
A 3,300-year-old tablet found at Büklükale tells of a catastrophic foreign invasion of the Hittite Empire
The Hittite Empire, considered to be the first centralized state of Anatolia, began to rise around 1600 BC and formed a strong political and military union. After ruling for nearly 400 years, the empire suddenly collapsed around 1200 BC. This sudden collapse has remained a mystery that has been investigated by historians and archaeologists for many years.
Was the mysterious disappearance the result of invasions from four sides?
Researchers have attributed the sudden collapse of the Hittite State, whose disappearance was as mysterious as its emergence on the stage of history, to the attack of sea tribes, natural disasters or civil wars.
The 3300-year-old tablet unearthed in Büklükale showed that the mysterious disappearance of the Hittites could be the result of invasions.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The tablet found in Büklükale, which has a strategic importance after the Hittite capital Hattusa, was written in Hittite and Hurrian.
The tablet describes a disastrous foreign invasion of the Hittite Empire. The invasion took place during a Hittite civil war, apparently to help one of the warring factions, according to a translation of the tablet’s cuneiform text.
The palm-sized tablet was found in May 2023 by Kimiyoshi Matsumura, an archaeologist at the Japanese Institute of Anatolian Archaeology, among Hittite ruins at Büklükale, about 37 miles (60 kilometers) southeast of the Turkish capital Ankara.
Matsumura said the tablet dates to the reign of the Hittite king Tudhaliya II, between 1380 and 1370 BC, about 200 years before the collapse of the Late Bronze Age.
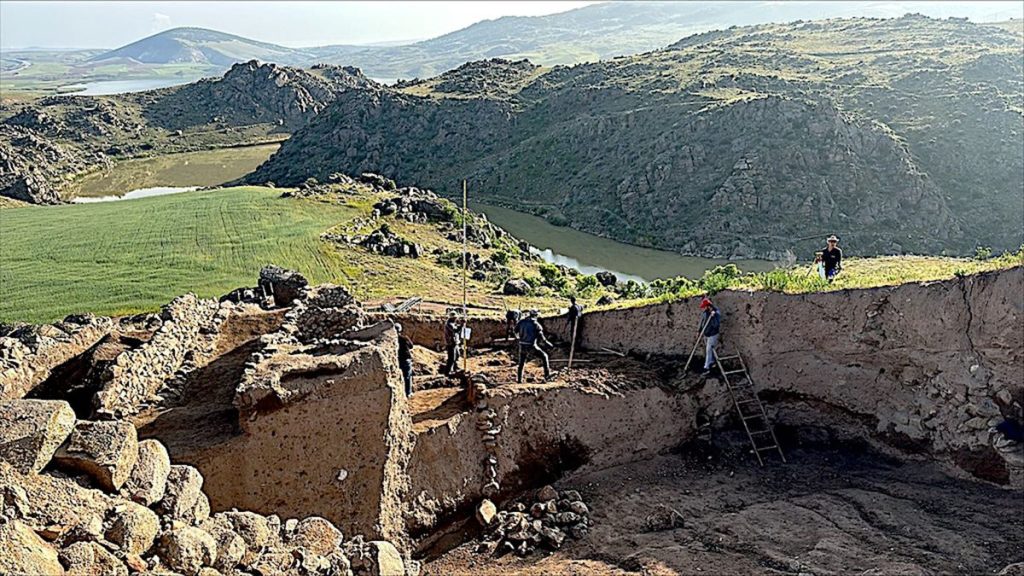

The tablet “seems to come from a period of civil war, which we know from other [Hittite] texts,” he said. “During this time, the Hittite heartland was invaded from many different directions simultaneously … and many cities were temporarily destroyed.” “The new find from Büklükale confirms the important role of Hurri religious traditions in the Hittite royal court during the early imperial period,”Daniel Schwemer, head of ancient Near Eastern studies at the University of Würzburg in Germany, told WordsSideKick.com.
Schwemer, who was not involved in the discovery, noted that the find has not yet been officially published in a peer-reviewed journal. But “the new tablet makes a very important contribution to our knowledge of Hurri language devotional literature,” he said.
Cover Photo: The ancient tablet is inscribed with cuneiform text in both the Hittite and Hurrian languages. The Hittite inscription describes the outbreak of war, and the Hurrian inscription is a prayer for victory. (Image credit: Kimiyoshi Matsumura, Japanese Institute of Anatolian Archaeology)
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply