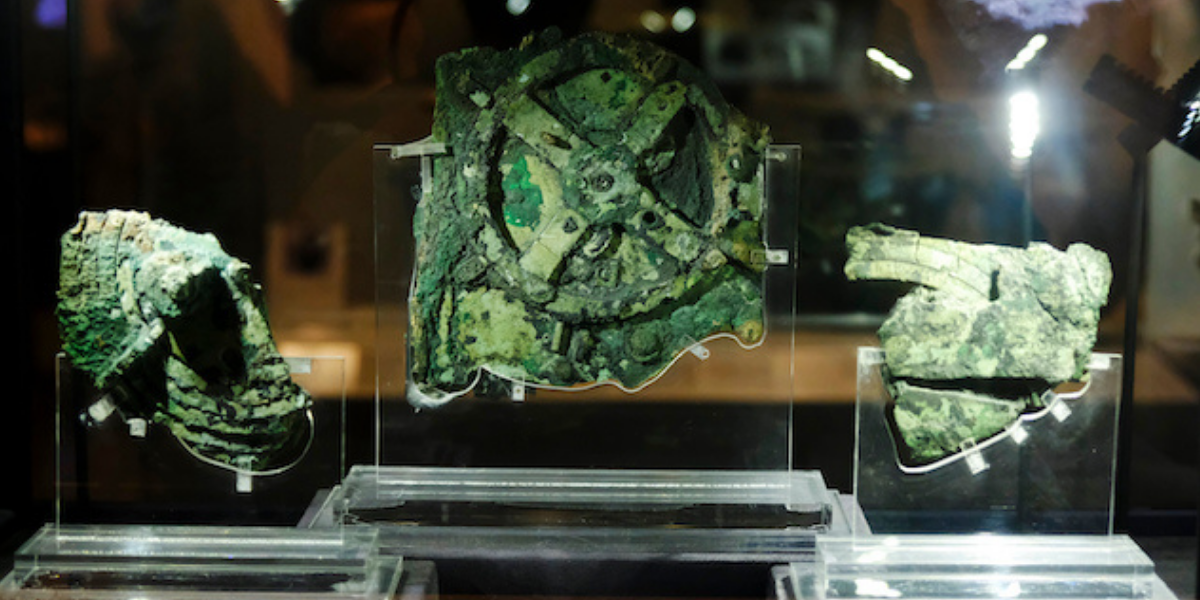
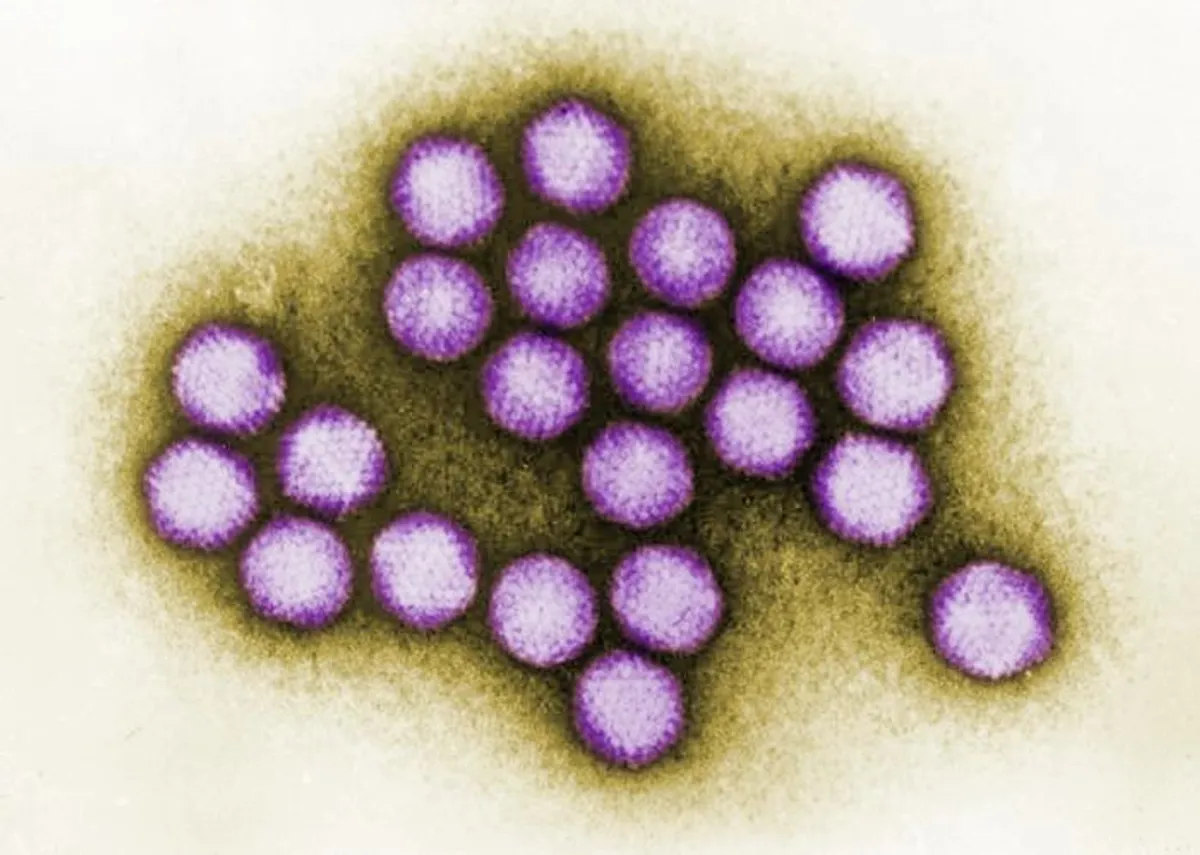
New study provides new evidence that the Antikythera mechanism was used to track the Greek lunar year
Astronomers from the University of Glasgow have found new evidence that one of the components of the Antikythera mechanism, the oldest known analog computer, was used to track the Greek lunar year. The researchers used statistical modeling techniques developed for analyzing gravitational waves to determine the possible number of holes in one of the broken

World’s oldest wine found in a Roman tomb in Spain
During excavations in a family mausoleum dating to the 1st century AD in the Carmona necropolis in Seville, they discovered a vase containing a reddish liquid. As a result of an archaeochemical study, experts identified this liquid as white wine. The wine inside the nearly 1900-year-old vase has become the world’s oldest wine preserved in

Scientists have discovered the smallest previously unknown monkey species in a clay quarry
An international research team has discovered the smallest previously unknown species of monkey during excavations in a clay quarry in Allgäu. The monkey was named Buronius manfredschmidi. Buronius manfredschmidi was found in the immediate vicinity of the great ape Danuvius guggenmosi “Udo” previously found in the same clay quarry. Danuvius was recorded as a species

Archaeologists discover submerged Roman structure on Italy’s west coast
An important submerged Roman building has been uncovered on the coastline of Campo di Mare on Italy’s west coast. The 50-meter-diameter circular Roman structure discovered underwater was connected to a Cipollino marble column with an Ionic capital in 2021. Initial investigations by experts suggest that the extent and complexity of the structure could be a
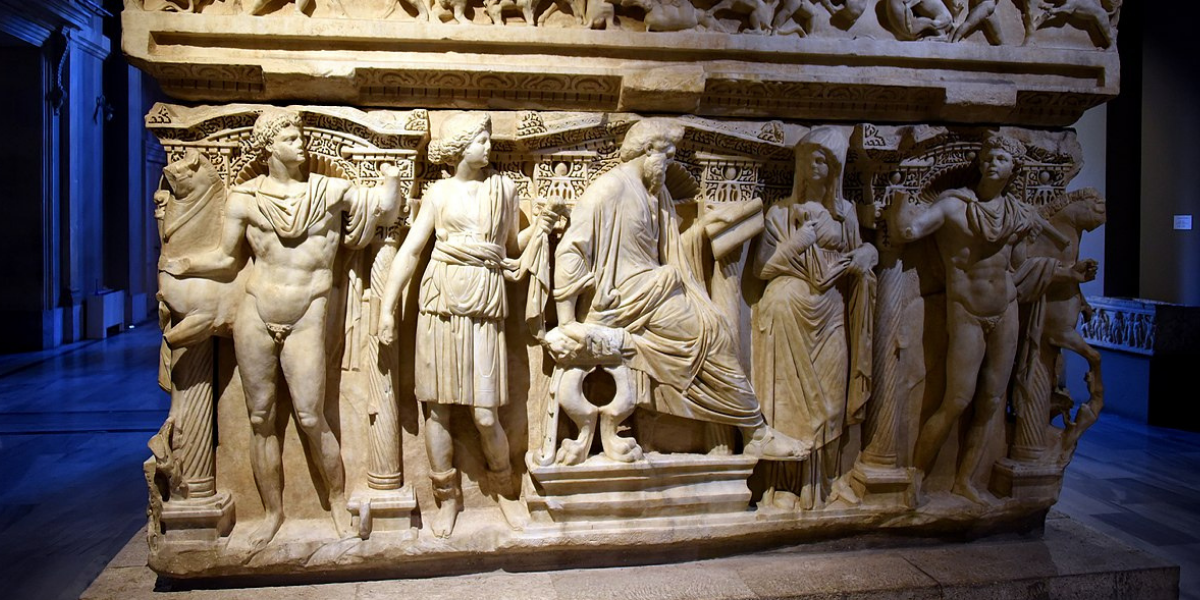

Sidamara, the heaviest sarcophagus in the ancient world
Weighing 32 tons, the Sidamara Sarcophagus, known as the heaviest sarcophagus in the ancient world, was found in the village of Ambar, formerly Sidamara, on the Konya Ereğlisi-Karaman road. The Sidamara Sarcophagus was found by a villager named Molla İbrahim. Molla İbrahim, known as İbrahim Gündoğdu from the Hocalar clan, found the sarcophagus while digging
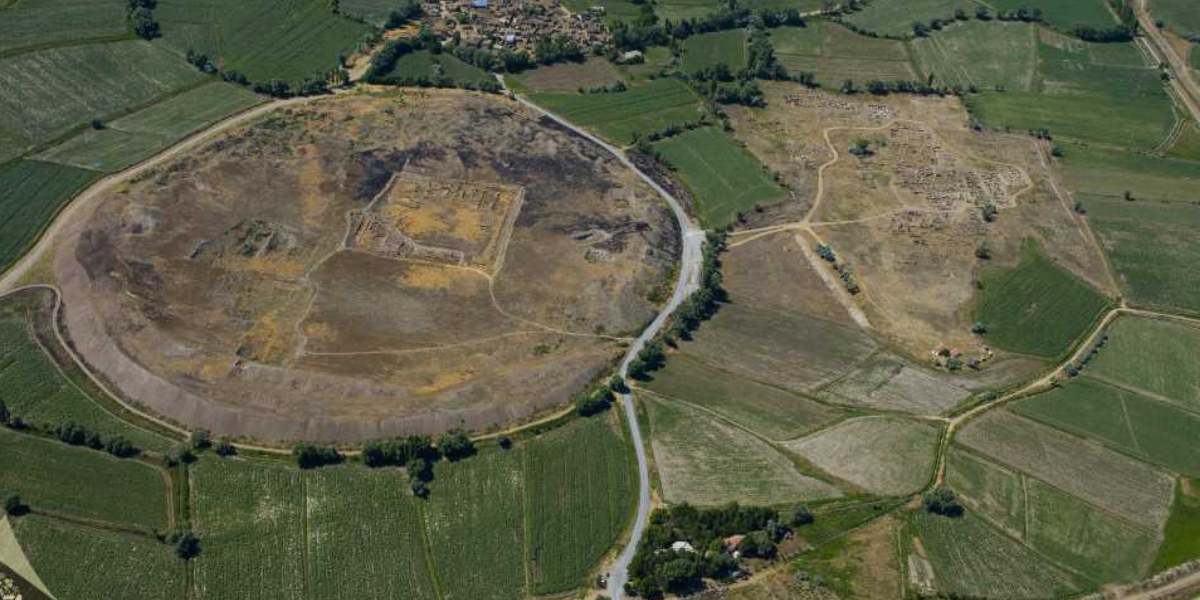

The first company in Anatolia was founded 4000 years ago in Kültepe with 15 kilos of gold
A 4000-year-old tablet found in Kültepe, one of the most important karums of the Assyrian trade colonies, shows that the first company in Anatolia was established in Kültepe. A 4000-year-old tablet found during excavations at Kültepe Karum, administrative center of the ten Karums established by the Assyrians in Anatolia, shows that the first company in
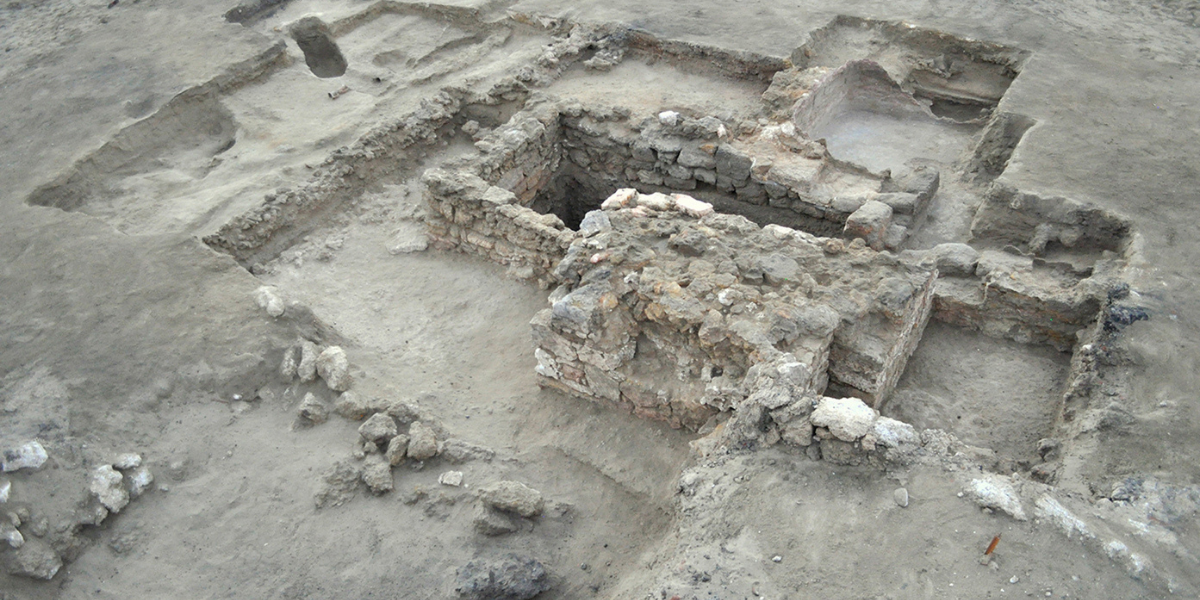

Polish archaeologists find papyri containing letters from Roman centurions in Berenike
Polish archaeologists have made a surprising discovery while excavating an animal cemetery at Berenike on the Red Sea. In the unique animal cemetery dating from the 1st and 2nd centuries, the archaeologists found several papyri that could be an invaluable source of information about the ancient inhabitants of Berenike. In addition to papyri, the archaeologists

The Touristic Salt Express, which will carry its passengers from the past to the future, makes its maiden voyage
It was reported that the Touristic Salt Express, which aims to introduce the historical and cultural beauties of Çankırı to local and foreign visitors, will make its first trip from Ankara on May 18. In a statement made by the Northern Anatolia Development Agency (KUZKA), it was stated that the Touristic Salt Express departing from