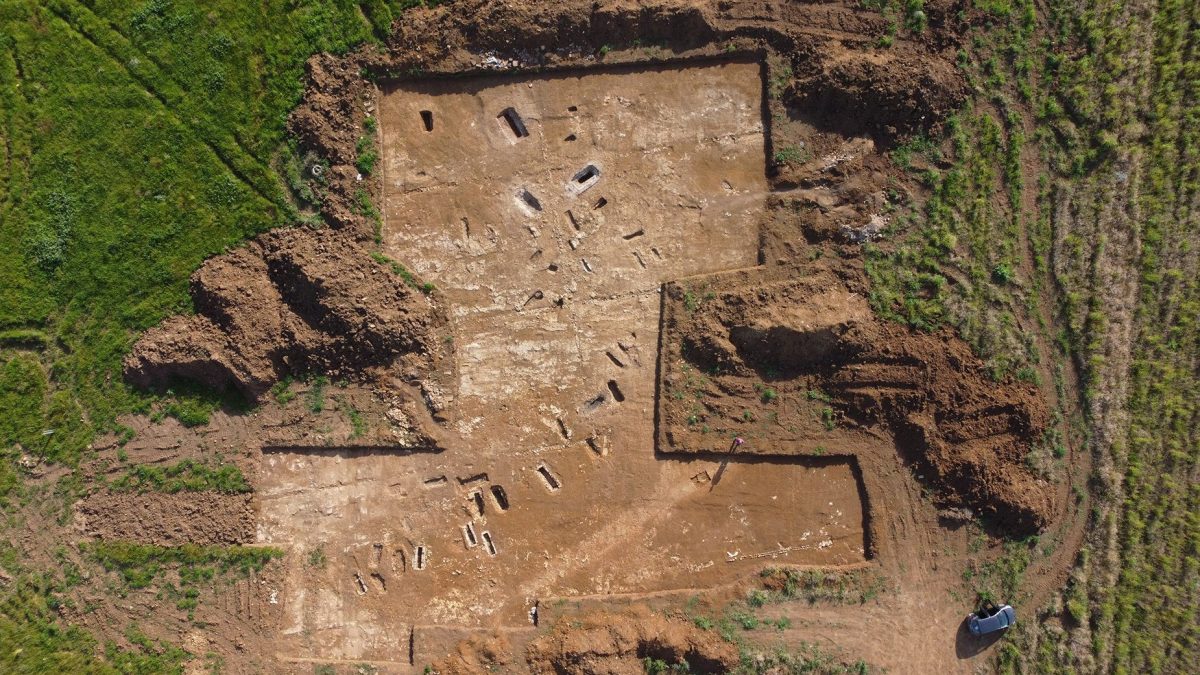
Archaeologists working on a two-year excavation effort at the site of a proposed solar energy plant in Tarquinia, north of Rome, discovered an old Roman necropolis with 67 bones buried in 57 magnificent tombs.
According to preliminary examination, the tombs’ occupants and dates range from the second to the fourth centuries AD.
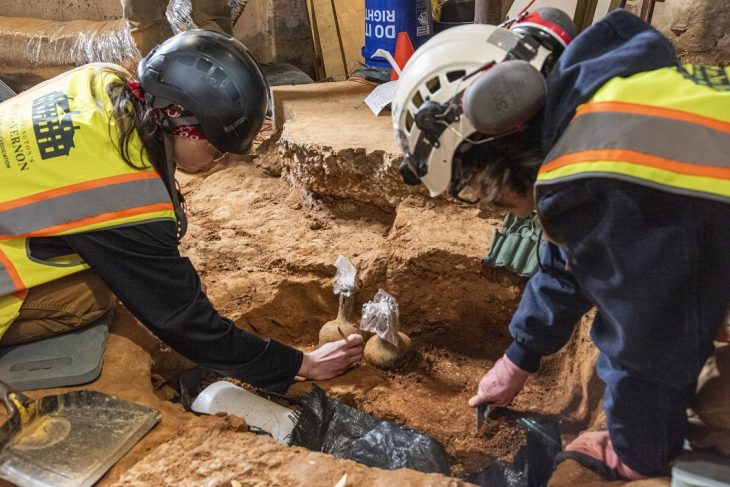
This was definitely a cemetery for powerful and affluent Roman aristocracy. The exquisite leather shoes and gold jewelry adorning the well-preserved skeletons suggest that the tombs’ architecture was modeled after that of the deceased people’s smaller-scale earthly residences.
Working for the private archaeological company Eos Arc, lead excavation archaeologist Emanuele Giannini told CNN, “We found several skeletons still wearing their expensive stockings and shoes.” “These appear to have been upper-class members of Roman families who came from the cities, given their wealth and the fact that the bones bear no indication of physical labor or stress.”
This was definitely a cemetery for powerful and affluent Roman aristocracy. The exquisite leather shoes and gold jewelry adorning the well-preserved skeletons suggest that the tombs’ architecture was modeled after that of the deceased people’s smaller-scale earthly residences.
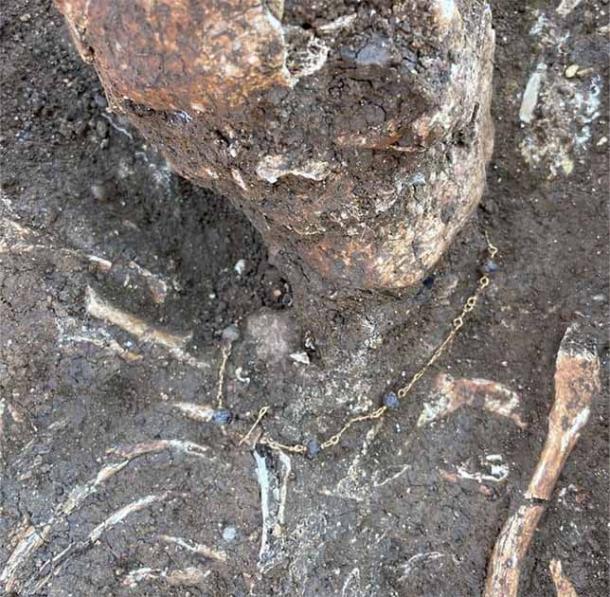

Working for the private archaeological company Eos Arc, lead excavation archaeologist Emanuele Giannini told CNN, “We found several skeletons still wearing their expensive stockings and shoes.” “These appear to have been upper-class members of Roman families who came from the cities, given their wealth and the fact that the bones bear no indication of physical labor or stress.”
Based on the variety of funerary artifacts discovered close to the remains and the opulent interior decorations and linings within the tombs, archaeologists surmise that the inhabitants intended to replicate celestial areas akin to their earthly residences. In the past, many tombs had ornate linen linings or were encircled by tiles or tiny, house-like pieces of clay.
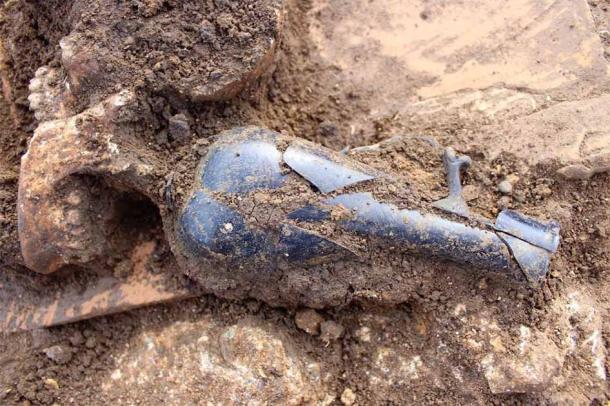

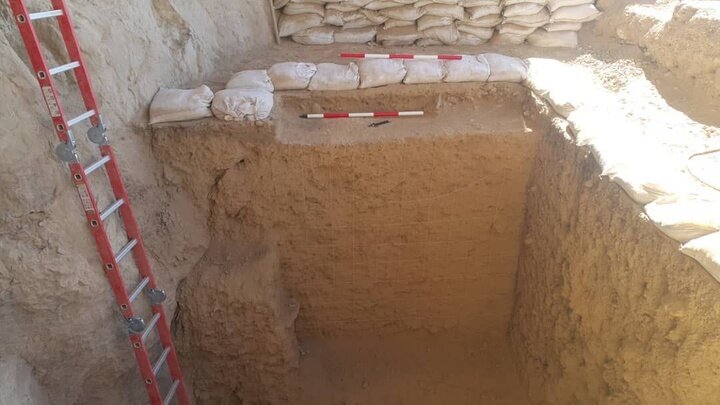
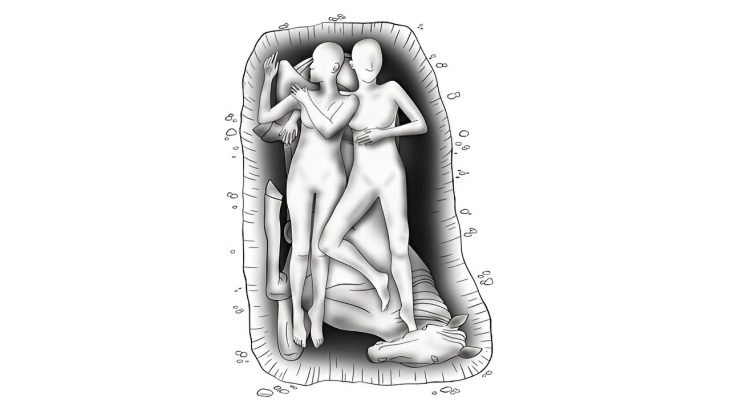
The skeletal bones were discovered buried at a depth of roughly 20 inches (50 cm), quite near the earth’s surface. The majority of the burials that were found belonged to communal groups; they were most likely constructed for two or more individuals with similar family ties. There were also multiple skeletons discovered intertwined.
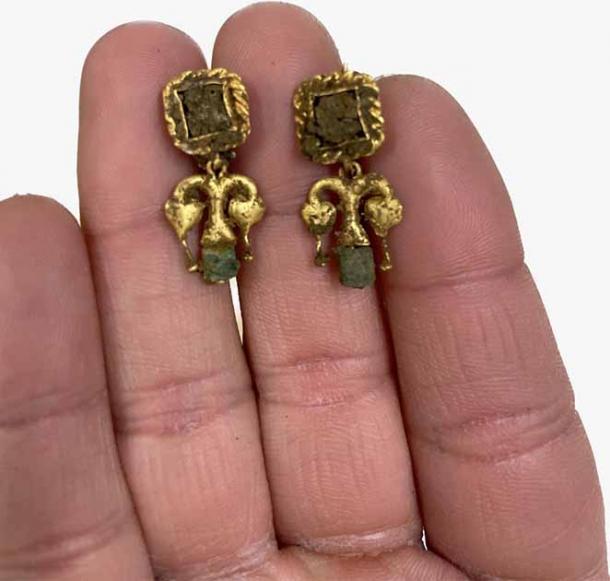

The site’s unusual state of preservation has been linked to the fact that “huge limestone blocks sticking out of the ground (made) plowing, seeding, and modern farming impossible in the area,” according to Giannini. “It has remained untouched (for) centuries.”
Authorities are confident that more hidden gems will be discovered as construction of the solar park moves to a new location nearby. The site of the necropolis will not be included in the solar park and will be roped off for safety reasons, with no public access.
Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti Paesaggio Etruria Meridionale