When it comes to underground city in Turkey, the first thing that comes to mind is the Cappadocia region.
Within the Cappadocia region, Göreme, Ürgüp, and the Ihlara Valley stand out with their Fairy Chimney formations.
Derinkuyu and Kaymaklı are among the most famous underground cities in Cappadocia, Turkey. These cities were thought to be built by the Phrygians in the 8th century BCE through carving into soft volcanic rocks. Subsequently, it is believed that the early Christians expanded these underground complexes by adding religious spaces like chapels and churches.
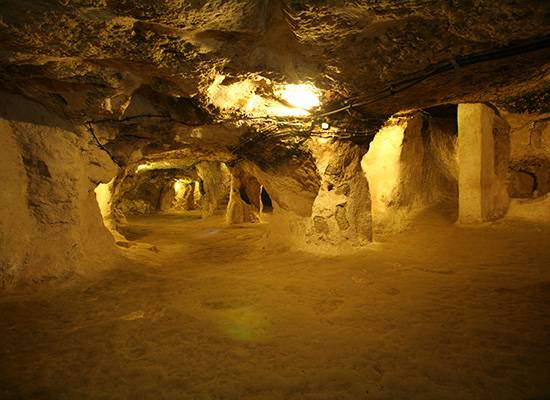

Christians used these underground cities for security purposes to protect themselves from the Arab invasions into Anatolia. These cities provided a refuge where they could seek shelter, live, and worship without the constant threat of the Arab armies.
Sarayini could be the largest underground city
It was known that the Derinkuyu and Kaymaklı underground cities were the largest cities in Anatolia. However, ongoing studies in the underground city of Sarayini seem to be changing this information.
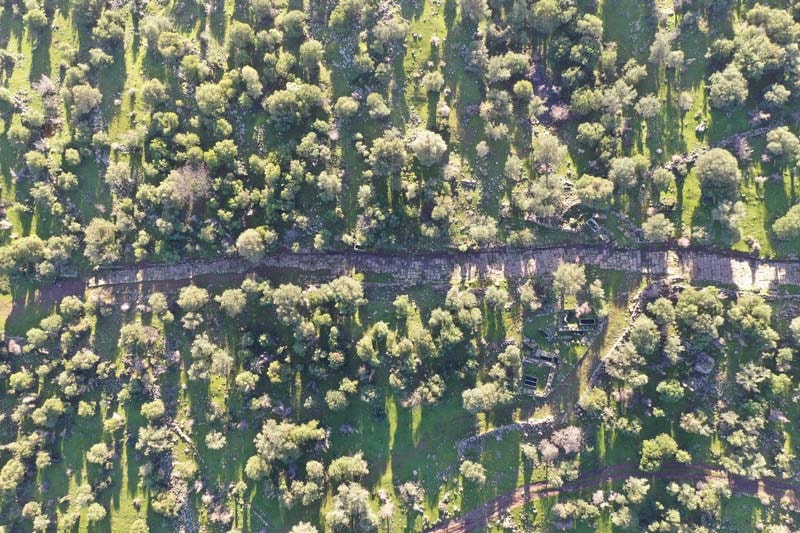
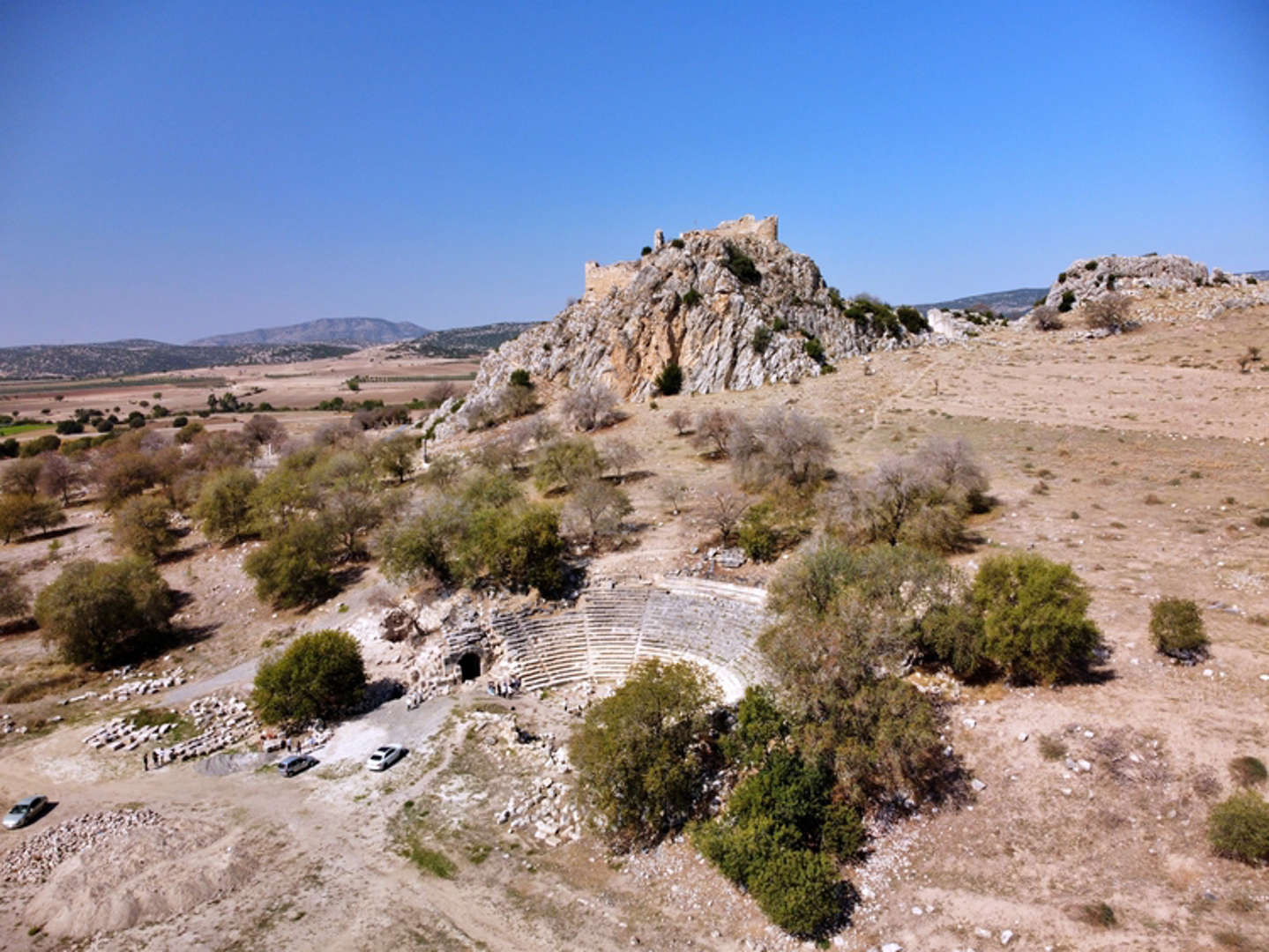
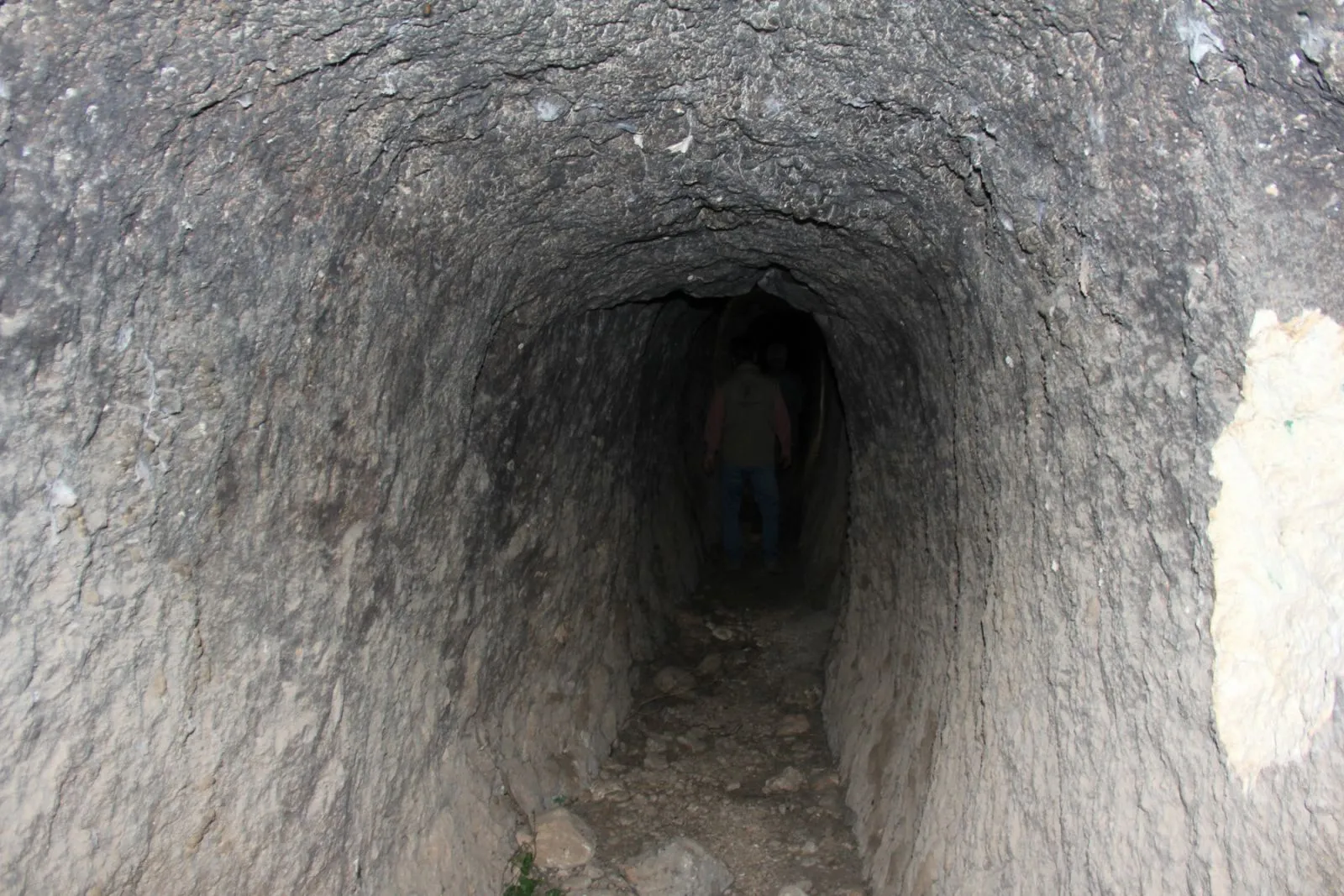
The underground city of Sarayini, located in the Sarayönü district of Konya province, is believed to date back to the Roman period.
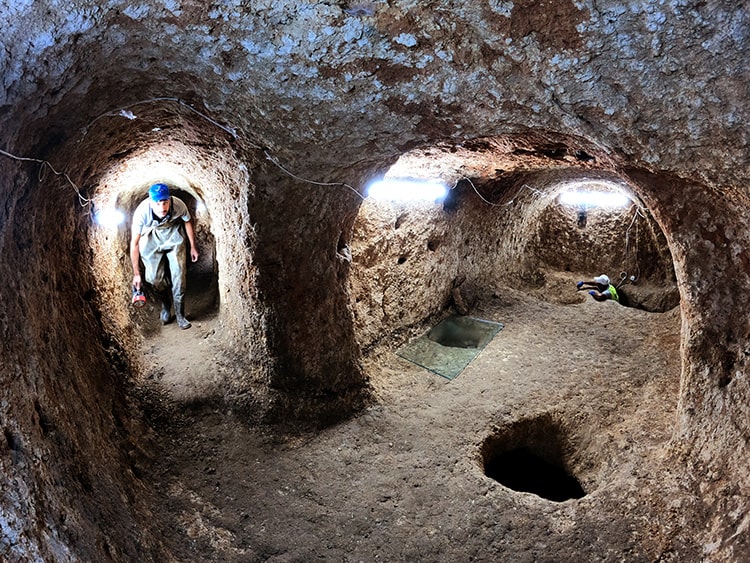
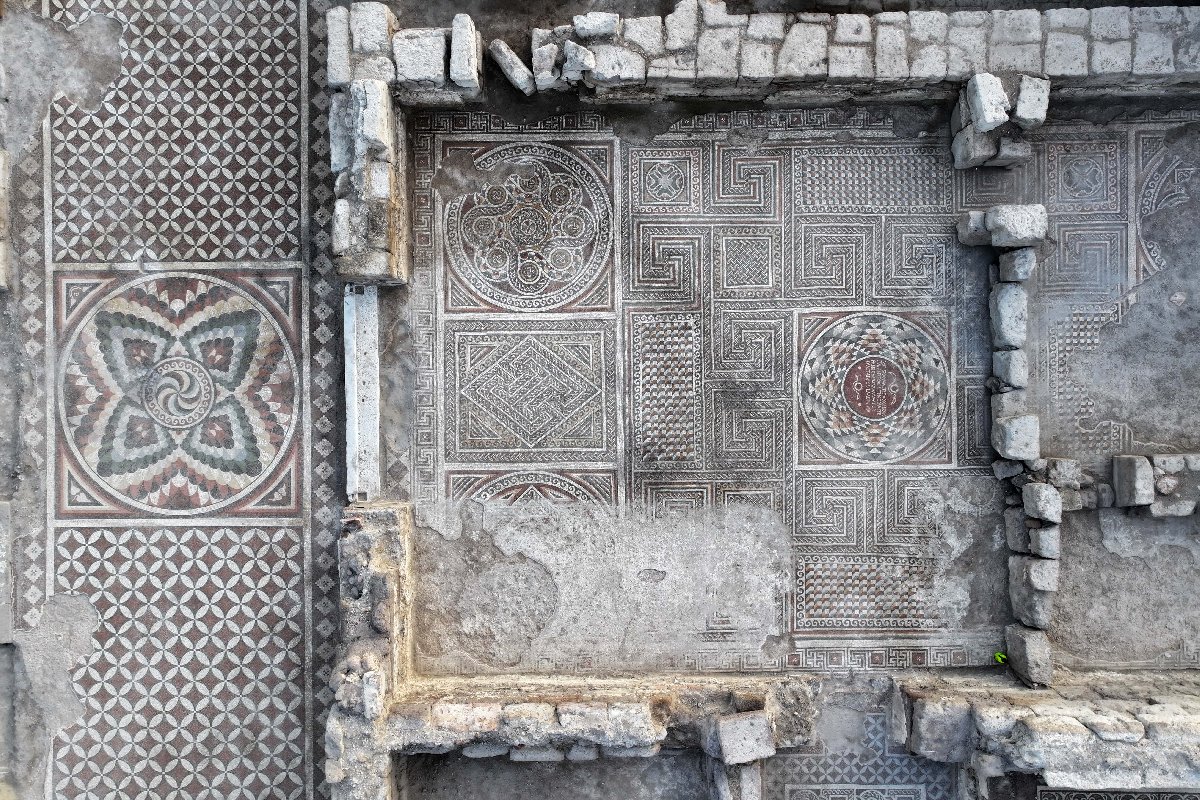
Recent discoveries in the underground city of Sarayini reveal that this ancient site comprised a complex of structures that offered a high level of comfort and extensive amenities for its time.
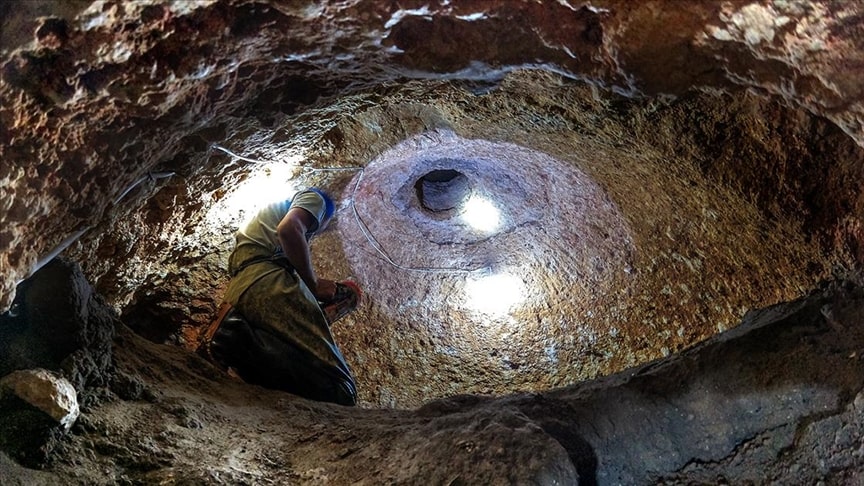

Konya Museums Directorate’s archaeologist and excavation director Hasan Uğuz stated that with the newly discovered areas this year, the total number of chambers reached 30, and the total sprawling area expanded to 20,000 square meters.
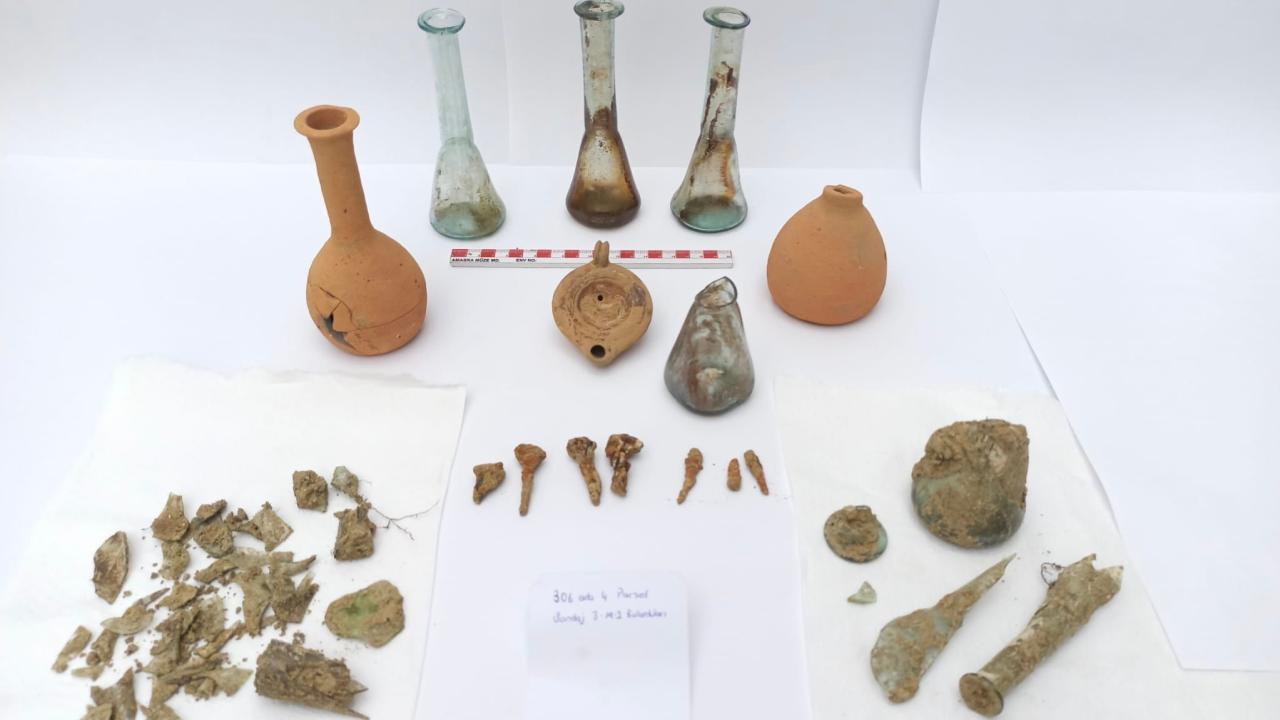
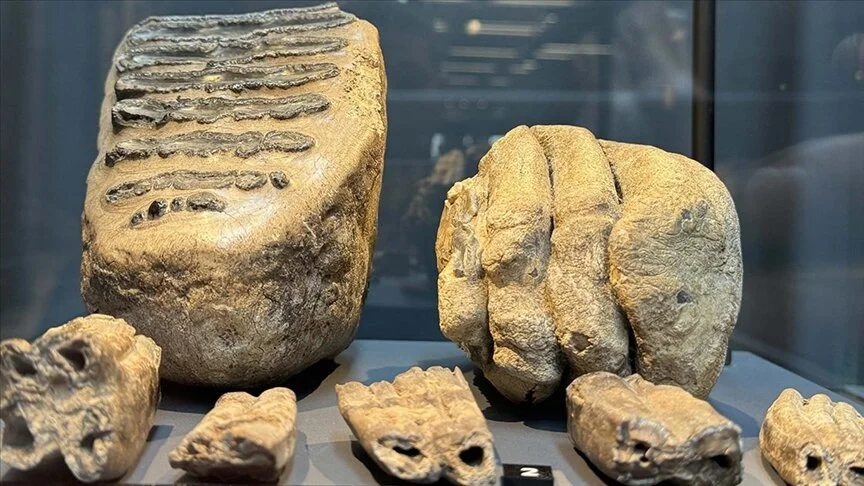
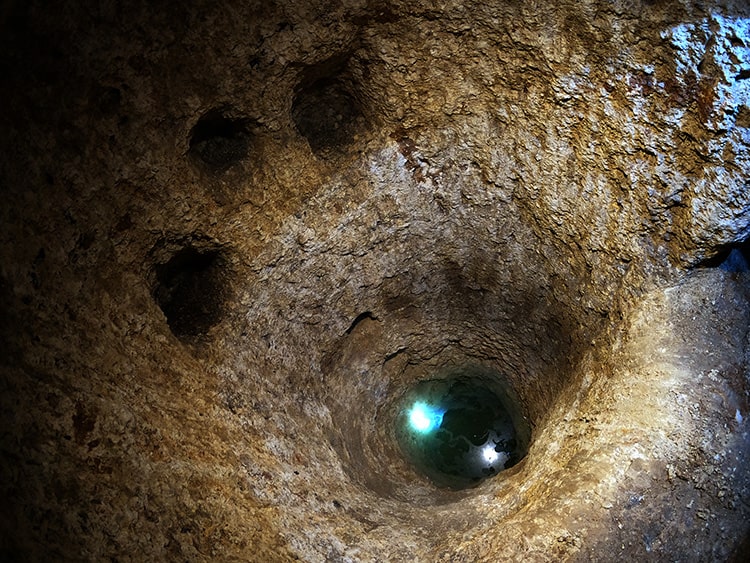
During the excavations, various findings were uncovered including domestic living spaces, interconnected galleries, room-like living areas, water wells, fireplaces, workshops, chimneys, places for lamps to provide illumination, cellars, storage areas, ventilation systems, and areas whose characteristics are still under investigation.
Uğuz indicated that they might have discovered Turkey’s largest underground city in terms of horizontal architecture, stating, “We didn’t think it could spread over such a vast area. During surface surveys, local elders mentioned that they had explored this place as children and described it as a very large underground city. This year, we realized that half of what they described turned out to be true. So, if the other half is also accurate, it covers an extremely large area.”

“In our research, we noticed that 19th-century European travelers referred to this area as Sarayini. The local residents also mention it. The actual name of this place is Sarayini. We observed that due to the inns’ expansive, comfortable, interconnected, and high-quality architectural design, it resembles a palace, leading us to the conclusion that it’s called Sarayini for this reason. In our discoveries this year, we have a very wide corridor, which can be likened to a main street. On the sides of this corridor, there are numerous galleries. There are tunnels and corridors connecting these galleries. What sets Sarayini underground city apart from the others is the significant number of chambers, the integration of corridors with galleries, and the provision of an underground city that offers a palace-like comfort to people.”
An unusual space was discovered whose purpose remains unknown
Uğuz mentioned that they came across an intriguing space that stands out from all the other areas. He continued as follows:
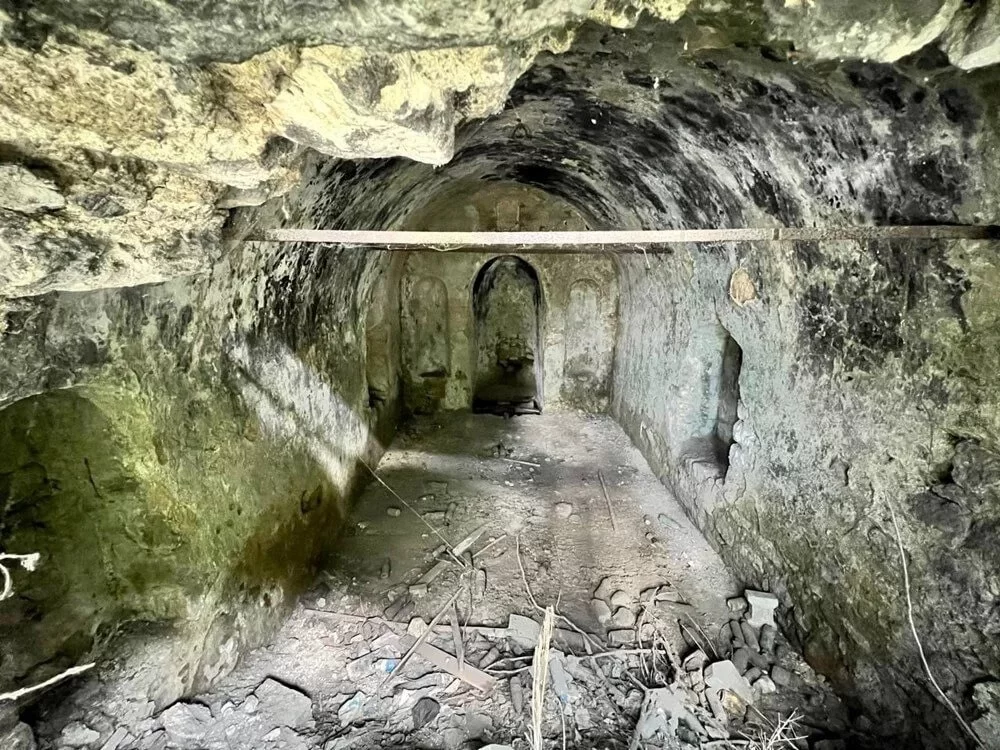
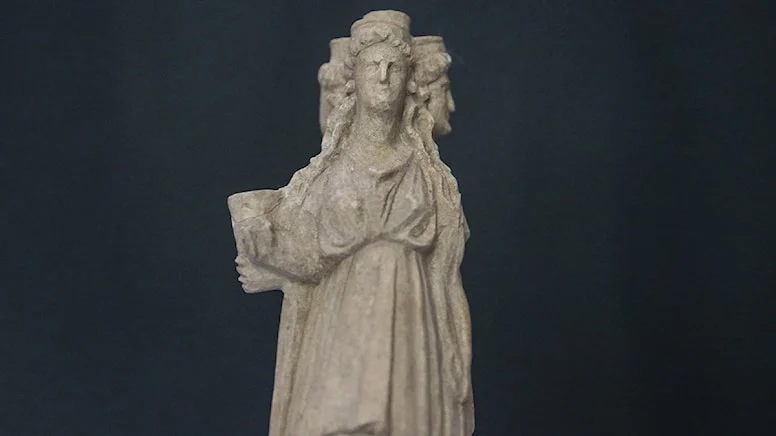
“During the excavations, we encountered a wall constructed using dry-stone technique, with some blocks being natural and others carved from architectural elements. Upon closer examination, we realized it had a connection to the surface. We removed the stones and found that some of them were altar-like tombstones from the Roman period, some were tomb stelae, some had honorary inscriptions, and some were column drums. We realized that the column drums had been transformed into tombstone styles of the period, and the room was filled with these elements. Additionally, we found a structure reminiscent of a cross with a wooden covering, resembling a pool, built in a north-south direction. Our research regarding the purpose of this area is ongoing.”
Cover Photo AA