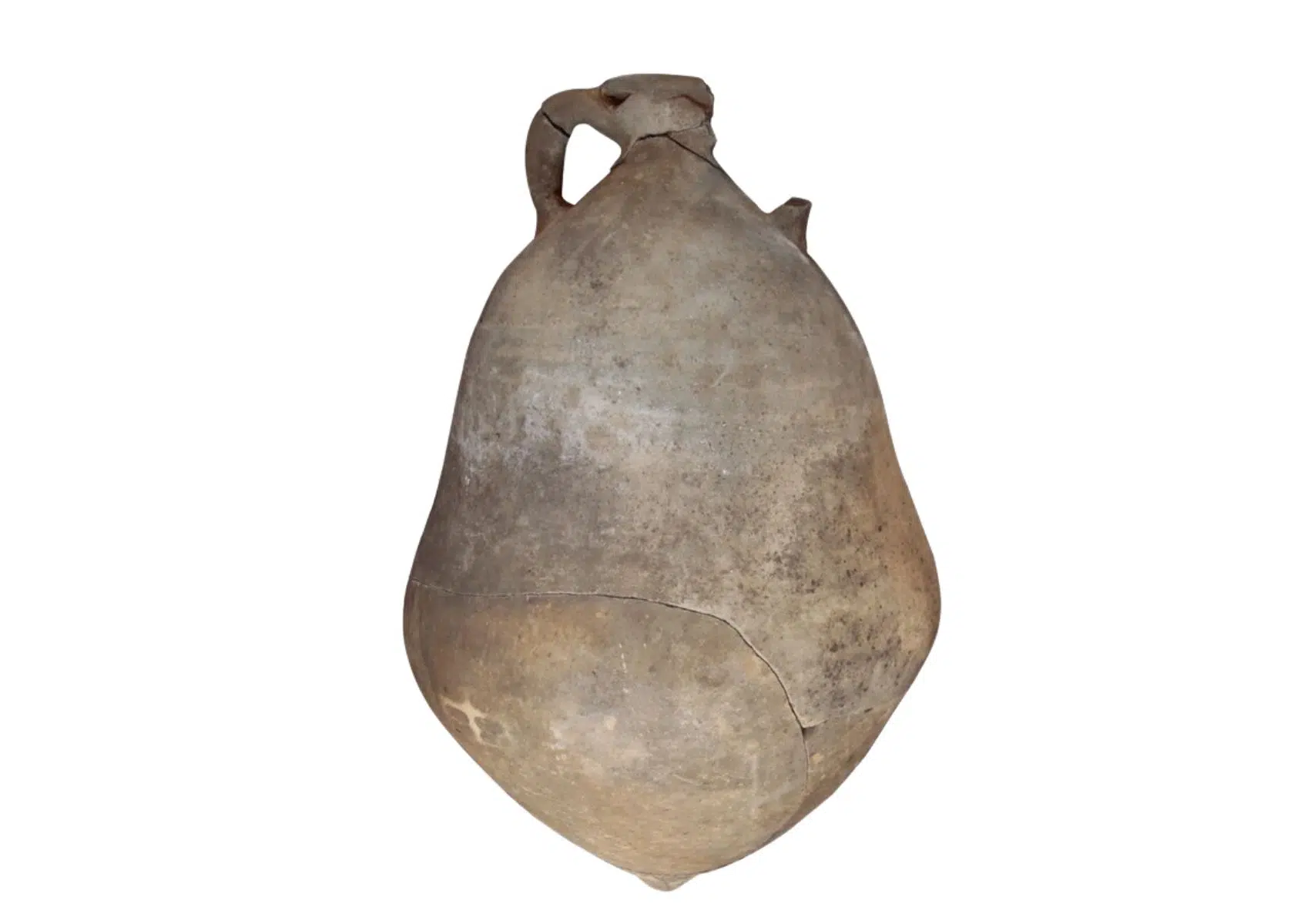
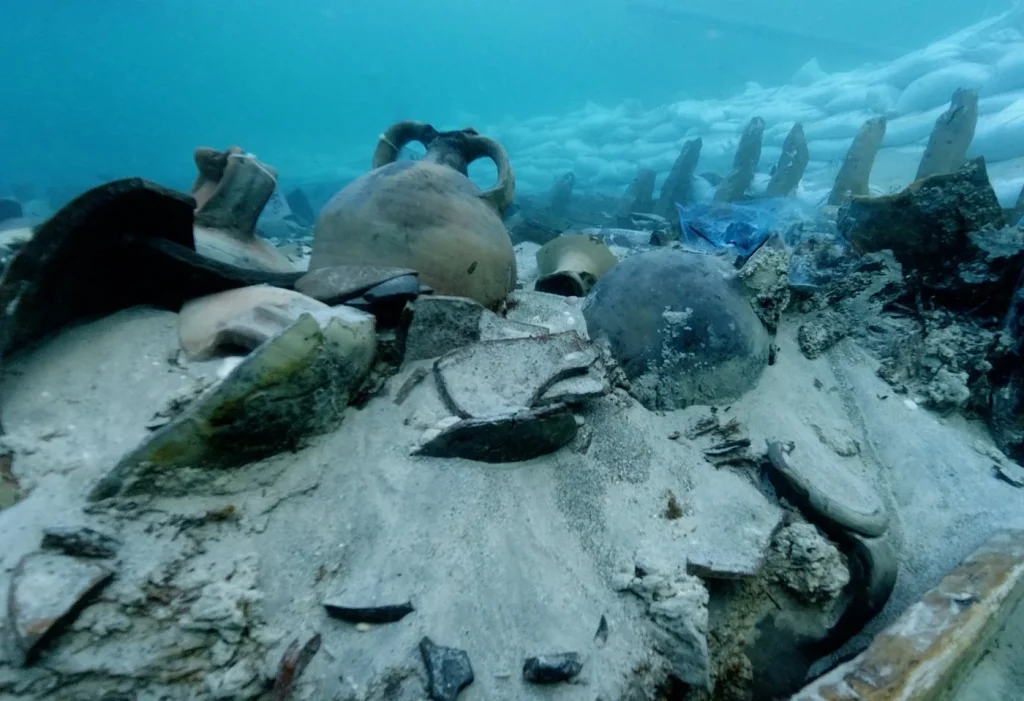
A unique amphora was found in an ancient Roman shipwreck near Mallorca, one of Spain’s Balearic Islands.
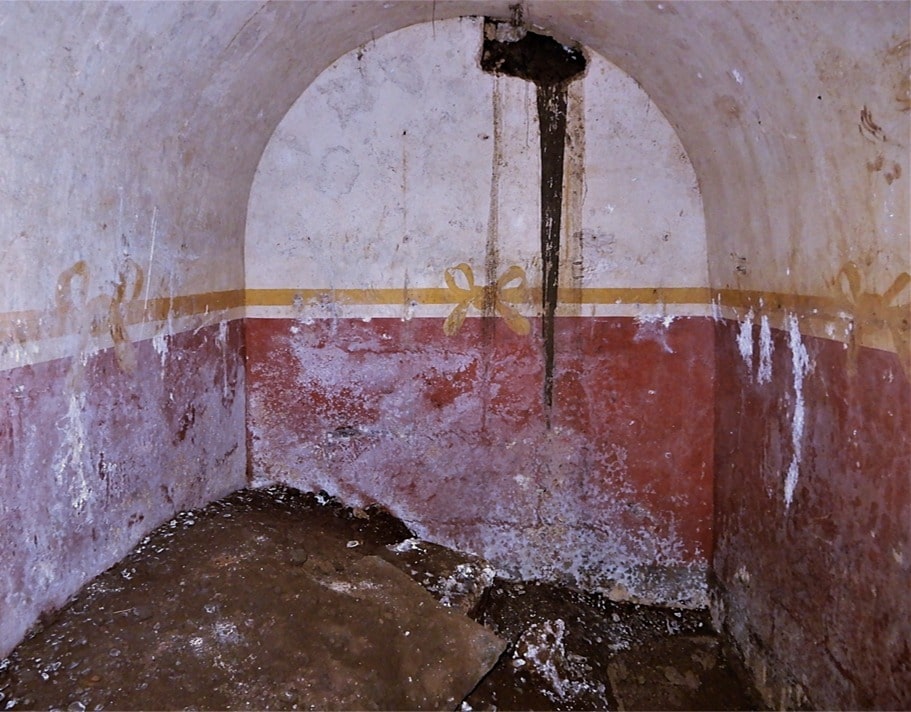
The Roman shipwreck has attracted the interest of many researchers due to its preservation and interesting cargo.
A new type of ampharo was identified during the studies on the remains found in the cargo hold of the ship.

A team of archaeologists and researchers used a detailed analytical method to obtain new information about the amphora.
The results of the analysis were published in the journal “Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences”.
The team used a variety of techniques to thoroughly investigate the site, including petrographic analysis, archaeozoology, relic analysis and the study of wood and plant remains.
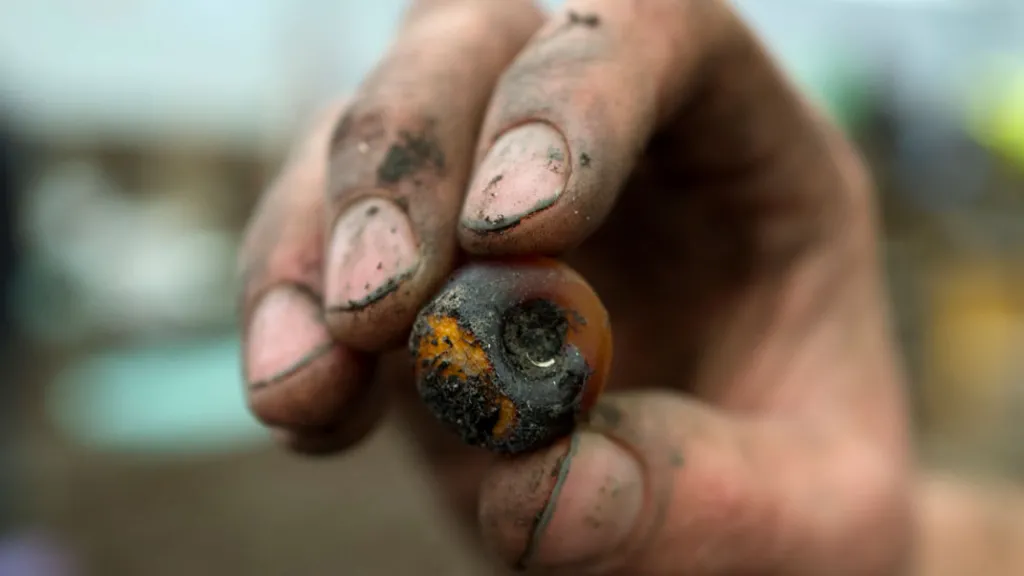
Among the classical amphorae used to carry cargo in the ship’s cargo hold, a different type stood out. It was a new type of amphora called Ses Fontanelles I, found only in this shipwreck.
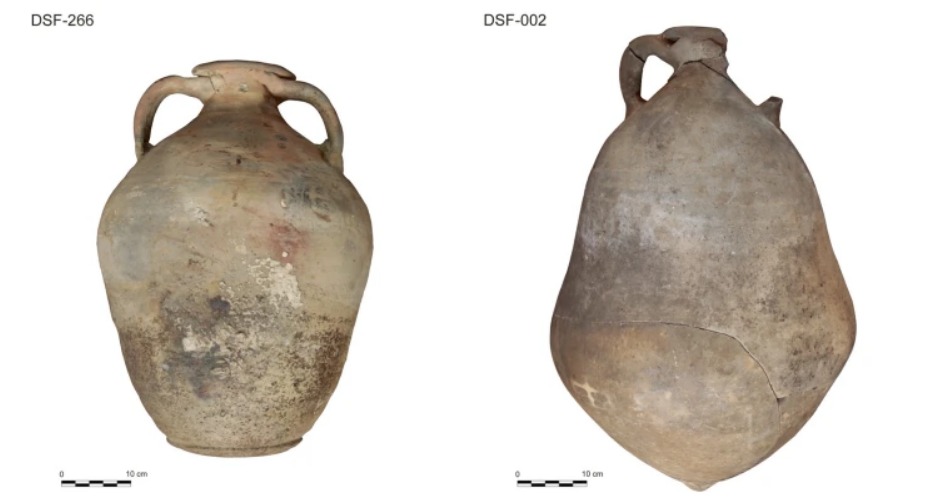

It was determined that more vegetable oil was transported with Ses Fontanelles I. It is heavier and larger than other amphorae.
On the amphorae, inscriptions called tituli picti, which contain information about who the amphora belongs to, what it contains and where it came from, attracted attention.
By reading these inscriptions, the researchers found out that the makers of the amphorae were Ausonius et Alunni and that the cargo contained fish sauce, olive oil and wine.
Residue analysis of the amphorae showed signs of grape derivatives, possibly used to add flavor or preserve its contents. In addition, traces of animal products were found, adding to the complexity of the cargo.
Cover Photo: Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences