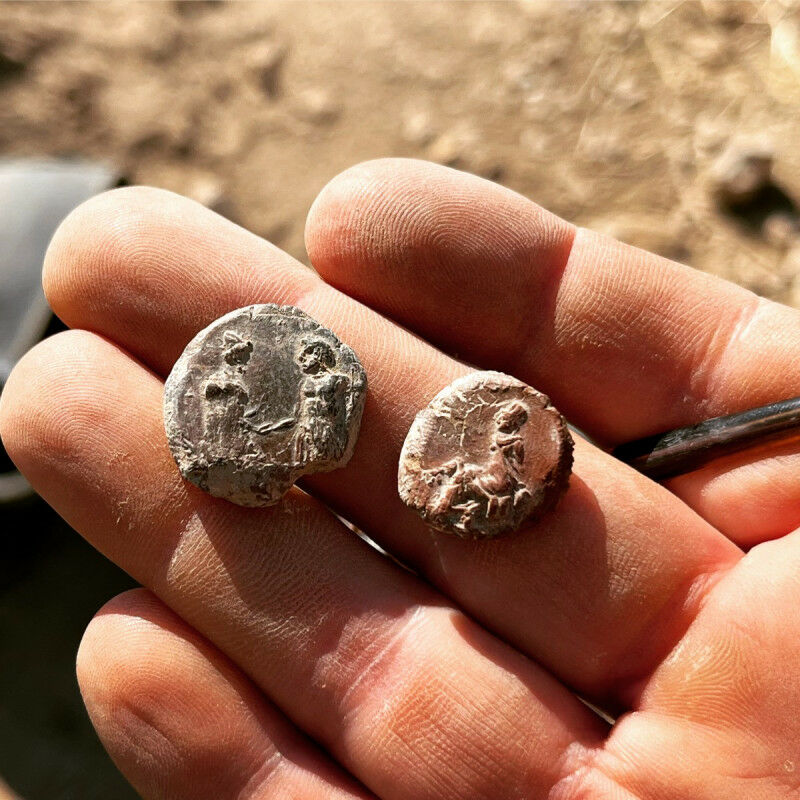
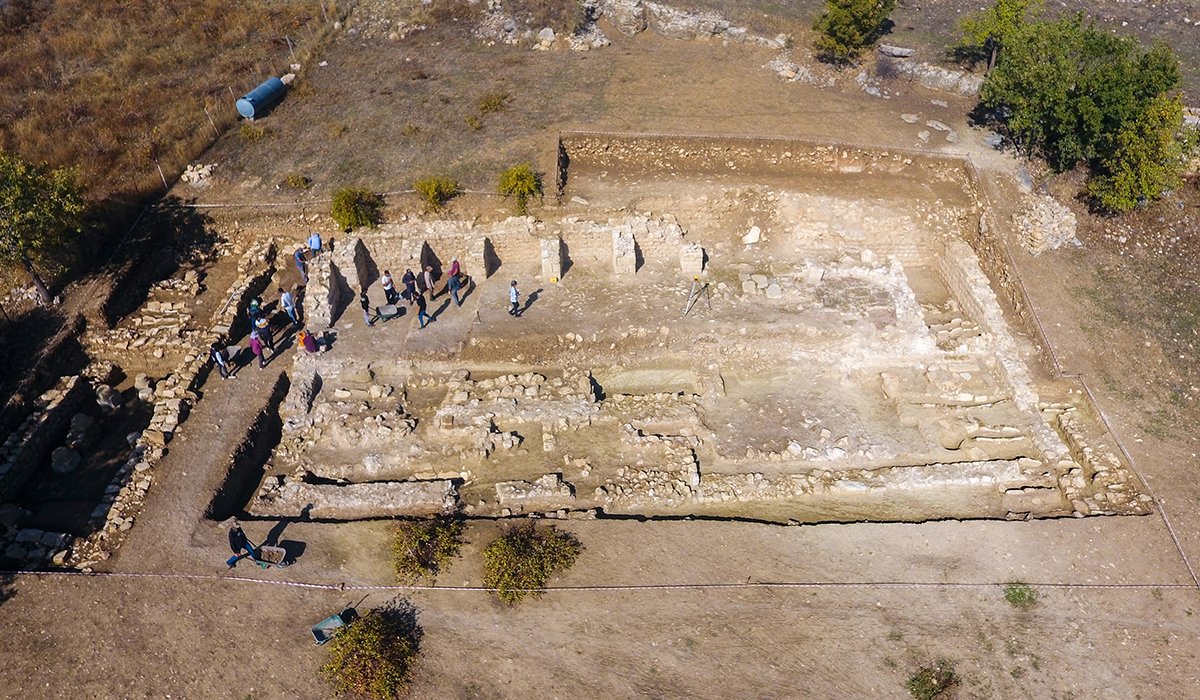
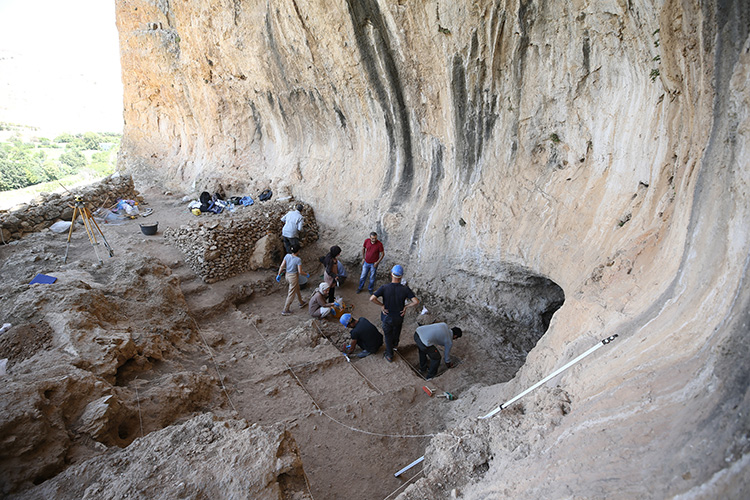
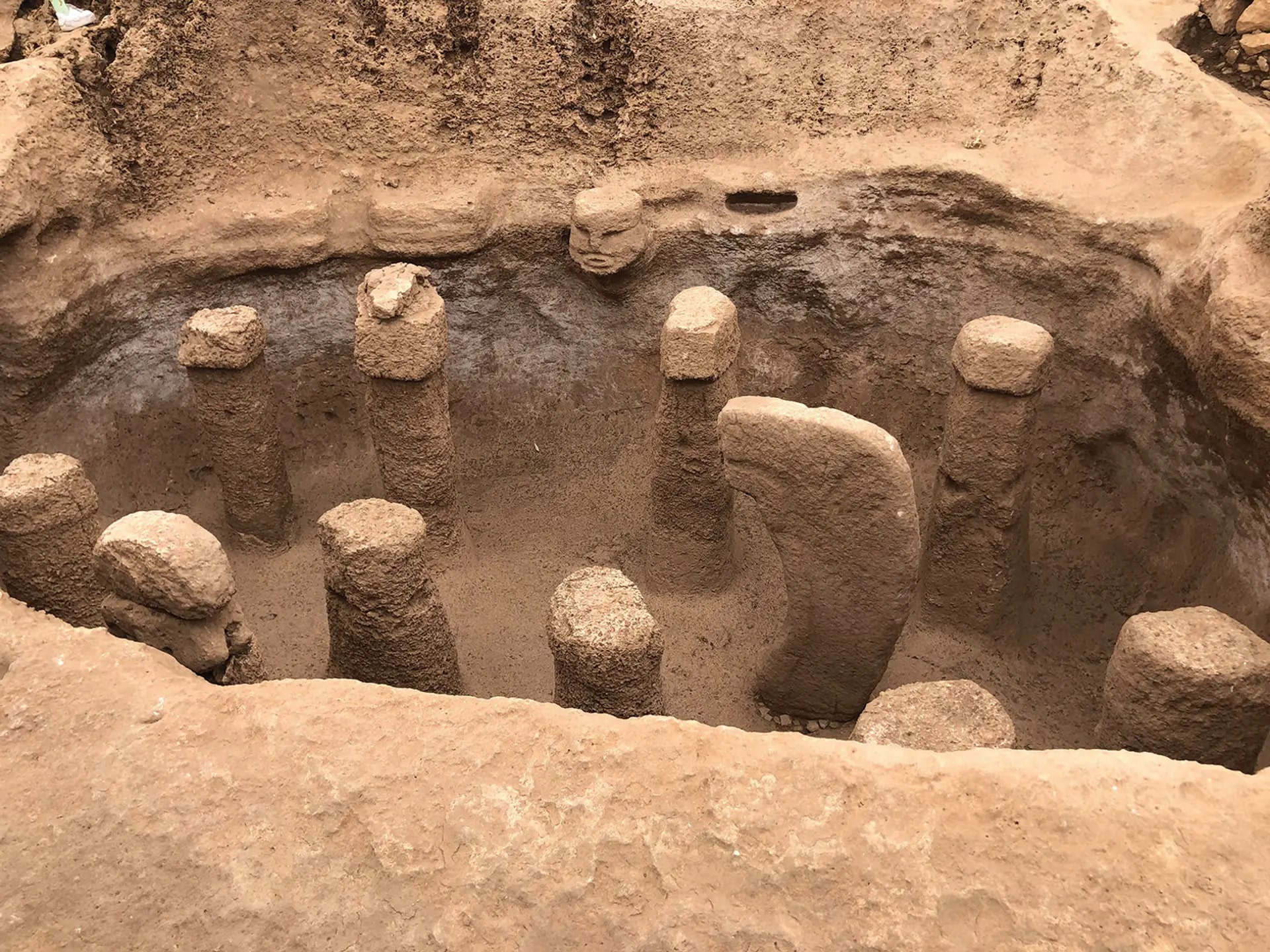
Archaeologists from the Asia Minor Research Center uncovered the city archives in the ancient city of Doliche in south-eastern Turkey and recovered over 2,000 seal impressions used to seal documents.
Doliche is an ancient city located at the northern fringe of Gaziantep in SE Türkiye. It is a significant religious center that has been associated with three different beliefs: Dülük during the Hittite Empire Period, Teshup during the Hellenistic Period, and Jupiter Dolikhenos during the Roman Period. The city’s remains reflect its history as an ancient Roman city that was established as a sacred site for Jupiter Dolikhenos.
The team led by Michael Blömer and Engelbert Winter from the University of Münster made a significant discovery: They has found over 2,000 seal impressions used to seal documents from the city municipal archive.
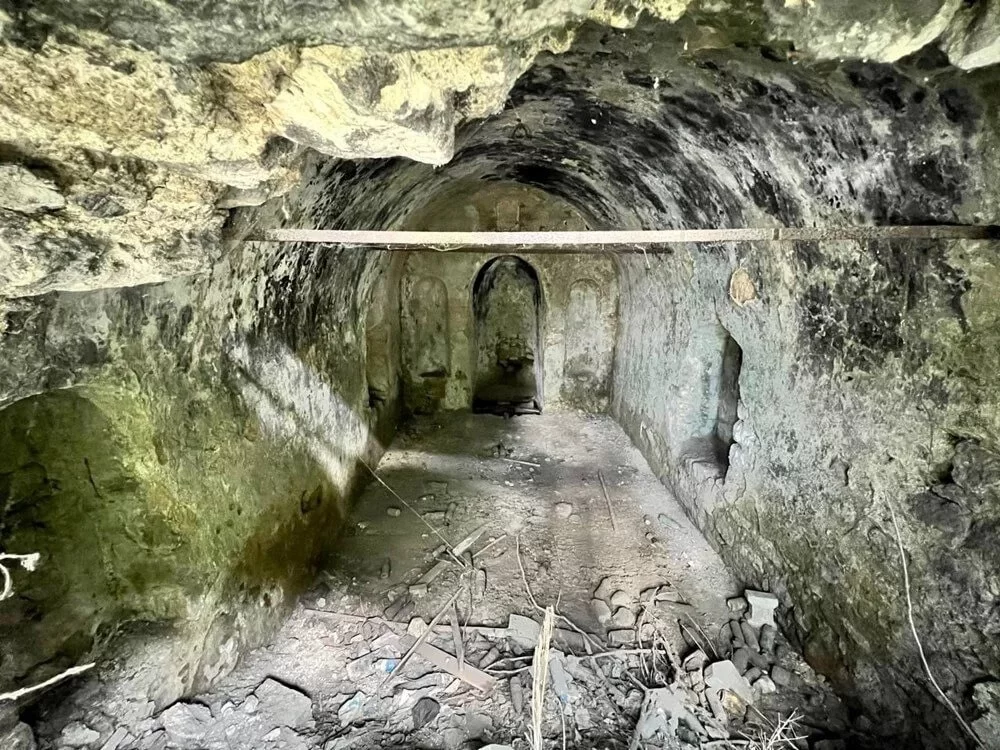
Although there were archives for storing contracts in every city, only a handful of archive buildings from the Roman Empire have been identified to date.

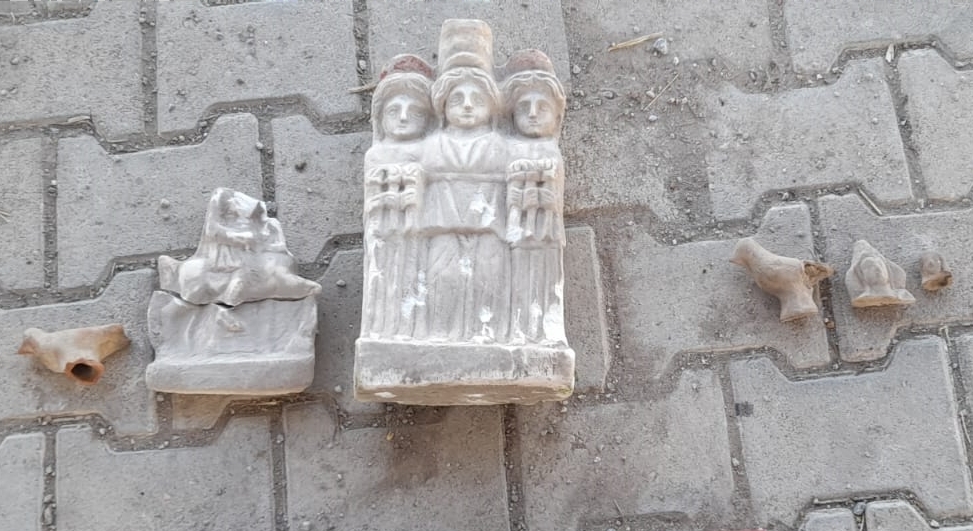
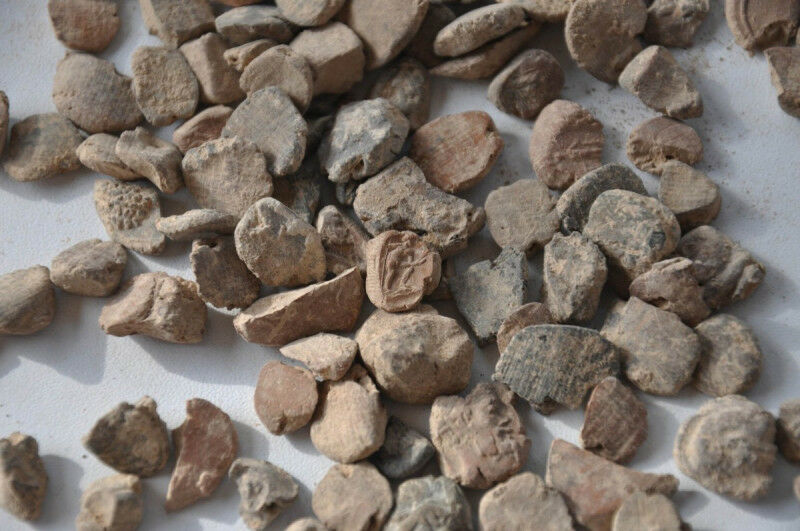
The impressions consist of stamped clay lumps that range from 5 millimetres to 2 centimetres in size. They were used to seal documents made of papyrus and parchment. The well-preserved seal impressions and their motifs also provide information about ancient administrative practice.
“The images on the official city seals are directly related to the city. They usually show their most important deities such as Jupiter Dolichenus, the city’s main god,” explains Michael Blömer.
The imprints of the smaller private seals show a wide range of images and symbols that reveal a lot about the cultural imprint of Doliche’s inhabitants. “The gods on the seals provide insights into the religious environment of the people. Mythical figures or rare private portraits indicate a strong Greco-Roman influence,” explains the scientist.
Between the mid-second and mid-third century AD, the veneration of Jupiter Dolichenus gained widespread popularity within the Roman military. Several religious structures dedicated to Jupiter Dolichenus identify him as the “deity of the Commagenians.”

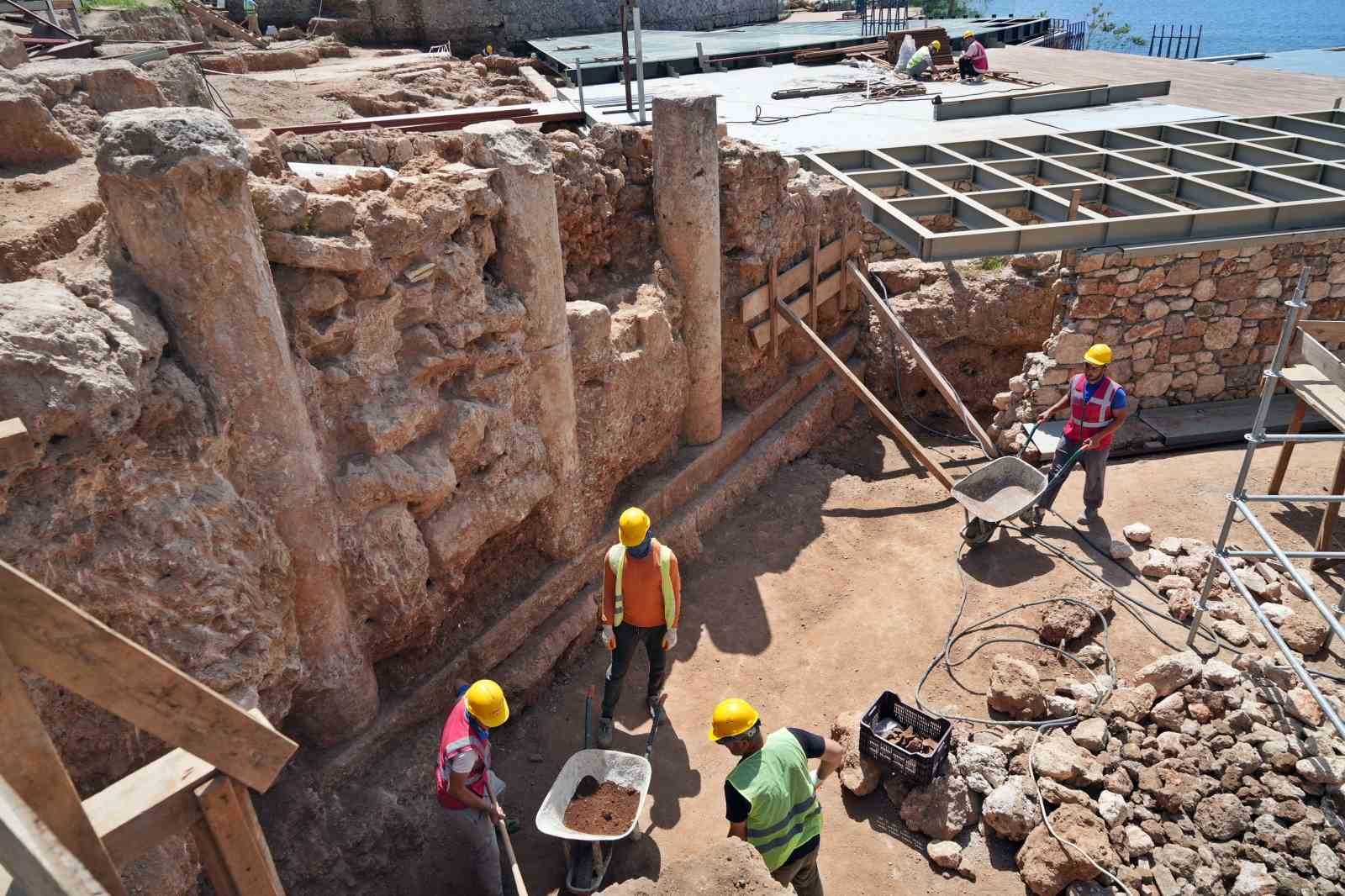
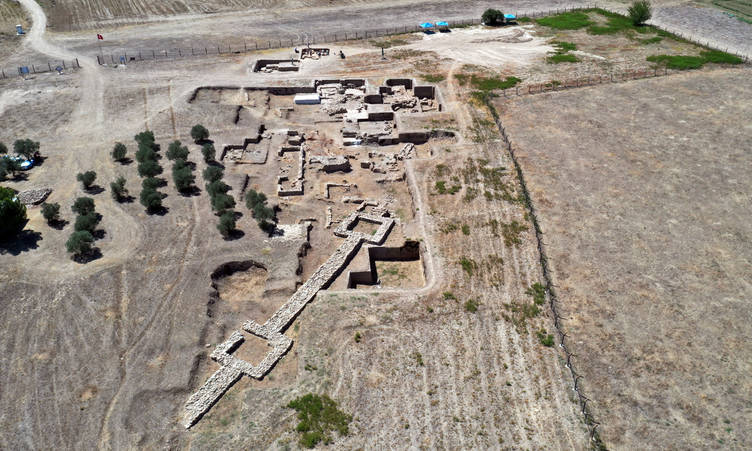
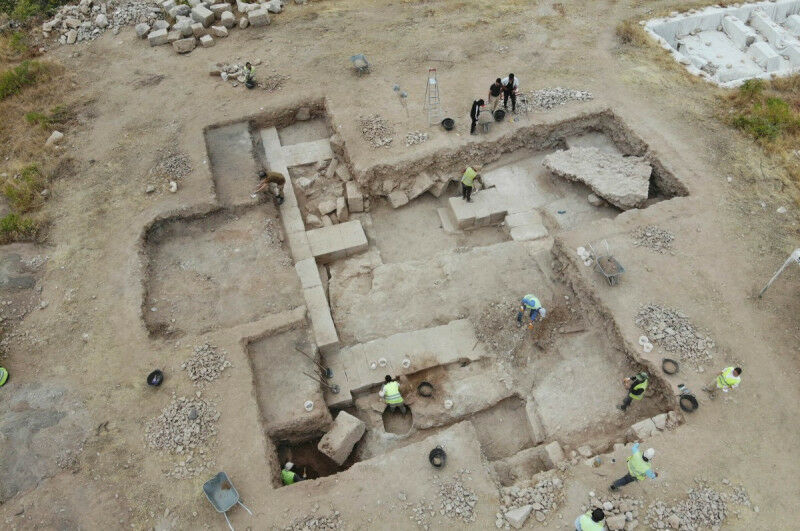
According to Engelbert Winter, all that remains of the archive building are the lower layers of the foundations, which are made of solid limestone blocks. “However, they reveal a sequence of rooms that form an elongated building complex,” he describes.
However, the precise size has yet to be determined. The building has so far been found to be eight meters wide and 25 meters long. The width of the walls also indicates that it had multiple stories. Over the course of eight weeks last summer, an international research team uncovered parts of the building.
According to the researchers: “The archive documents themselves were destroyed in a major fire, possibly in AD 253 when the Persian king, Šāpūr I, destroyed numerous cities in the Roman province of Syria.”
The city center, which also included a bath complex and a monumental temple, was not rebuilt after the fire. “This is a stroke of luck for archaeology, as it means that the condition from the period up to 253 AD has been preserved,” the researchers emphasize.
Cover Photo: © Forschungsstelle Asia Minor