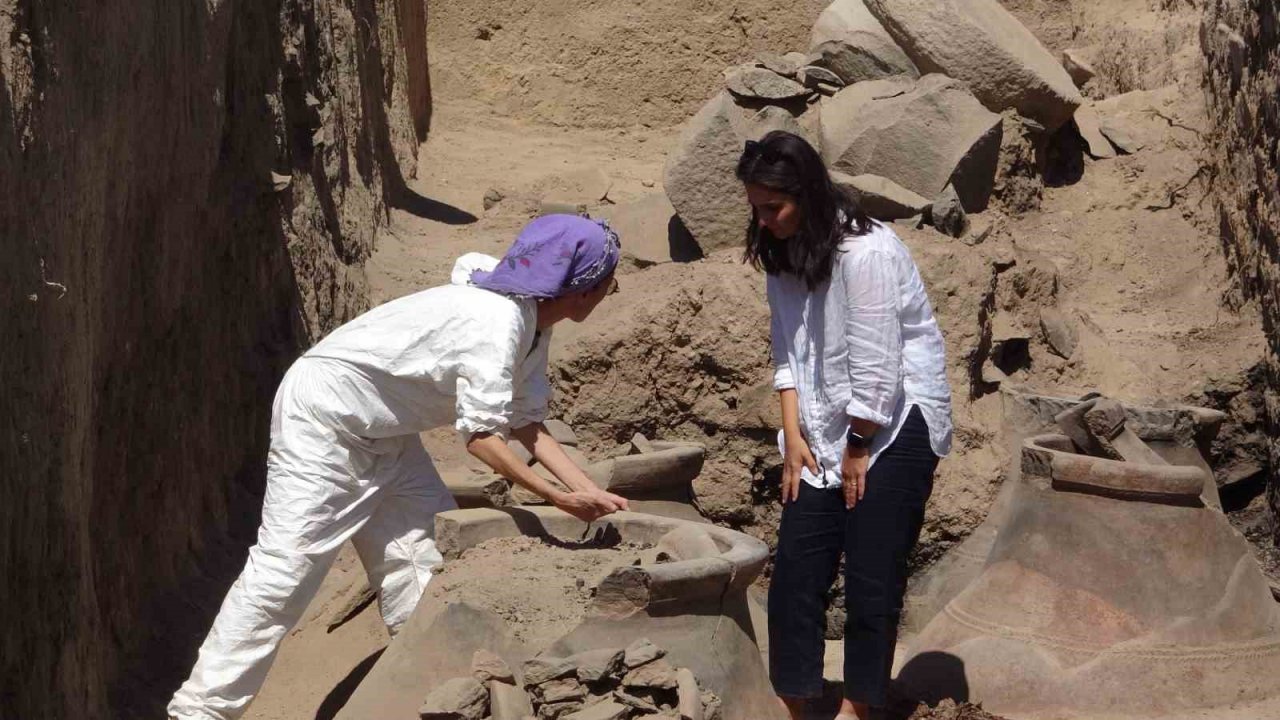
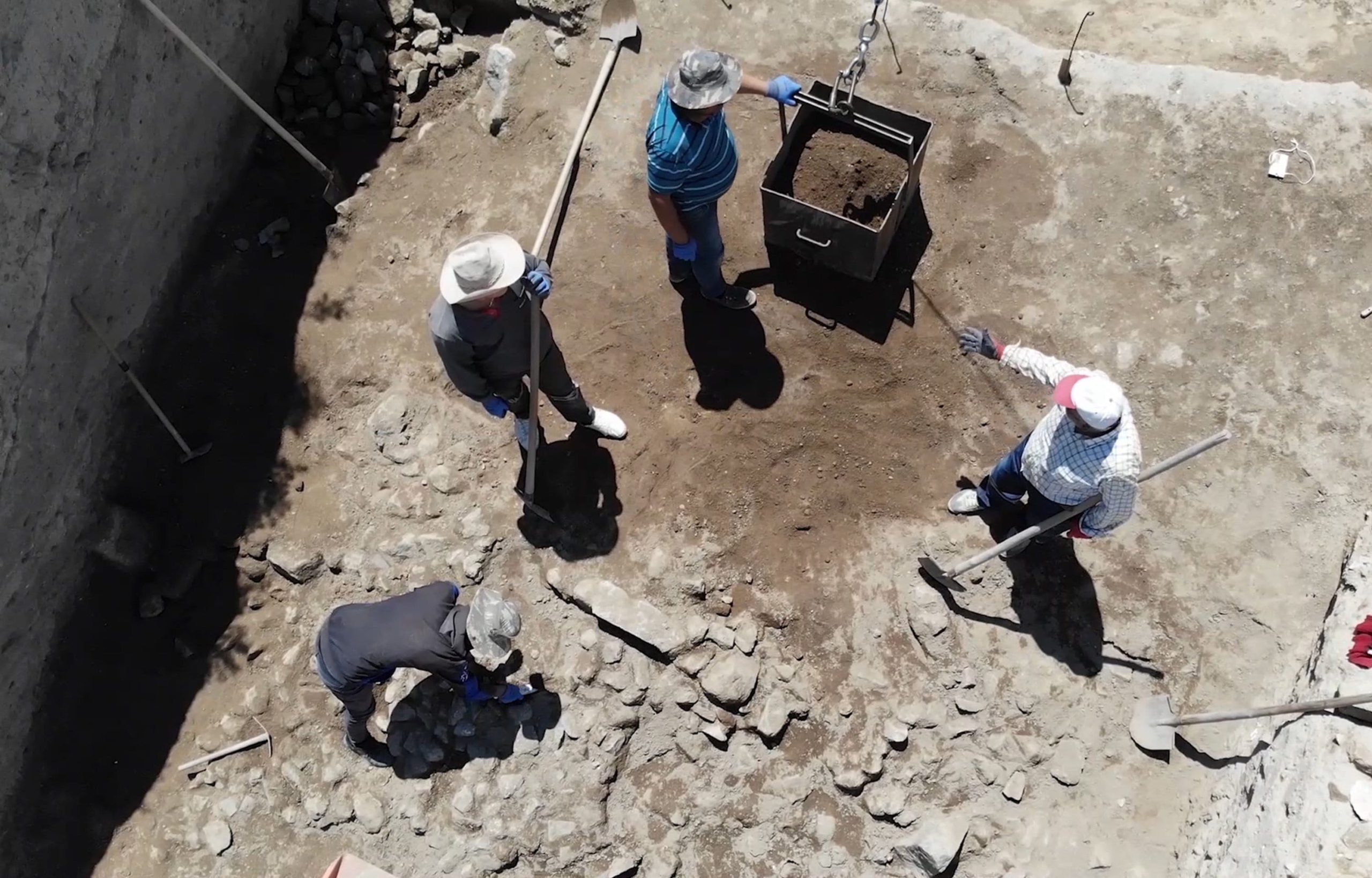
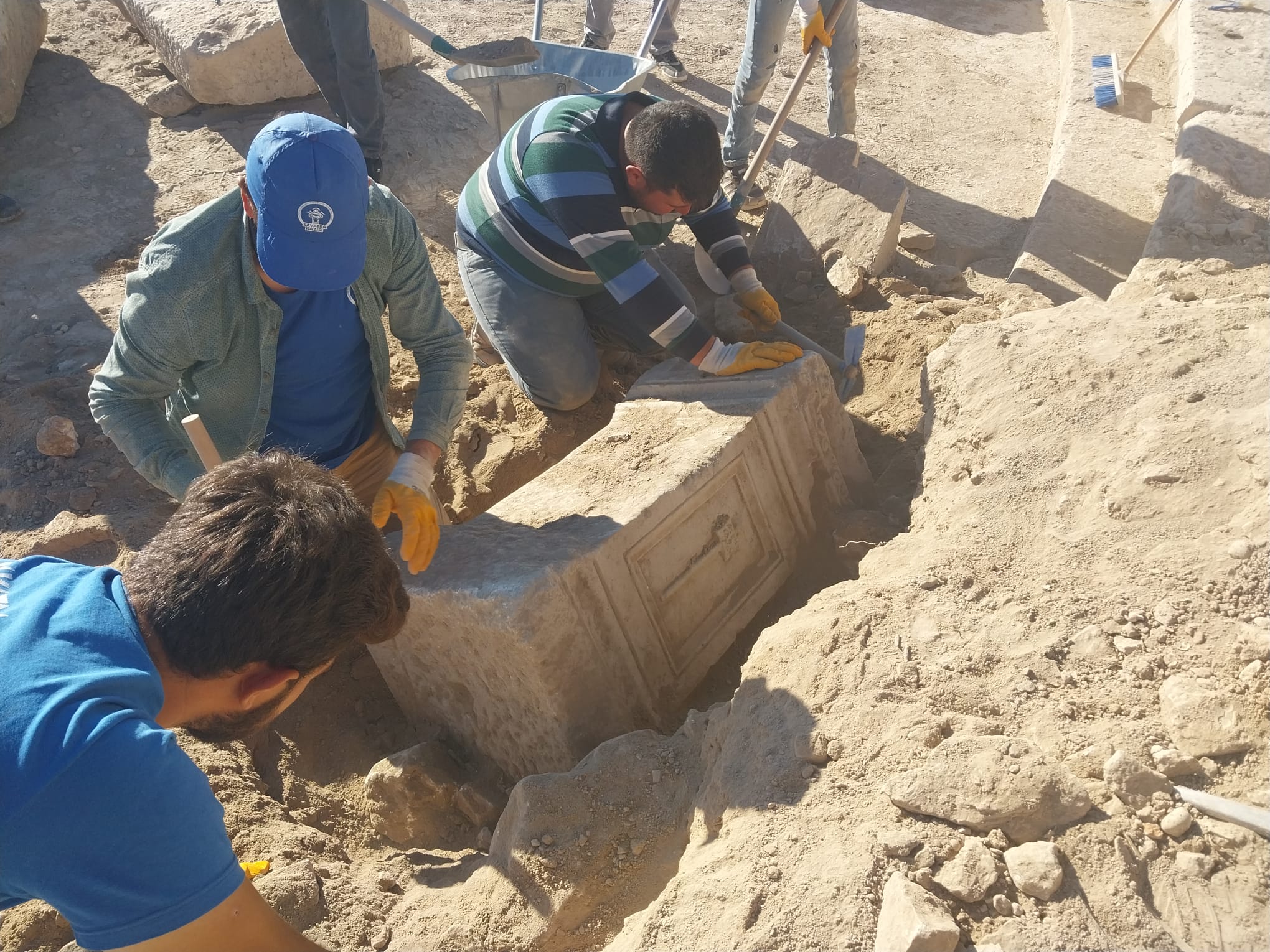
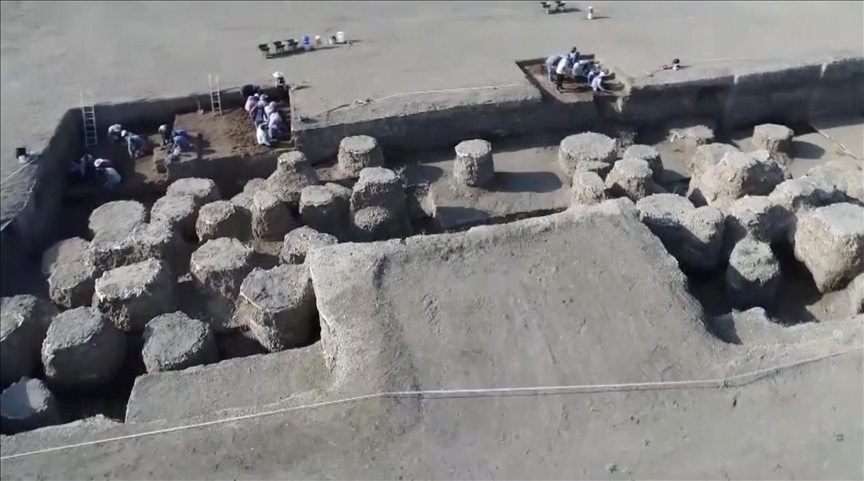
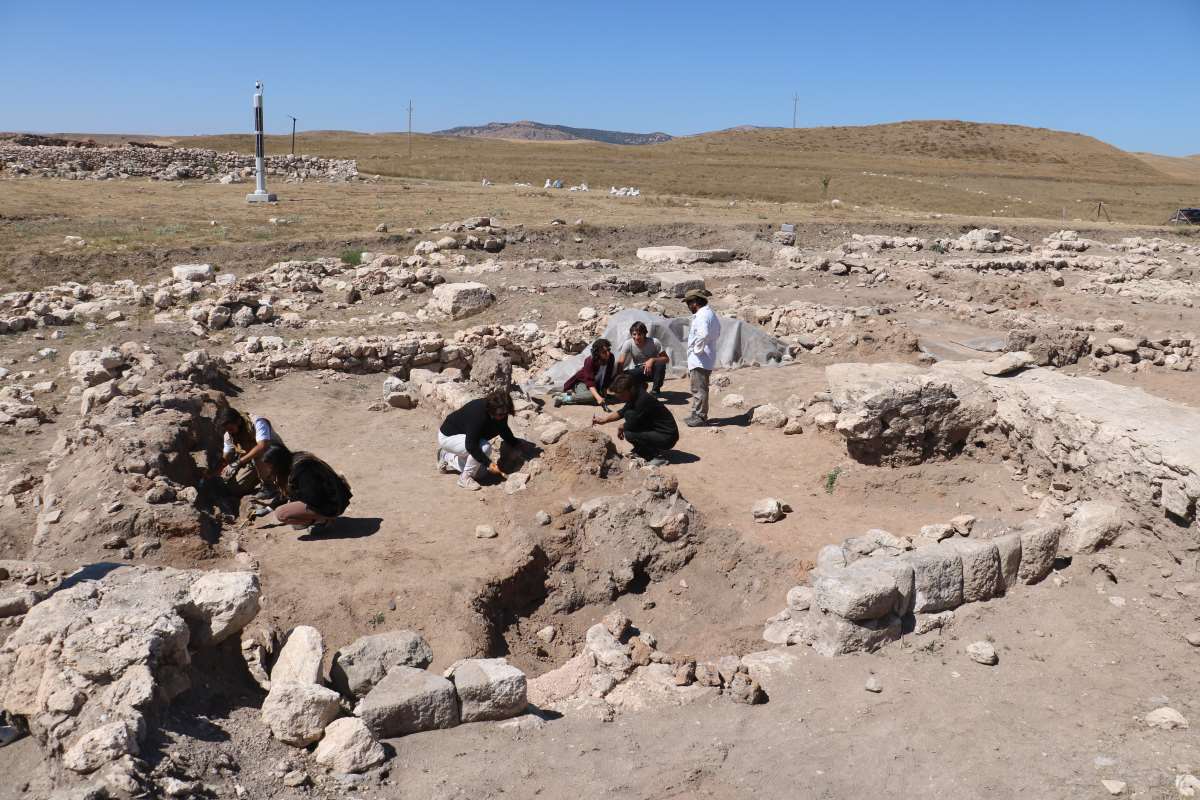
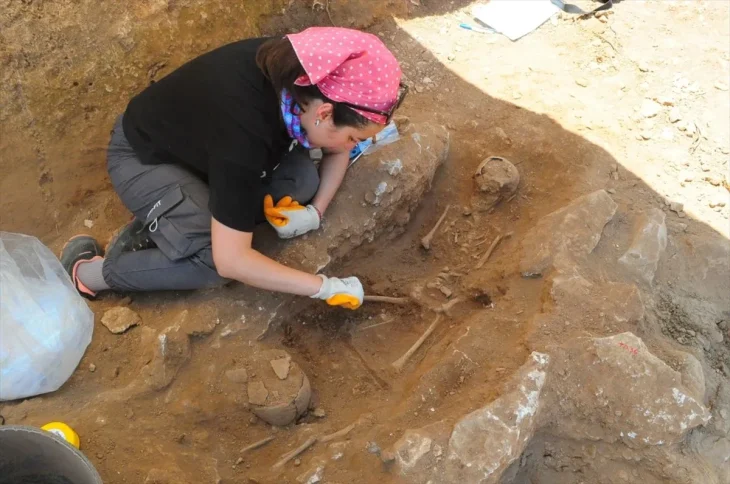
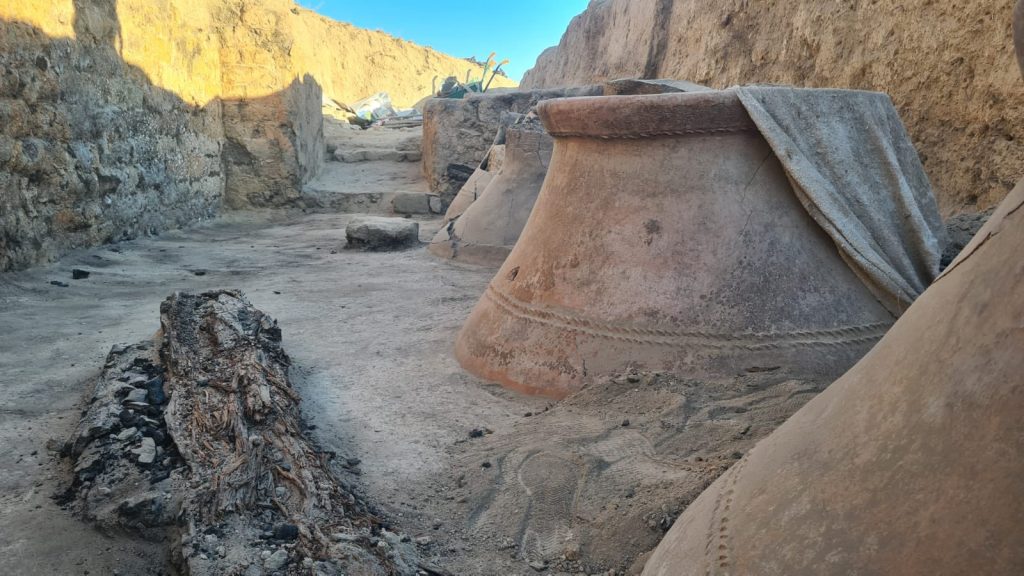
Archaeologists unearthed well-preserved 2,700-year-old pithoi in an area known as ‘Garibin Tepe,’ which was discovered during illegal excavations in the central Tuşba district of Van in eastern Turkey.
Garibin Tepe is located 3 kilometers away from Ayanis Castle, one of the most magnificent structures of the Urartian civilization.
The Ministry of Culture and Tourism initiated rescue excavations at Garibin Tepe, which had been looted by treasure hunters, in order to uncover the Urartian structures.
The rescue excavations are being conducted under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Mehmet Işıklı, a faculty member of the Department of Archaeology at Atatürk University in Erzurum.
During examinations conducted in the protected area last year, 2,700-year-old blue and maroon frescoes, unlike any seen before from the Urartian era, were discovered within a 16-meter-long tunnel. As part of the conservation measures, the tunnel had been sealed off from direct contact with air to prevent any damage to the frescoes. In this year’s excavations at the site, 2,700-year-old pithoi were also unearthed.
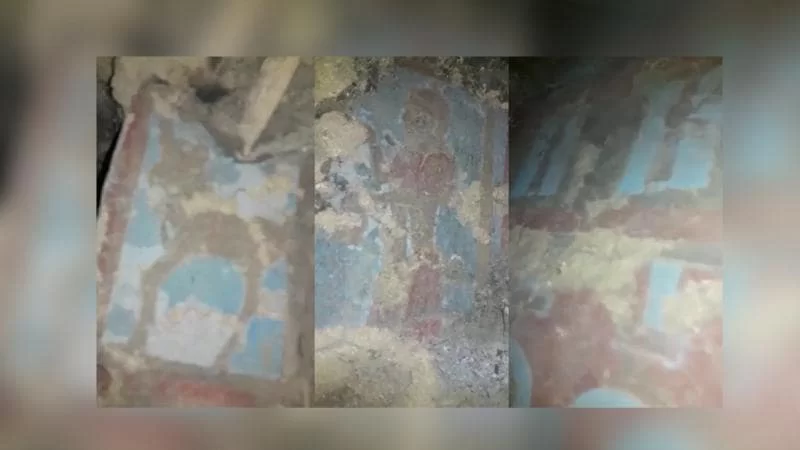

Professor Dr. Mehmet Işıklı, a faculty member, stated, “Later, with a rapid intervention, our general directorate decided to start a rescue excavation here. One of the most significant findings in this area, uncovered as a result of illegal excavations and immediately protected, is the wall paintings. So far, the number of well-preserved examples of wall paintings in Urartian art is extremely limited. This came as a great surprise to the archaeological community. These paintings have come down to us in good condition.”
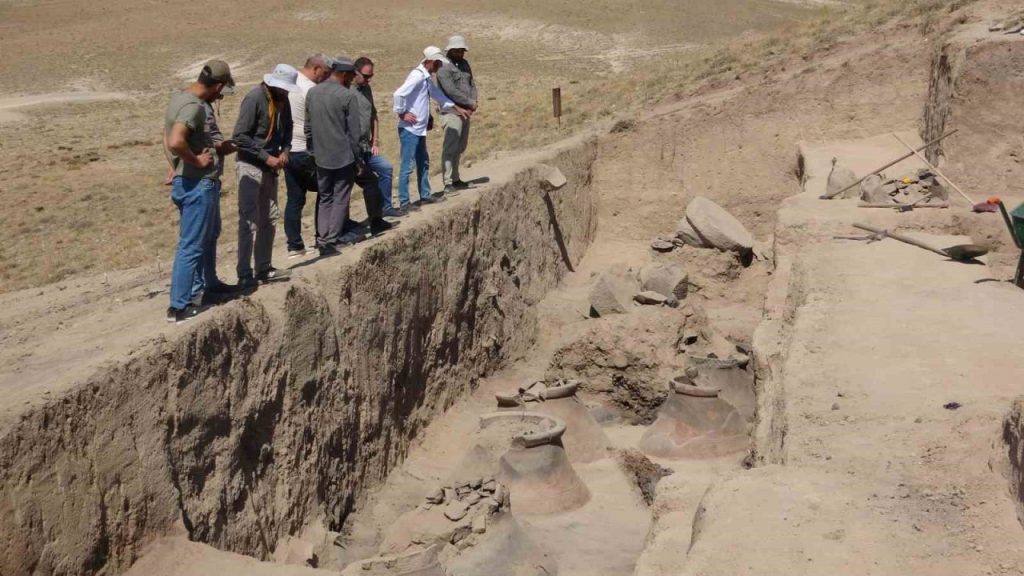
Işık, who stated that incredibly well-preserved large storage areas and pithoi (clay jars) were discovered in their excavations this year, continued his words as follows:
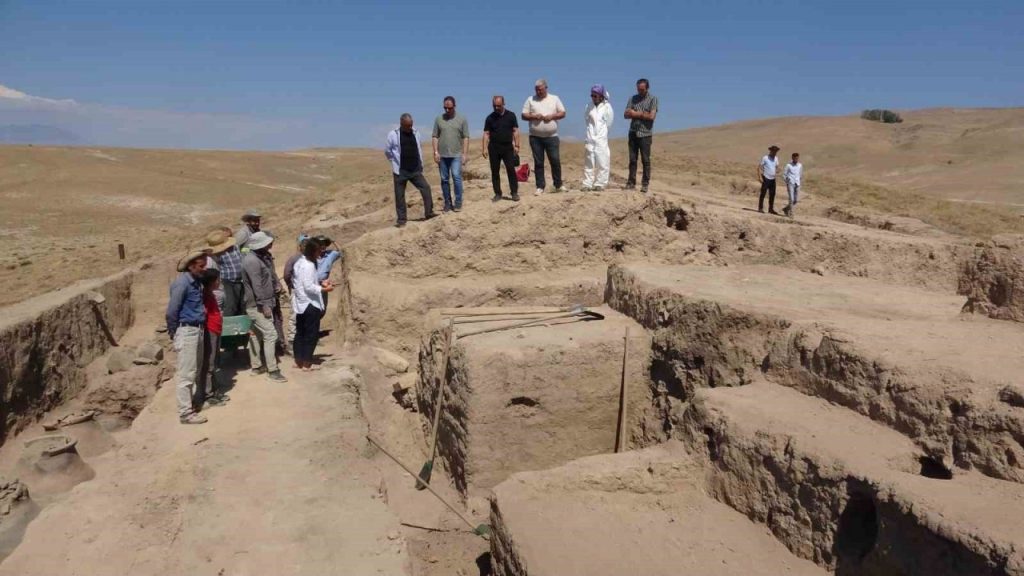

“Other than that, we encountered a very well-preserved adobe architecture. But still, there are question marks about how Garibin Tepe should be described in Urartian archaeology literature. Is this a fortress, a settlement, or a special area? It is very difficult to answer this. However, the initial evidence we see indicates that we are in a very special settlement area where the king and religious spaces are emphasized, just like in Aynis Castle. It is a bit challenging to think of this place as a fortress because, so far, in our findings, we have not come across a surrounding wall or a defensive wall. On the contrary, we encountered architecture with very special decorations. Hopefully, the excavations will continue in this way in the upcoming season.”

High Restorer and Conservator at Istanbul Restoration and Conservation Laboratory, Özlem Toprak Cihan, stated that as a result of their work, they determined that the 2,700-year-old Urartian paintings were undamaged this year. Cihan mentioned that after the excavation is completed, the paintings will be covered to protect them. She also noted that both scientific excavations and conservation work will continue simultaneously.

Cover Photo IHA