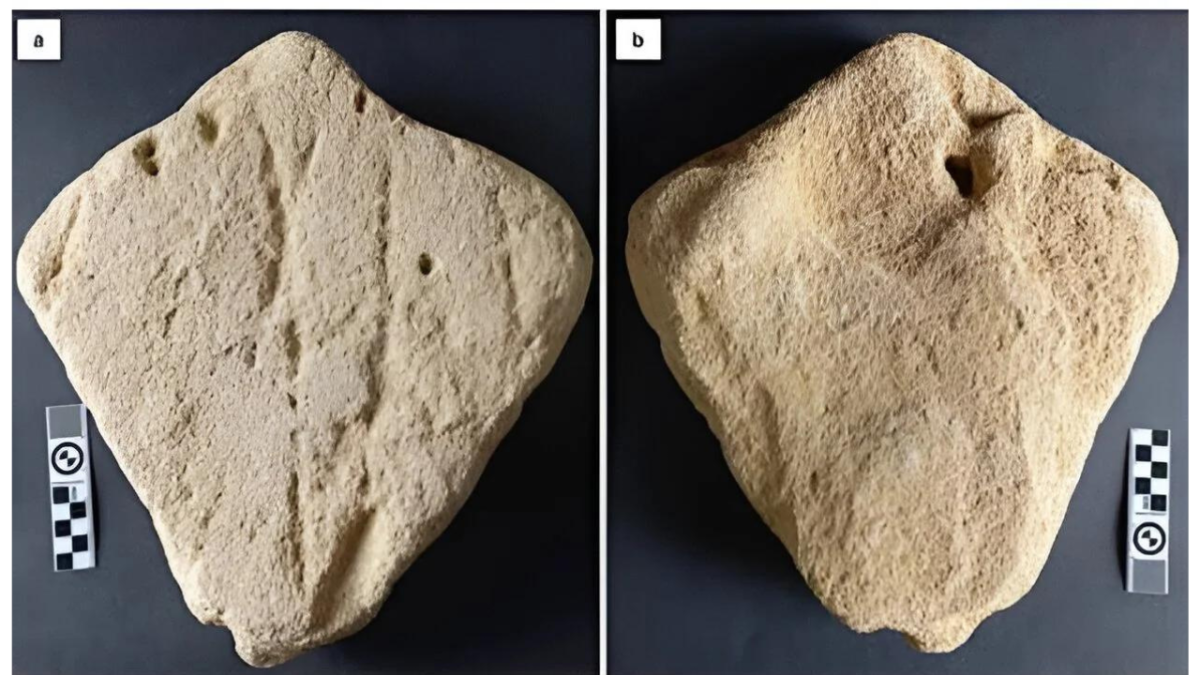
According to new research, chipped stone tools made from volcanic rock discovered in western Ukraine could be the oldest evidence of human presence in Europe.
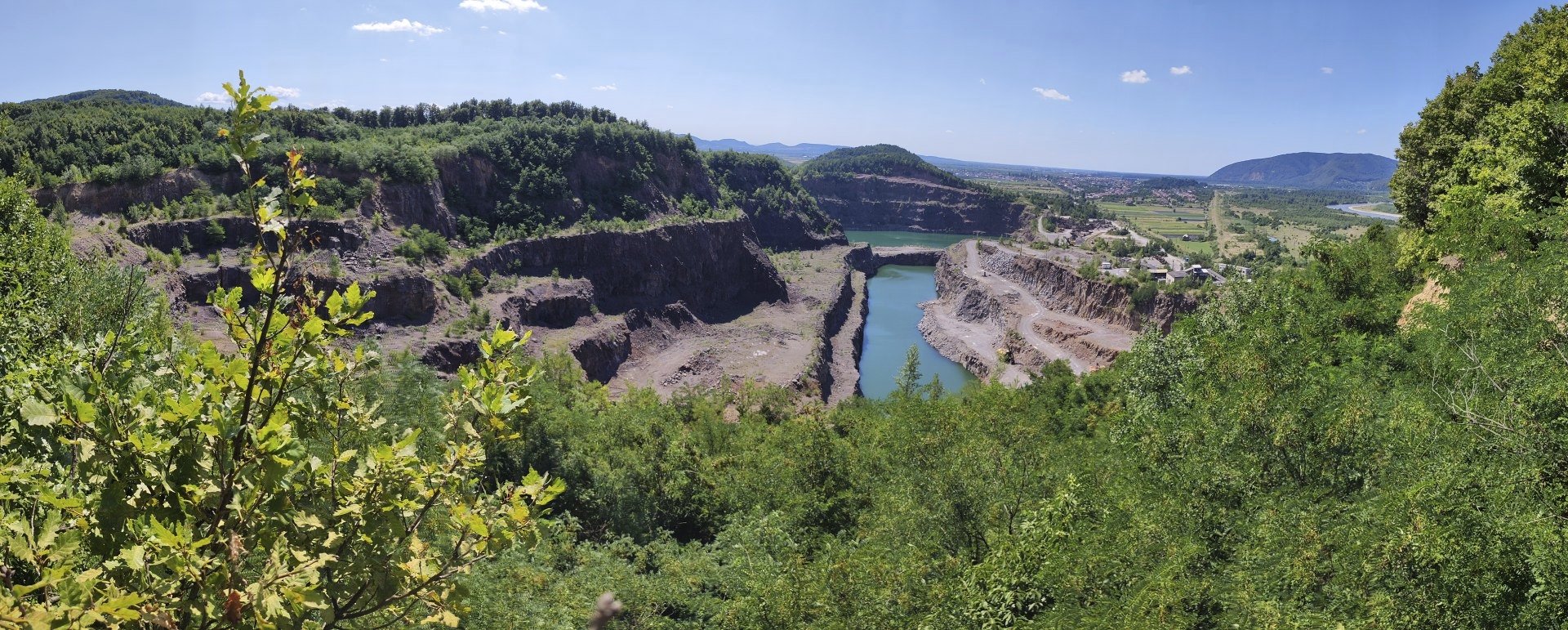
Chipped stone tools made from volcanic rock were extracted from a quarry in Korolevo in the 1970s. Archaeologists used new methods to date the sedimentary rock layers surrounding the tools to over 1 million years old.
Mads Faurschou Knudsen, a geophysicist at Aarhus University in Denmark and one of the co-authors of the study published on Wednesday, said, “This is the oldest evidence of any human species dated in Europe.”
He said it’s not certain which early human ancestors fashioned the tools, but it may have been Homo erectus, the first species to walk upright and master the use of fire.
The study was published in the journal Nature.
“We don’t have fossil remains, so we can’t be sure,” said Roman Garba, an archaeologist at the Czech Academy of Sciences and co-author.
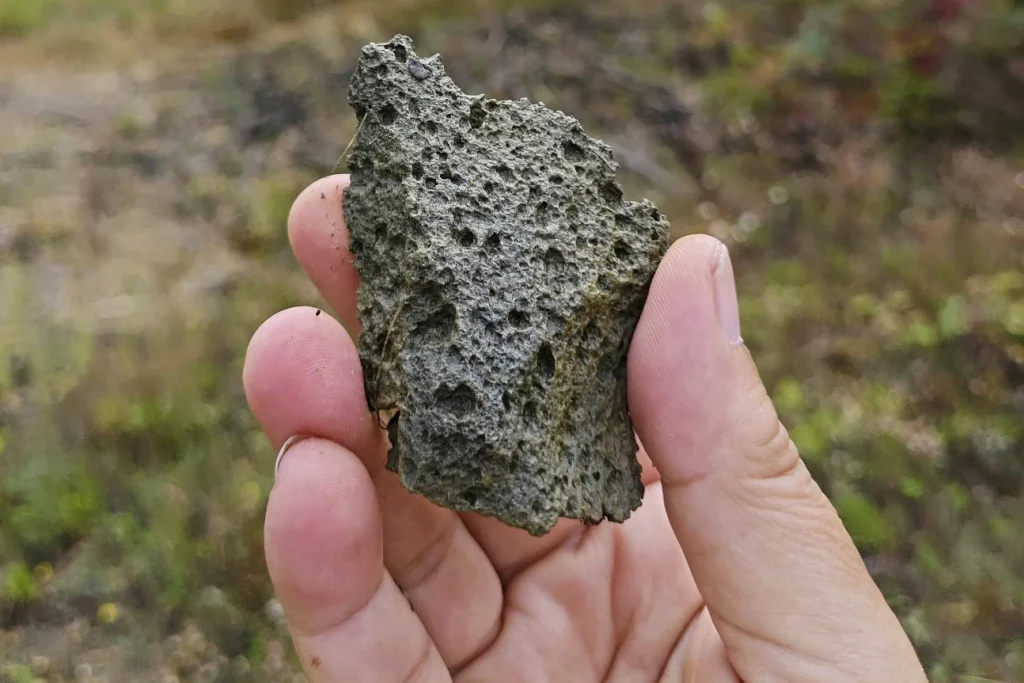

The chipped stone tools were likely used for cutting meat and perhaps scraping animal hides, he said.
The researchers suggest the tools may be as old as 1.4 million years, but other experts say the study methodology suggests that they may be just over 1 million years old, placing them in roughly the same date range as other ancient tools unearthed in Spain.
The very earliest stone tools of this type were found in eastern Africa and date back to 2.8 million years ago, said Rick Potts, who directs the Smithsonian Institution’s Human Origins Program.
The Ukraine site is significant because “it’s the earliest site that far north,” suggesting that the early humans who dispersed from Africa with these tools were able to survive in diverse environments.
“The oldest humans with this old stone tool technology were able to colonize everywhere from warm Iberia (Spain) to Ukraine, where it’s at least seasonally very cold – that’s an amazing level of adaptability,” said Potts.
Cover Photo: Gostry Verkh area of the Korolevo I archaeological site in western Ukraine in August 2023, with the Korolevo II site behind a body of water. (AP Photo)
Source. AP