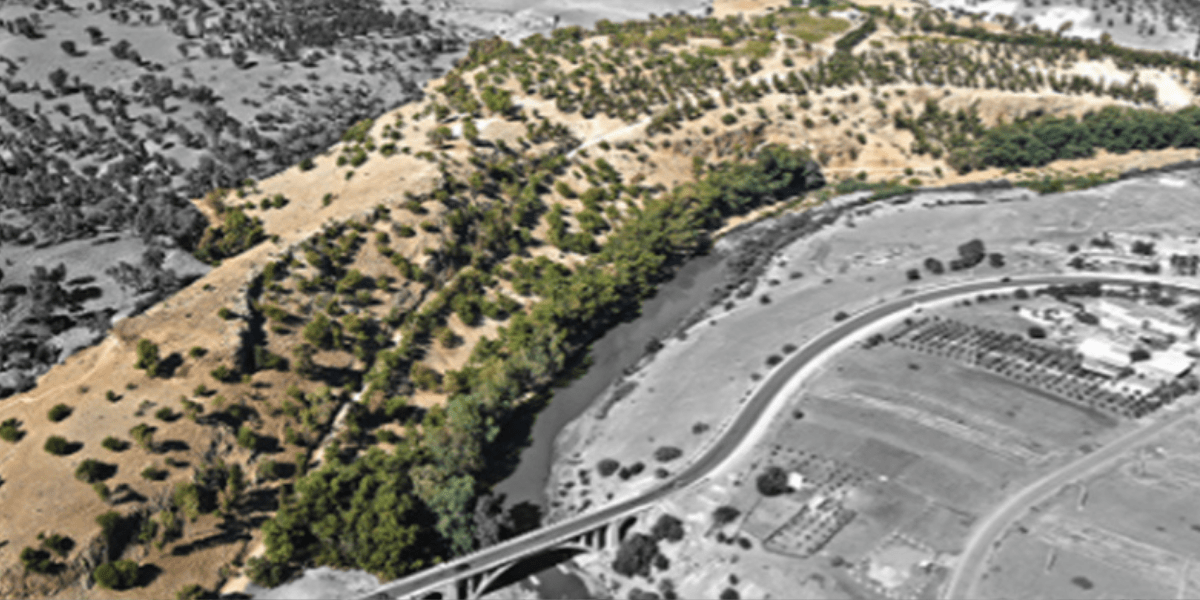

Previously unknown Neolithic farming community discovered in Morocco
Previously unknown Neolithic farming community discovered in the Oued Beht region of Morocco.
The traces of the 3400-2900 BC farming community were revealed as a result of multidisciplinary archaeological research.
The article written after the research was published in the journal Antiquity. The study sheds new light on the role of North Africa in Mediterranean prehistory.
Multi-disciplinary archaeological research in the Oued Beht region of Morocco has uncovered a previously unknown farming society of 3400-2900 BC, shedding new light on North Africa’s role in Mediterranean prehistory.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The site of the 3400-2900 BC farming community is the oldest and largest agricultural complex found in Africa beyond the Nile.
A team of archaeologists led by Prof. Cyprian Broodbank from the University of Cambridge, Prof. Youssef Bokbot from INSAP and Prof. Giulio Lucarini from CNR-ISPC and ISMEO carried out the collaborative work at Oued Beht in Morocco.
“For more than three decades, I have been convinced that Mediterranean archaeology has missed something fundamental in later prehistoric North Africa,” said Prof. Cyprian Broodbank. “Now, finally, we know this to be true, and we can begin to think in new ways that acknowledge the dynamic contribution of Africans to the emergence and interactions of early Mediterranean societies.”
“For more than a century the last great unknown of later Mediterranean prehistory has been the role played by the societies of Mediterranean’s southern, Africa shores west of Egypt,” say the authors of the new study. “Our discoveries prove that this gap has been due not to any lack of major prehistoric activity, but to the relative lack of investigation, and publishing. Oued Beht now affirms the central role of the Maghreb in the emergence of both Mediterranean and wider African societies.”
These results reveal that the site was the largest agricultural complex from this period in Africa outside of the Nile region. All of the evidence points to the presence of a large-scale farming settlement—similar in size to Early Bronze Age Troy.
Archaeologists found unprecedented remains of domesticated plants and animals, pottery and lithics dating to the late Neolithic period. The excavation also revealed extensive evidence for deep storage pits.
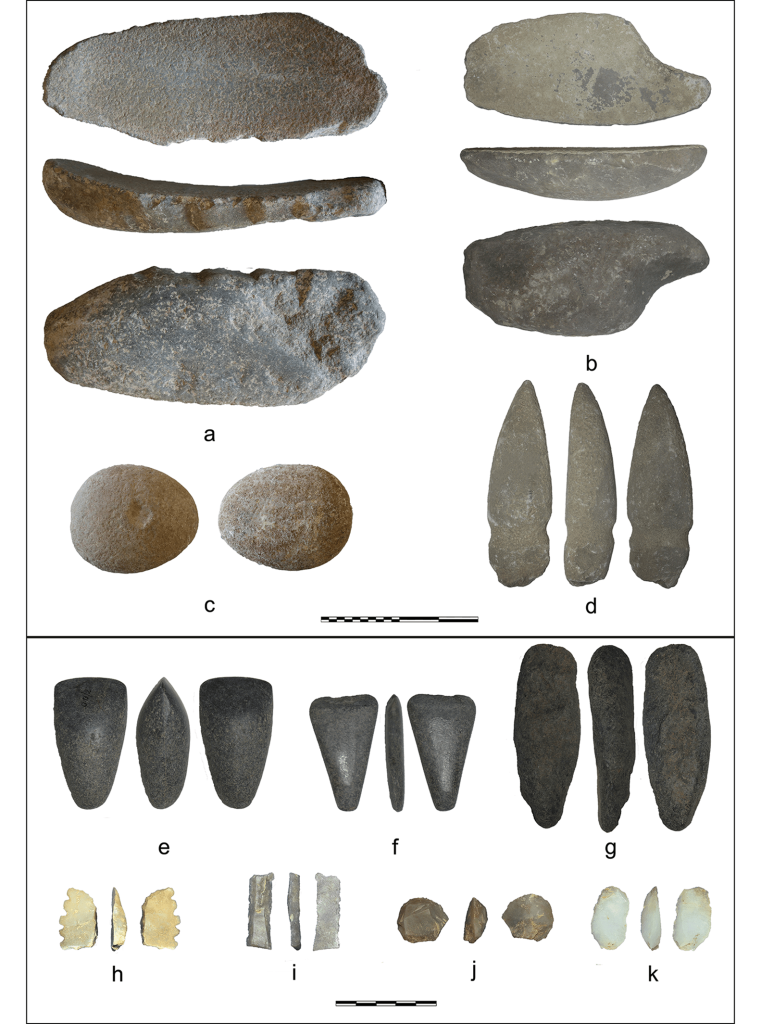
Contemporary sites with similar pits have been found on the other side of the Strait of Gibraltar in Iberia, where finds of ivory and ostrich eggs have long pointed to African connections. The site, the most important step in the discovery, shows that the Maghreb was influential in wider Western Mediterranean developments during the fourth millennium BC.
These discoveries in Oued Beht and the northwestern Maghreb, clearly integral parts of the wider Mediterranean region, significantly alter our understanding of the later prehistory of the Mediterranean and Africa.
As the authors of the Antiquity article state: “It is crucial to consider Oued Beht within a broader, co-evolving and unifying framework that embraced peoples on both sides of the Mediterranean-Atlantic gateway in the late fourth and third millennia BC – and despite the possibility that it could have moved in either direction, it is crucial to recognize it as a distinctly African-centered community that contributed significantly to the shaping of this social world.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2024.101
Cover Photo: Antiquity
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply