
Surprising discovery in the ‘holy water’ of the Hittites
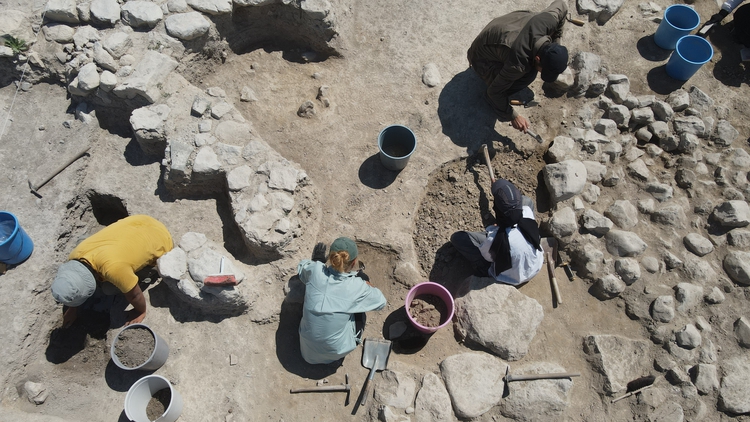
Ongoing archaeological excavations in the sacred Hittite city of Nerik (today’s Oymaağaç Mound) are revealing surprising discoveries.
With a 3500-year history, Nerik, which is considered a sacred city by the Hittites, is located 7 kilometers northwest of Vezirköprü district of Samsun.
Nerik was founded by the Hattis and after the fall of the Hittite empire, it was never inhabited again.
The city was dedicated to the Hatti storm god Teşup. It retained the same importance during the Hittites. Many clay tablets unearthed during the excavations, describing festivals and rituals organized for the gods, document this sanctity of the city.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The team, including academics from the United States, Australia, Germany and Türkiye, has been excavating the site for 17 years.
A team working in a temple in Nerik discovered a tunnel. Continuing excavations towards the end of the tunnel, the team found the area the Hittites called “holy water”.
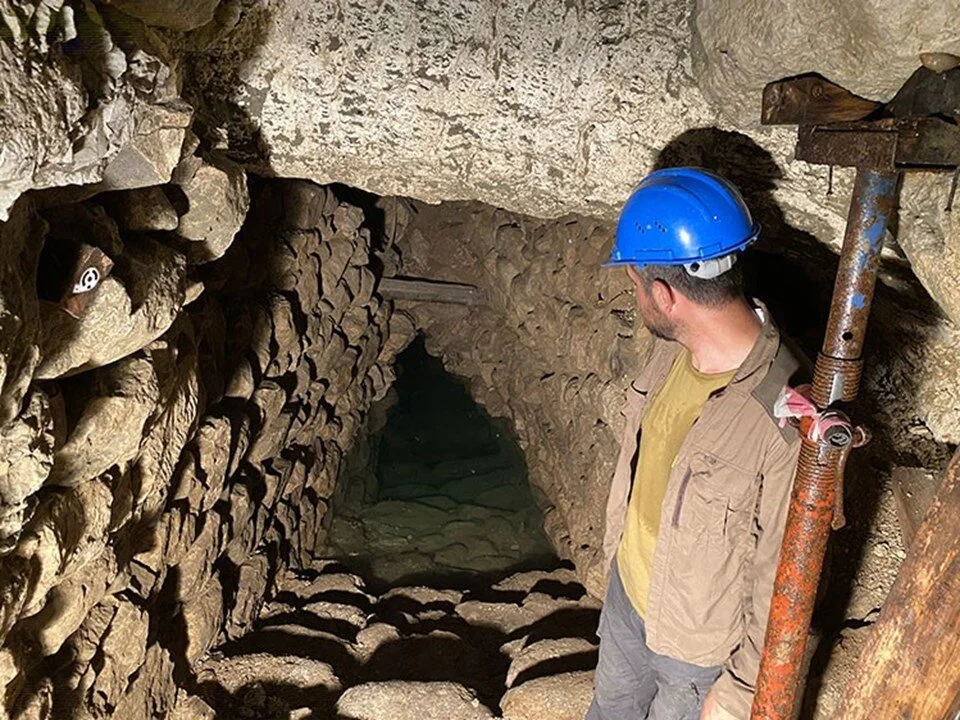

Noting that 3,000-year-old hazelnut shells were extracted from the sacred water inside the tunnel, the excavation team said, “We believe that the temple there was used for many years. We see in the Oymaağaç Mound that it was used in the Old Hittite period, that is, from the 16th century B.C. to the 12th century B.C. We found a tunnel above the temple, and as we excavated the tunnel, we moved toward the water. At a depth of approximately 8 meters, we reached the area that the Hittites called ‘holy water.'”
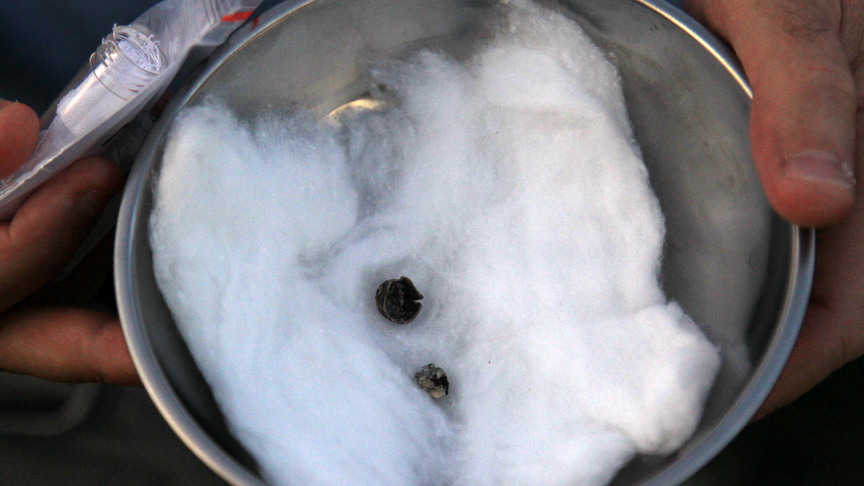

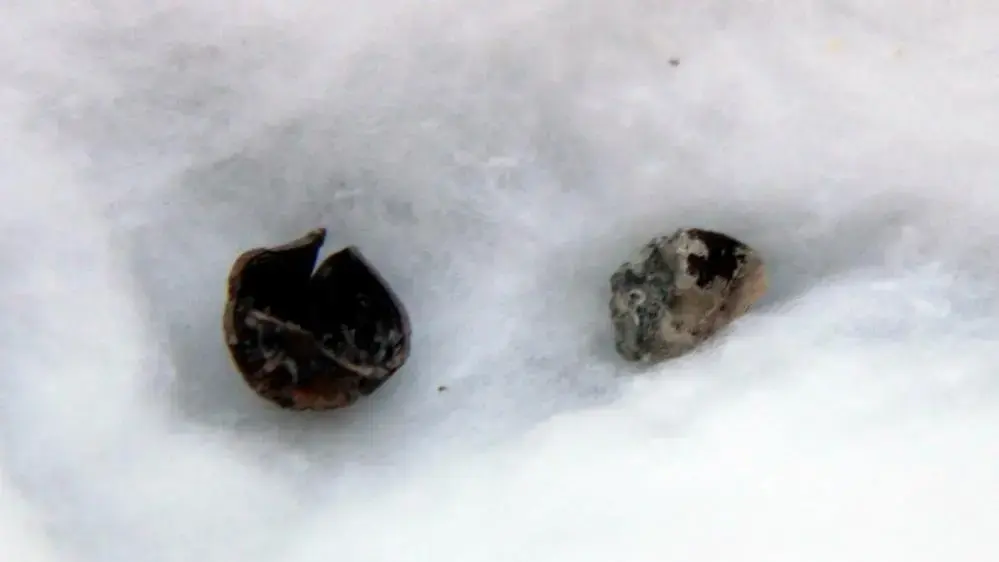
“We believe that Nerik had a history of 3,500 years. But we were shocked when we found wooden remains inside the pool as there is no wet material in Anatolia. When we dug a little more in that area, we also found hazelnut shells. The 3,000-year-old hazelnut shells confirmed that the Black Sea Region was a hazelnut production center. Carbon dating tests on the wooden findings and hazelnut shells revealed they are approximately 3,000 years old.”

According to experts, the cuneiform tablets found during excavations at Nerik are the most important remains of material culture. As a result of the studies conducted on the tablets, the location of the sacred city of Nerik, which was thought to be on the northern borders of the Hittite Empire, was definitely Oymaağaç Mound.
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply