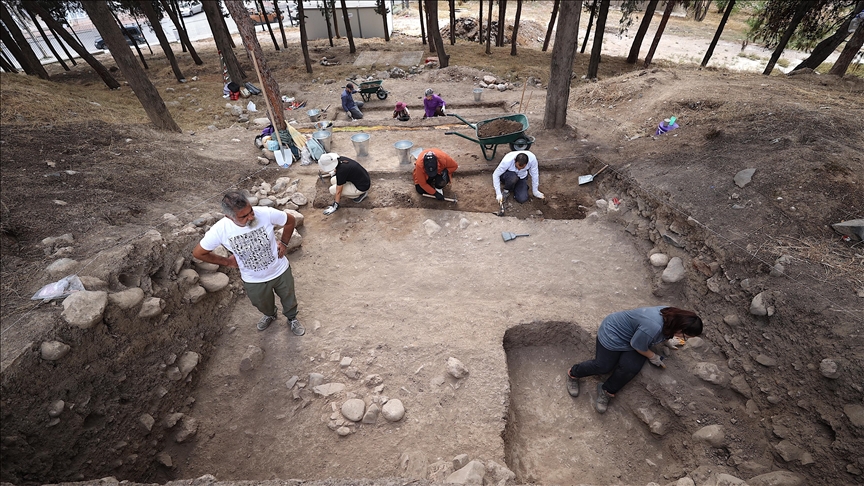

Two wheat species dating back 9000 years identified at Yumuktepe
Archaeobotanical research at the Yumuktepe Mound in Mersin has uncovered two types of wheat seeds dating back 9000 years.
Considered one of the oldest settlements in Anatolia, Yumuktepe Mound has been continuously inhabited since the Neolithic period.
Excavations at Yumuktepe revealed traces of many different cultures starting from the Neolithic period to the Roman and Byzantine periods.
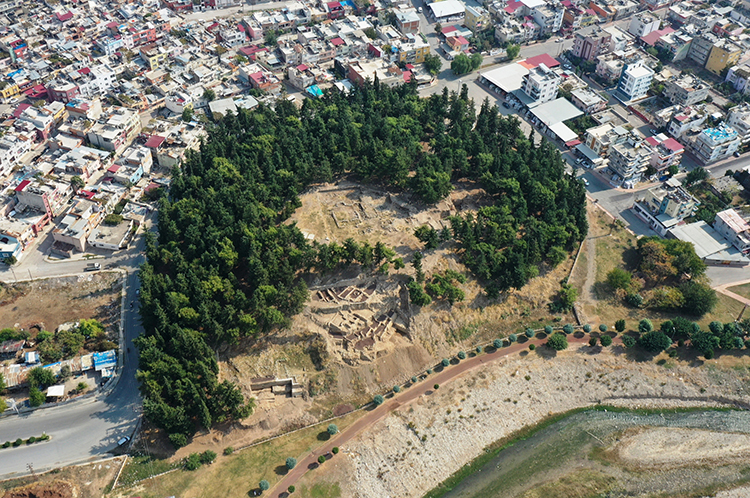

Yumuktepe was under the influence of different cultures in different periods. Traces of many civilizations such as Hittites, Luwians, Greeks, Romans and Byzantines can be seen on the mound. This makes Yumuktepe a cultural mosaic.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Archaeobotanical research at Yumuktepe Mound, where the first archaeological excavations began in 1937, is being carried out under the direction of Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burhan Ulaş, a faculty member at the Department of Archaeology, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, İnönü University.
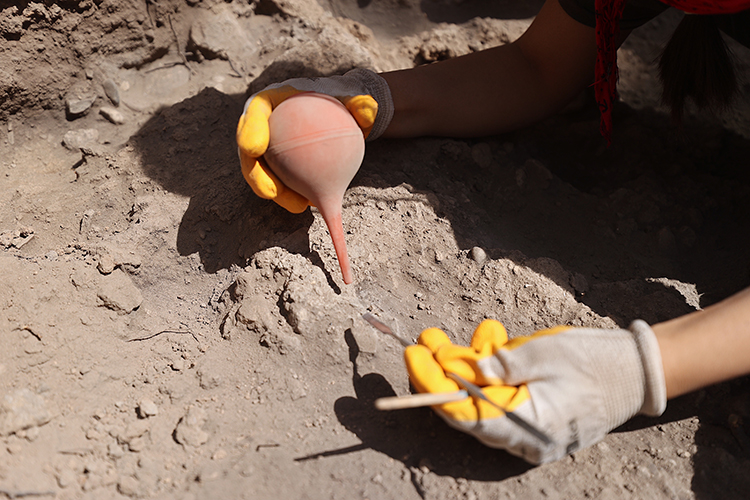

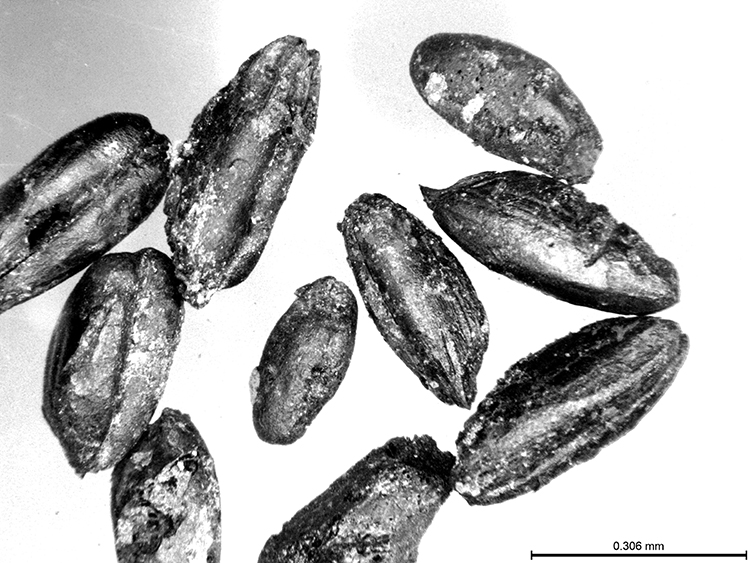
The team studied the “ancient DNA” of wheat seeds. The results showed that the seeds belonged to varieties called “Triticum timopheevii” (a new type of spa wheat) and “Triticum spelta” (the most primitive type of bread wheat) with a history of 9 thousand years.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Burhan Ulaş, who is also the excavation coordinator, said that archaeobotanical research has been carried out at the mound since 2000.

Explaining that they mostly found carbonized plant remains in the excavation areas in the mound, Burhan Ulaş said, “We analyze these remains in the laboratory environment. We carry out these studies on the Neolithic, Chalcolithic and Byzantine periods in Yumuktepe Mound.”
Stating that they have identified a type of wheat called ‘new type of spa’ in recent studies, Ulaş said, “The earliest place where this wheat was identified is the Cafer Mound settlement, which dates back to approximately 8,500 BC. Later, it is found in Central Anatolia, in Aşıklı Höyük (Aşıklı Mound) and Boncuklu Höyük (Boncuklu Mound). Yumuktepe Mound is one of the oldest settlements of the wheat species called ‘Triticum spelta’ identified in the literature so far. The peculiarity of these two wheat varieties is that they were preferred by European Neolithic farmers rather than those from the Near East. With the current findings, we think that Yumuktepe played a key role in the spread of Neolithic agriculture from the Eastern Mediterranean to Europe via the Balkans both by sea and land.”
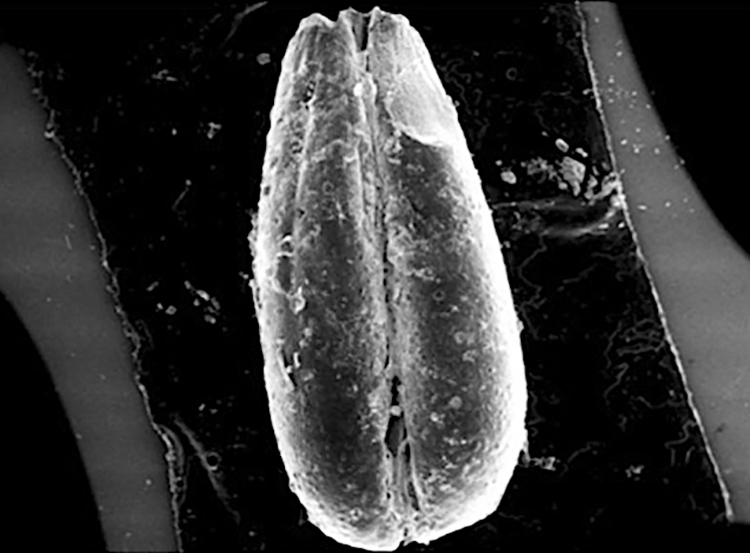
Underlining that the “Triticum timopheevii” species is about to disappear, Ulaş said:
“It is cultivated only in a narrow region in Georgia. The situation is the same for Triticum spelta. Since these are carbonized seeds, they cannot be used in modern agriculture. They are considered dead. It was previously thought that Triticum spelta was cultivated in the Bronze Age, but with our study, we have revealed that this species was cultivated approximately 3-4 thousand years before the Bronze Age. This is very important information that changes what we know about the origin and spread of Neolithic agriculture.”
Cover Photo: Serkan Avcı/AA
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply