
World’s oldest wine found in a Roman tomb in Spain
During excavations in a family mausoleum dating to the 1st century AD in the Carmona necropolis in Seville, they discovered a vase containing a reddish liquid. As a result of an archaeochemical study, experts identified this liquid as white wine. The wine inside the nearly 1900-year-old vase has become the world’s oldest wine preserved in liquid form.
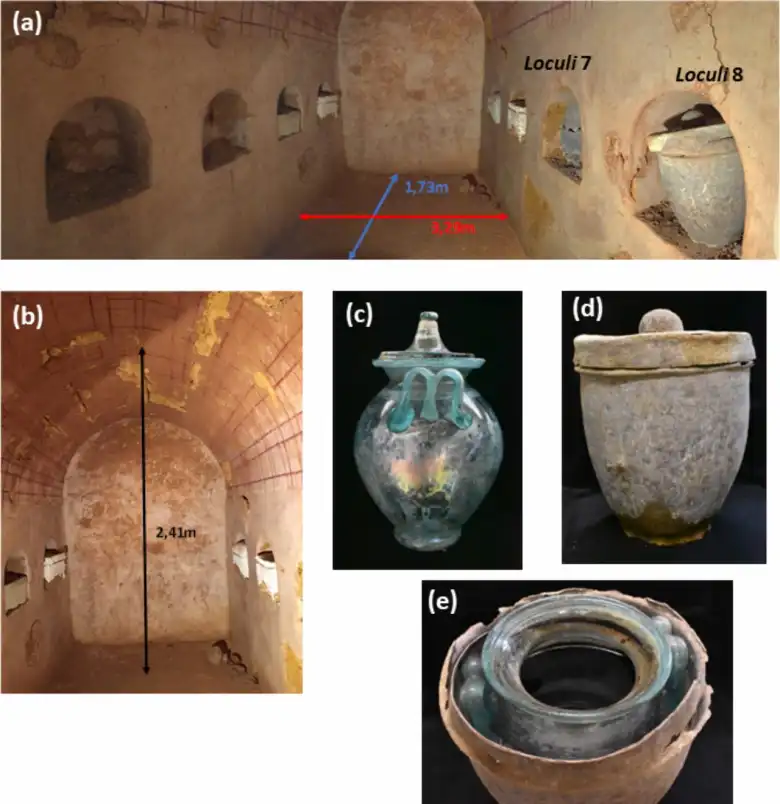
The Spanish vase was recovered in 2019 after a family doing some work on their home in Carmona came across a sunken tomb on their property. This tomb, dated to the early 1st century AD, contained eight niches, six of which contained cremated remains and urns with various objects typical of Roman funeral rituals.
The tomb contained eight burial niches, six of which held pots made of limestone, sandstone or glass and lead. Each jar contained the cremated remains of a single individual, and two of the jars were inscribed with the names of the deceased: Hispanae and Senicio.
The urn in Niche 8 is what set this discovery apart. Inside an oval lead box with a flat domed lid was this urn, a glass burial vessel with an M-shaped handle. Inside, five liters of a reddish liquid were discovered, estimated to be part of the original contents, along with the remains of cremated bones.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
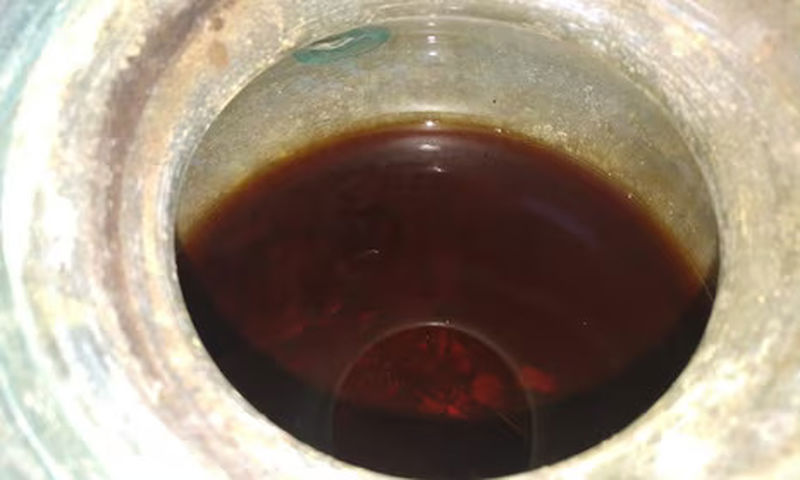

Analysis by experts at the University of Córdoba revealed that the ancient yellowish liquid inside the urn was a local, sherry-like wine.
“The wine turned out to be quite similar to wines from Andalusia: Montilla-Moriles; sherry-type wines from Jerez and manzanilla from Sanlúcar,” said José Rafael Ruiz Arrebola, an organic chemist at the University of Córdoba, according to the archaeonews news portal.
Using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), the scientists were able to identify the chemical constituents of the mineral salts of wine, which include common elements found in old wines such as potassium, calcium and magnesium. In addition, using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry, or HPLC-MS, they identified polyphenols, compounds found in grapes and therefore in wine. The researchers were able to identify the liquid as white wine due to the presence of specific polyphenols and its mineral salt profile.
The extraordinary longevity of the wine in liquid form testifies to sophisticated Roman preservation and storage methods, as well as the different climatic conditions that allowed it to be preserved for nearly two millennia.
Prior to the discovery, reported in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, the oldest wine preserved in liquid form was the Speyer wine bottle dated to 325 AD, excavated in 1867 from a Roman tomb near Speyer, Germany.
According to researchers, the use of wine in Roman funerals is well known and documented. Therefore, once the cremated remains were deposited inside, they must have been filled with wine during the funeral rite or in some kind of drinking ritual as part of the funeral rite to help the deceased transition to a better world.
They conclude that the results of this study strongly suggest that the reddish liquid in the urn was originally wine that decomposed over time, making it about 2,000 years old and the oldest wine found to date.
Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports
doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104636
Cover Photo: Daniel Cosano et al.
You may also like
- A 1700-year-old statue of Pan unearthed during the excavations at Polyeuktos in İstanbul
- The granary was found in the ancient city of Sebaste, founded by the first Roman emperor Augustus
- Donalar Kale Kapı Rock Tomb or Donalar Rock Tomb
- Theater emerges as works continue in ancient city of Perinthos
- Urartian King Argishti’s bronze shield revealed the name of an unknown country
- The religious center of Lycia, the ancient city of Letoon
- Who were the Luwians?
- A new study brings a fresh perspective on the Anatolian origin of the Indo-European languages
- Perhaps the oldest thermal treatment center in the world, which has been in continuous use for 2000 years -Basilica Therma Roman Bath or King’s Daughter-
- The largest synagogue of the ancient world, located in the ancient city of Sardis, is being restored











Leave a Reply