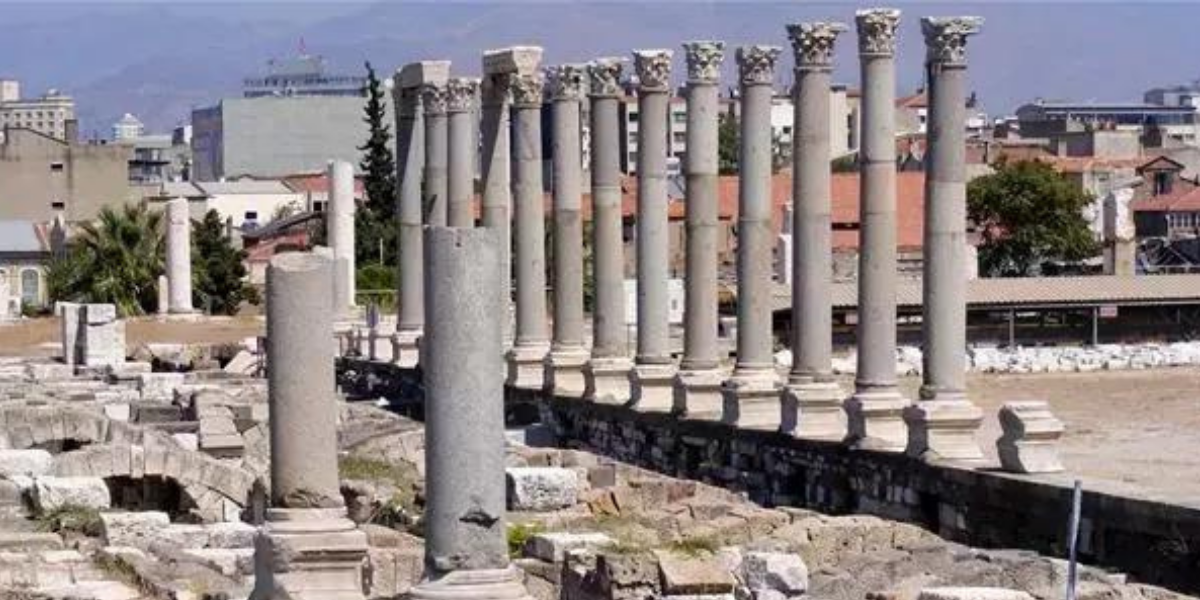
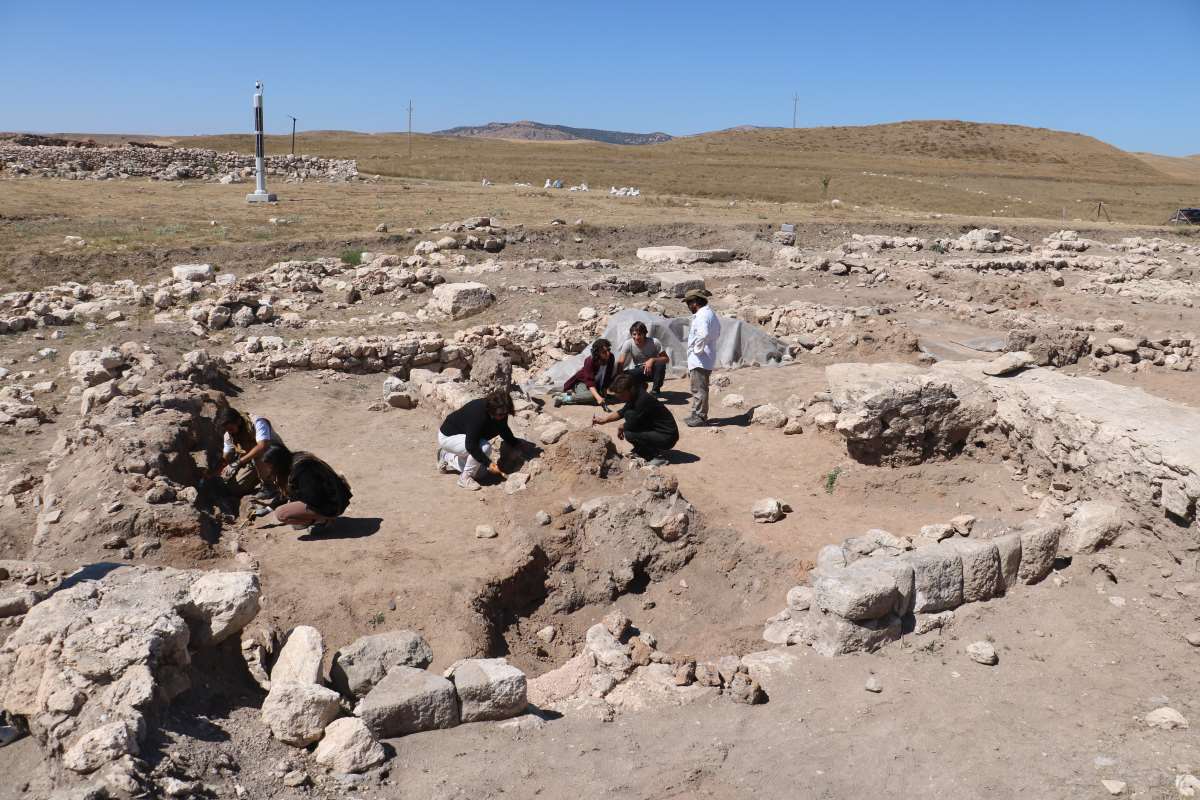
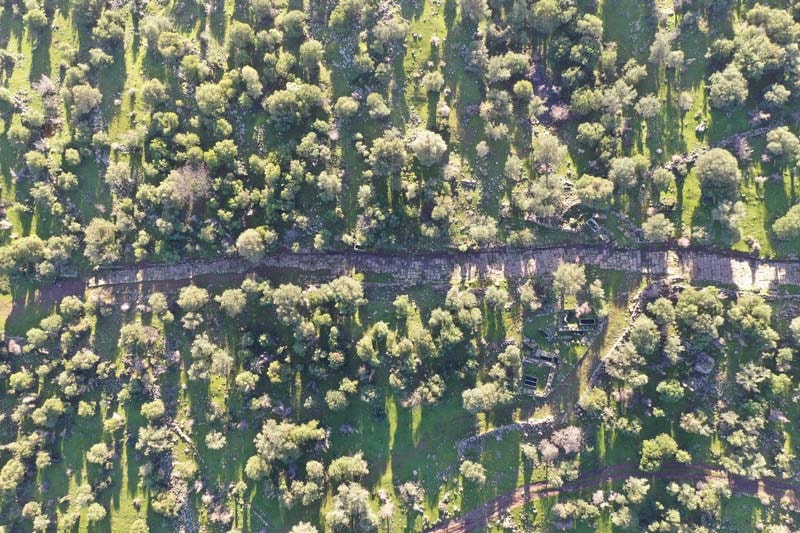
Artifacts reflecting Egyptian influence were found during excavations in the ancient city of Smyrna, which has one of the largest theaters in the Mediterranean.
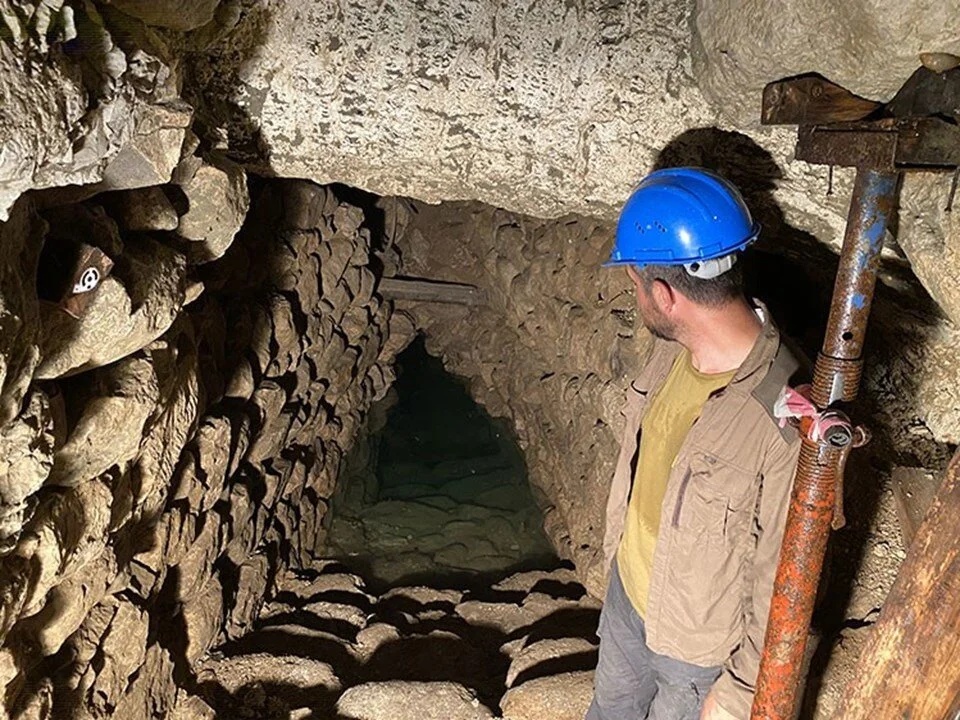
Figures and objects influenced by the Egyptian civilization were found during the ongoing excavations in the theater of the ancient city under the direction of İzmir Katip Çelebi University faculty member Prof. Dr. Akın Ersoy.
Prof. Dr. Akın Ersoy said, “In recent years, we have been carrying out excavations intensively, especially in the Smyrna Theater. In these excavations, we come across many Egyptian influenced finds. We know that the political, cultural and commercial relations between Egypt and Anatolia date back to the early ages. Now we see concrete examples of this relationship in the excavations at the Smyrna Theater.”
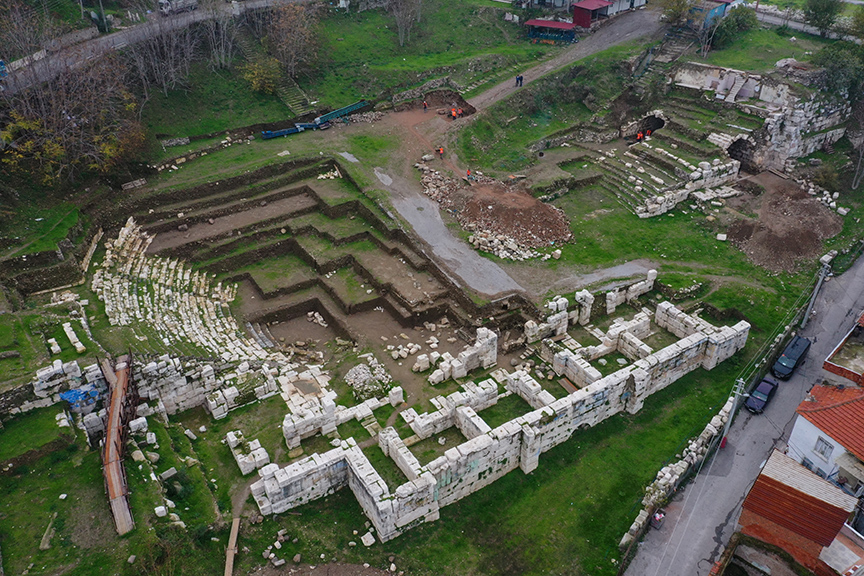

The ancient city of Smyrna is a Greek and Roman city located in İzmir, modern-day Türkiye. It was one of the most important cities of Asia Minor in ancient times.
Smyrna, whose name is mentioned in the 7th century BC in the first written sources, was ruled by the Ions, Aeolians, Lydians, Persians, Romans, Byzantines and Ottomans throughout its history.

The first settlers of Smyrna are thought to be the Aeolians. The city was captured by the Ionians in the 11th century BC and became one of the most important members of the Ionian League.
Hellenistic and Roman Periods: Smyrna, which came under the rule of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC, continued to develop as an important trade center during the Roman Period. During this period, the city became the fifth largest city of the Roman Empire.
It was included in the Tentative List of World Heritage Sites by UNESCO in 2020 as part of the heritage area created under the name ‘İzmir Historic Port City’.

Prof. Dr. Akın Ersoy gave information about the figures and objects with Egyptian influence obtained during the excavations concentrated in the theater area and said, “We know that the relations between Egypt and Anatolia date back to the early ages in political, cultural and commercial terms. Now we see concrete examples of this relationship in the excavations at the Smyrna Theater.”

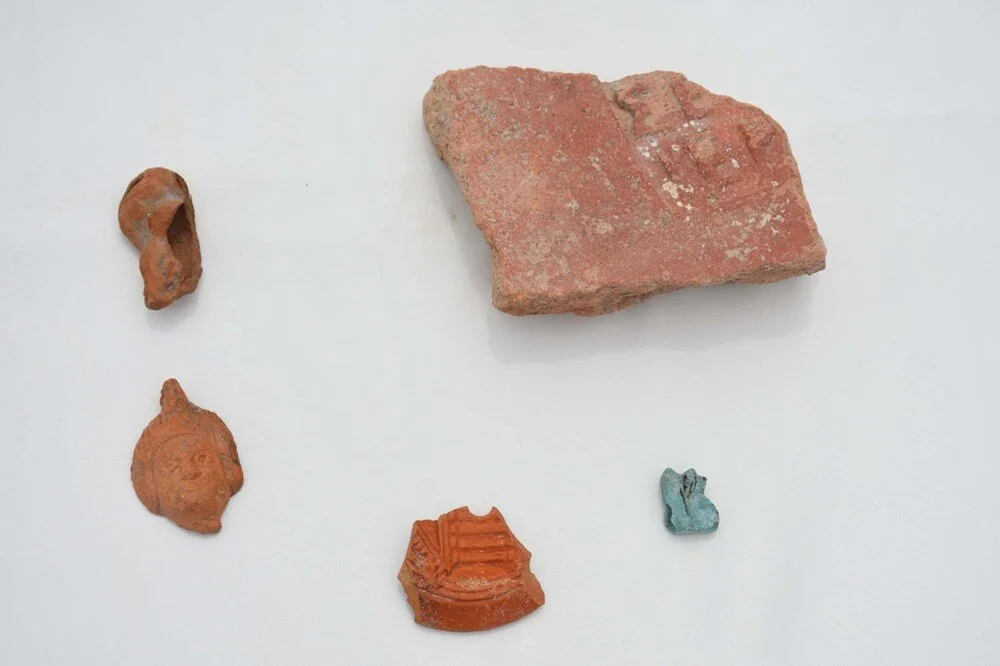
“The fact that these objects are mostly found in the Smyrna Theater shows us that there was perhaps a worship area for Egyptian gods in the area where the theater was located. Of course, we need to prove this architecturally. But these objects at least point to a temple of Egyptian gods. We also know from the inscriptions that Egyptian influence was present in Izmir and of course in Anatolia as a whole. Because especially after Alexander the Great and with the Roman Empire’s domination of Egyptian lands, this cultural rapprochement took place rapidly.”
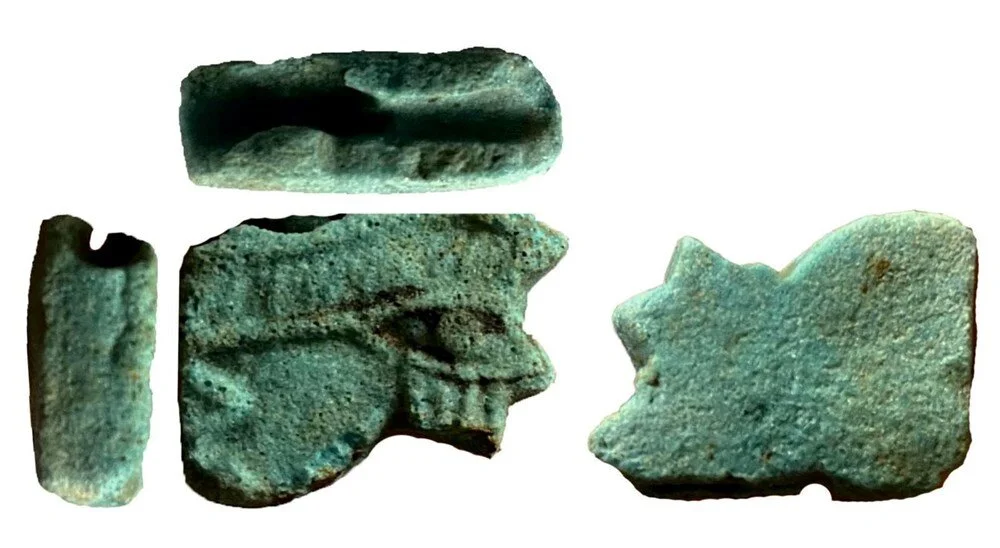

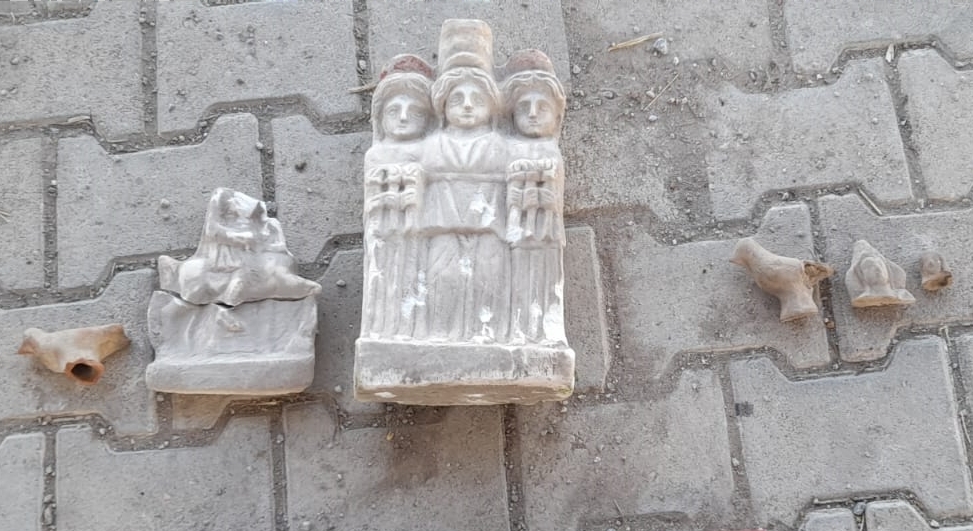
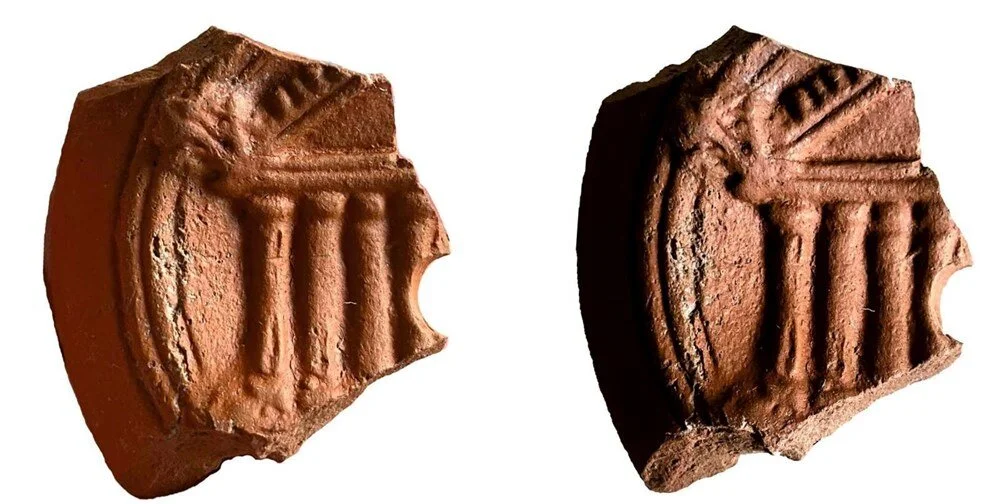
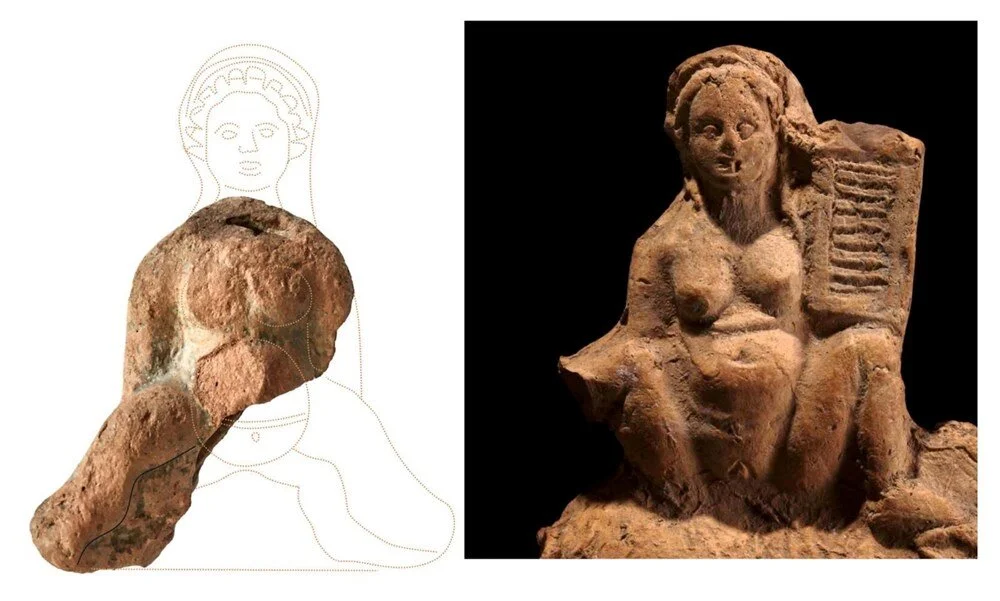
Prof. Dr. Ersoy said, “There are 5 samples here. The first of these is a mask. This figure is a cover used in the burning hole of oil lamps. It is an Egyptian influenced figure. Another object is a figure of a woman in the position of giving birth, half of it is missing. But we know from other examples that this object is a figure associated with a healthy childbirth and a healthy child. This is a feature mostly seen in Egypt. Another object is an oil lamp fragment. It has an image of the Temple of Isis on it. The 4th object is a brick fragment. It has the inscription ‘Serapis Hiera’ on it. It means ‘the sanctuary of Serapis’. Therefore, based on all these finds, we say ‘There may be a sanctuary here’. The 5th object is the figure of the eye of Ra. This is also called the ‘eye of Horus’. It expresses that there is only one god. It is also the eye of conscience. It shows Egyptian influence.”