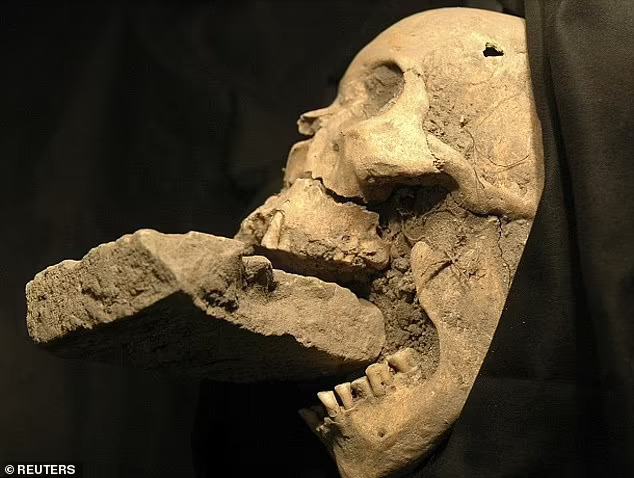
In one of the graves, a female skeleton was found with a brick in its mouth.
The woman, who was buried with a brick in her mouth, is estimated to be 61 years old and of European origin.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Researchers believe that the woman died during the plague and that bricks were placed in her mouth to prevent her from returning as a vampire.
Another idea is that it was placed there by locals who feared that the plague would feed on its other victims.

Forensic anthropologist Matteo Borrini led the discovery of the mass grave from the 1576 plague epidemic. “Vampires don’t exist, but research shows that people at the time believed they did,” Morrini said in 2009 after studying the case for two years. “For the first time, we have found evidence of an exorcism against a vampire.“
Dietary analysis shows that she ate mostly cereals and vegetables, suggesting that she was from the lower class of Europe at the time.
Researchers theorize that a gravedigger may have wedged a rock between the corpse’s teeth to prevent the alleged vampire from chewing through its shroud and infecting others with the plague.
To determine whether the brick was intentionally placed in the woman’s mouth after her death, Moraes replicated the brick using Styrofoam and conducted a series of tests. Their tests revealed that the brick could be compressed into the human mouth without damaging teeth or soft tissue. Compared to the team’s live subjects, the study authors believe it would be even easier with a corpse, although it is still unclear whether this was done intentionally.
The research was published in the journal OrthogOnline.
“The researchers found that when they observed the corpse with the shroud, those in charge of the burial noticed a depression in the mouth area, indicating potential chewing,” the study authors write in the journal OrthogOnline.
“By identifying a vampire, who according to popular legend of the time was one of the culprits of the plague, they introduced the stone as an element of protection, preventing it from feeding and infecting other humans.”
Cover Photo: Reconstruction of the woman’s face using 3D software allowed examination of whether a brick had been inserted into her mouth. Image Credit: SWNS
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply