New research shows that Ötzi the Iceman had dark skin, a bald head, and Anatolian origins
A recent study on Ötzi, the ice man found in the Alps in 1991 and dated to 3300-3100 BC, revealed that Ötzi has Anatolian origins.
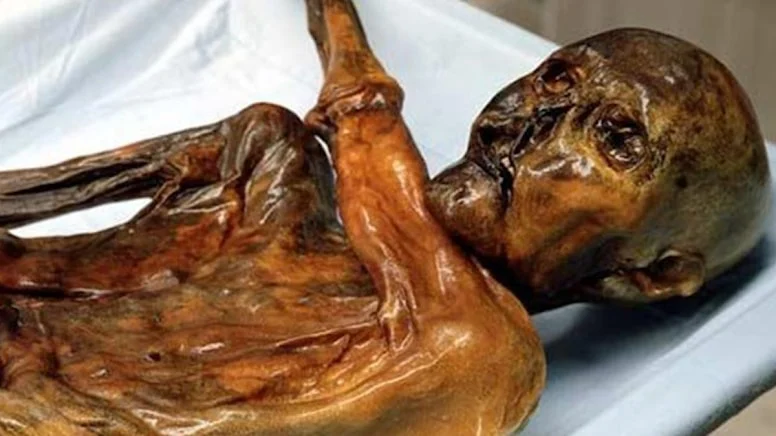
The body of Ötzi, extracted from within an ice sheet on the Similaun Mountain located on the border of Italy and Austria, was remarkably well-preserved.
The studies and analyses conducted on Ötzi’s well-preserved body within the glacier have provided significant insights into the living conditions, diet, health status, and lifestyle of his era.
The initial studies had indicated that Ötzi was a Neolithic European hunter-gatherer. However, a new genetic study conducted by scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig revealed that Ötzi was likely a member of an Anatolian migrant family and, contrary to what was previously known, had a bald head and dark skin at the time of his death.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In the research, advanced sequencing technology was employed to analyze Ötzi’s genome.
The study was published in Sciencedirect.
Advancements in sequencing technology enabled a research team from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and Eurac Research to more accurately reconstruct Ötzi’s genome. The results of this recent analysis refine the genetic portrait of the Iceman: Compared to other contemporary Europeans, Ötzi’s genome has an unusually high proportion of genes shared with the first farmers from Anatolia. Contrary to previous findings, he had advanced hair loss and may have even been bald at the time of his death. Furthermore, his skin was darker than previously thought. Ötzi’s genes also indicate a predisposition to diabetes and obesity.
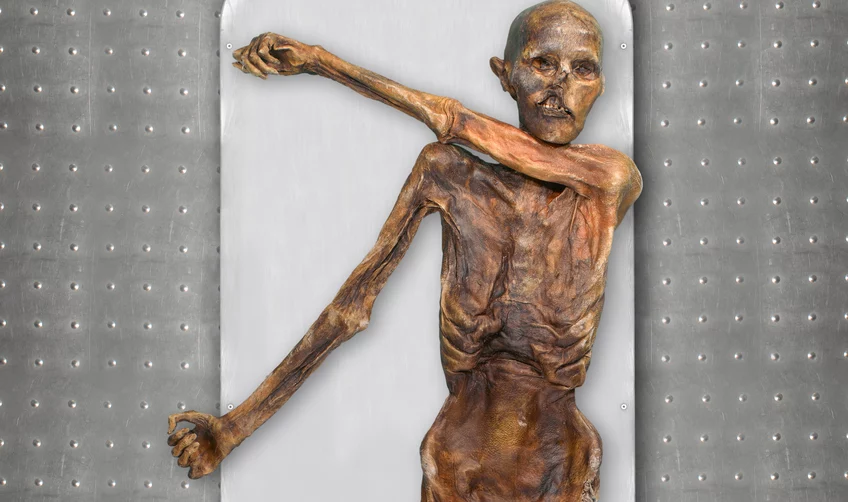
“The initial analysis of the Iceman’s genome revealed the genetic traces of Steppe Herders. However, the refined new results no longer support this finding. The reason for the error: the original sample had been contaminated with modern DNA. Since this initial study, not only has sequencing technology advanced significantly, but many more genomes of other prehistoric Europeans have been fully deciphered, often from skeletal remains. This has enabled a comparison of Ötzi’s genetic code with his contemporaries. The result: among the hundreds of early European individuals whose genomes are currently available, Ötzi’s genome shares more common ancestry with early Anatolian farmers than with his European counterparts.
The research team concludes that the Iceman hailed from a relatively isolated population with minimal contact with other European groups. “We were quite surprised that we didn’t find traces of Eastern European Steppe Herders in the Iceman’s genome in the latest analysis; the proportion of hunter-gatherer genes in Ötzi’s genome is also quite low. Genetically, he appears to have come directly from Anatolia without much mixture with the hunter-gatherer groups,” explains Johannes Krause, the Department Head of Archaeogenetics at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig and co-author of the study.
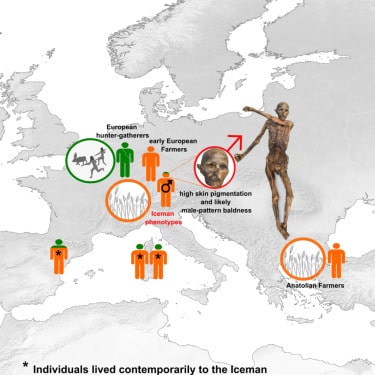
The study also provided new insights into Ötzi’s appearance. The skin type initially identified as Mediterranean-European was darker than previously thought. Albert Zink, co-author and Head of the Institute for Mummy Studies at Eurac Research in Bolzano, explains, “It is the darkest skin tone recorded in contemporary European individuals: previously, it was thought that the skin darkened during preservation in the ice, but what we see now is most likely Ötzi’s original skin color. Of course, knowing this is also important for the appropriate preservation of the mummy.”
Our previous image of Ötzi is also incorrect regarding his hair: as a mature individual, he most likely did not have long, thick hair on his head, but at most had a sparse hair crown. In fact, his genes indicate a predisposition to baldness. Zink states, “This is a relatively clear result and could also explain why there is almost no hair left on the mummy.” Genes indicating an increased risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes were also found in Ötzi’s genome, but these factors likely did not come into play due to his healthy lifestyle.”
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply