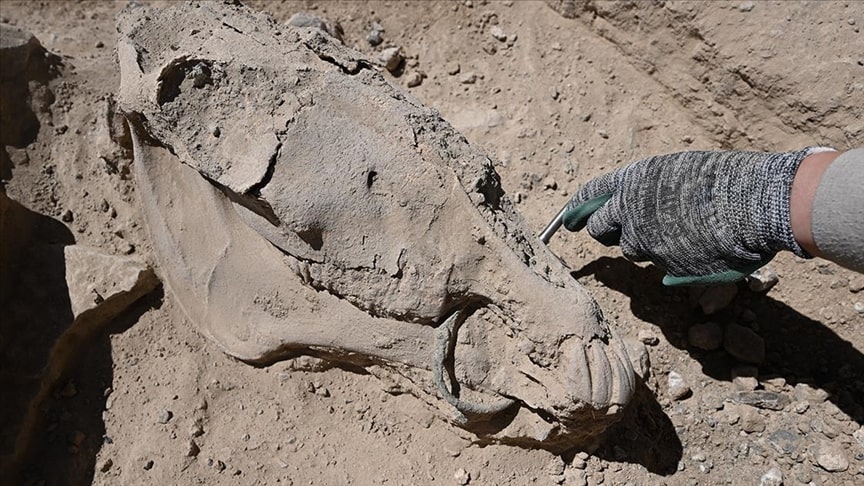
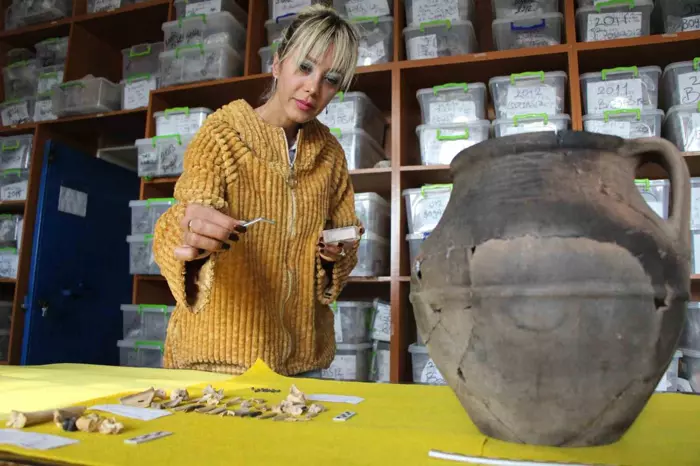
Kibyra Ancient City Excavation Head Prof. Dr. Şükrü Özüdoğru announced that the Medusa mosaic and the Odeion stoa floor mosaic, which were closed during the winter months to protect them from climatic conditions, were opened to visitors.
The Medusa mosaic will be open to visitors until the end of November.
The ancient city of Kibyra is located near Gölhisar district of Burdur province in southwestern Turkey.
Kibyra, an important center during the Lycian and Roman periods, is also known as the “City of Gladiators”. It is thought that the city functioned as a center of justice in the region due to its strategic location. It is also famous for its fast horse breeding.
The ruins that can be seen in the city today mostly belong to the Roman period. These include the theater, agora, temples, baths and cisterns.

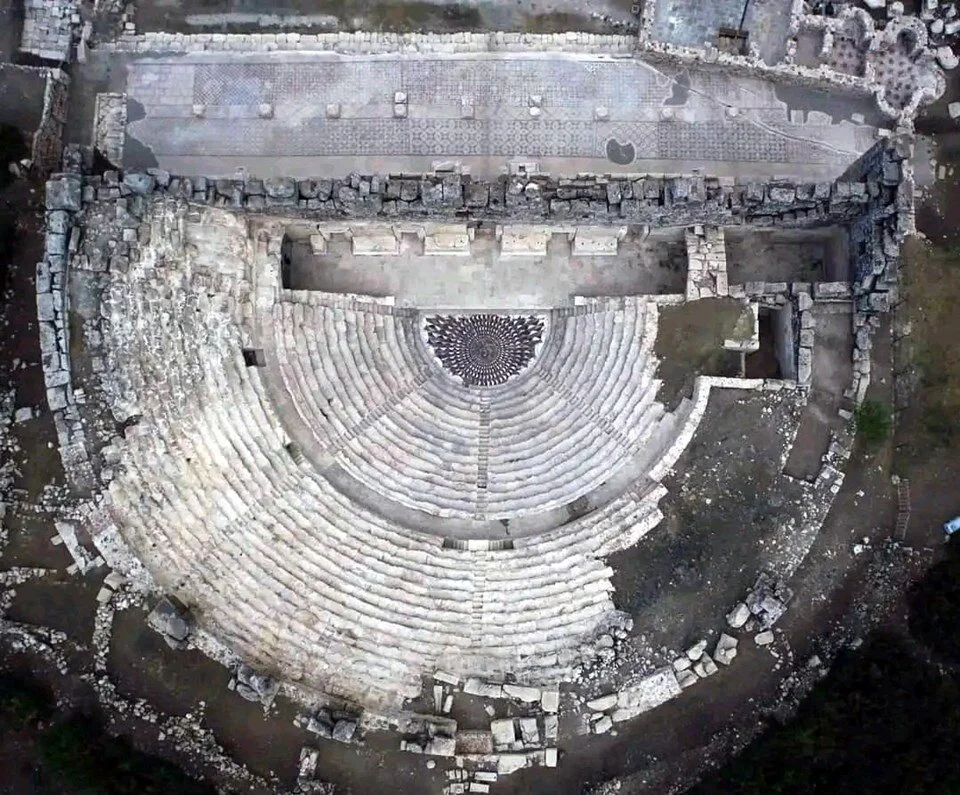
One of the most well-known ruins of the city is the Medusa mosaic.
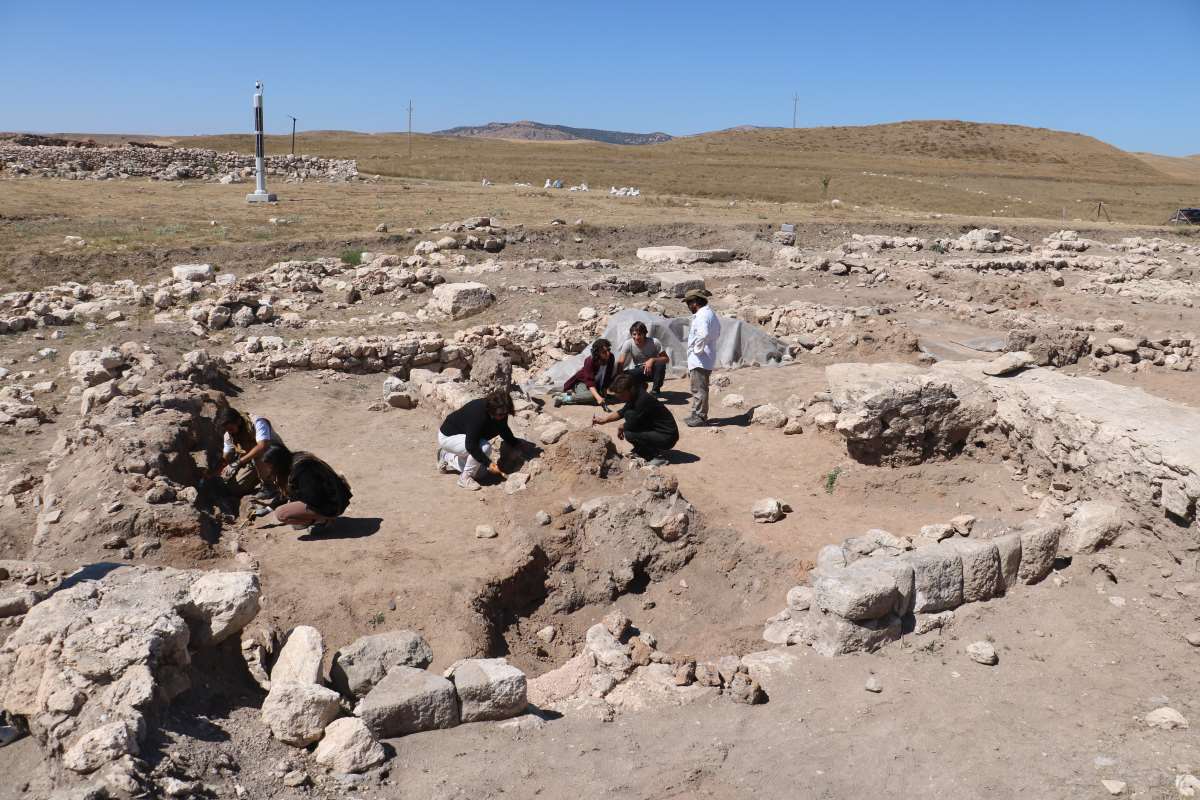
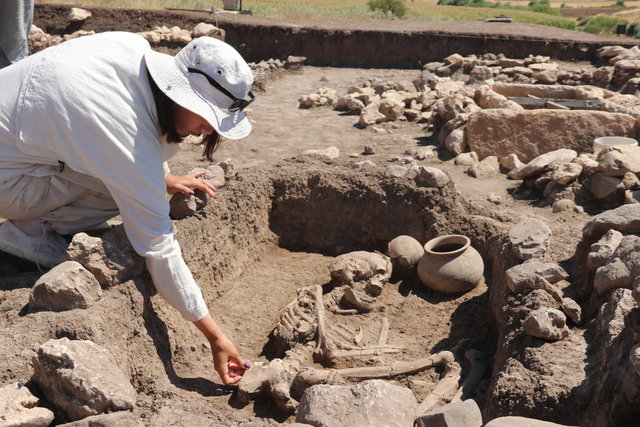
The excavations started in 2006 in the ancient city of Kibyra have been carried out since 2010 by the team headed by Assoc. Prof. Dr. Şükrü Özüdoğru, a faculty member of the Department of Archaeology at Burdur Mehmet Akif Ersoy University.
The Medusa mosaic, built of colored marbles with the ‘Opus Sectile’ technique, is unique in the world.
The most important find from the excavations of the ancient city is the Medusa mosaic. The mosaic, built of colored marbles with the ‘Opus Sectile’ technique, is unique in the world.
Medusa is one of the three monsters known as Gorgons in Greek mythology. The Gorgons are the daughters of Phorcys, god of the sea, and Ceto, goddess of sea monsters. Medusa has two immortal sisters: Stheno and Euryale. But Medusa is mortal.

Medusa is initially depicted as a beautiful virgin. She has golden hair and sparkling eyes. But when Poseidon falls in love with Medusa and has sex with her in Athena’s temple, the goddess Athena is enraged. To punish Medusa, Athena turns her hair into snakes and curses her with the curse “May everyone who looks into her eyes turn to stone”.
After this curse, Medusa retreated to a cave in western Libya and turned many unfortunate heroes into stone.
Medusa, which was closed to protect it from winter conditions, opens to visitors again
Prof. Dr. Şükrü Özüdoğru, Head of Excavation of Kibyra Ancient City, shared on his social media account, “Kibyra odeion opus sectile Medusa mosaic and Odeion stoa opus tessellatum floor mosaic, which were closed during the winter months to protect them from climatic conditions, have been opened and can be visited until the end of November.”