The mysteries of the historical sword, which researchers have dubbed ‘Excalibur’ because of its location and which bears similarities to the legendary sword of King Arthur, have finally been solved.
The iron sword was found stuck vertically into the ground in 1994 at an archaeological site in the old settlement of Valencia, a city on Spain’s east coast.
Ahead of the 75th anniversary of Valencia’s archaeological department, the Valencian City Council said on April 22 that it had decided to catalog and study artifacts in its collection. One of these artifacts was the Excalibur sword.
However, the work of the Archaeological Service of the Valencian City Council (SIAM) has shed light on the age and origins of the sword. Through rigorous dating techniques, they have determined that the sword dates from the 10th century, firmly placing its antiquity more than a thousand years ago.
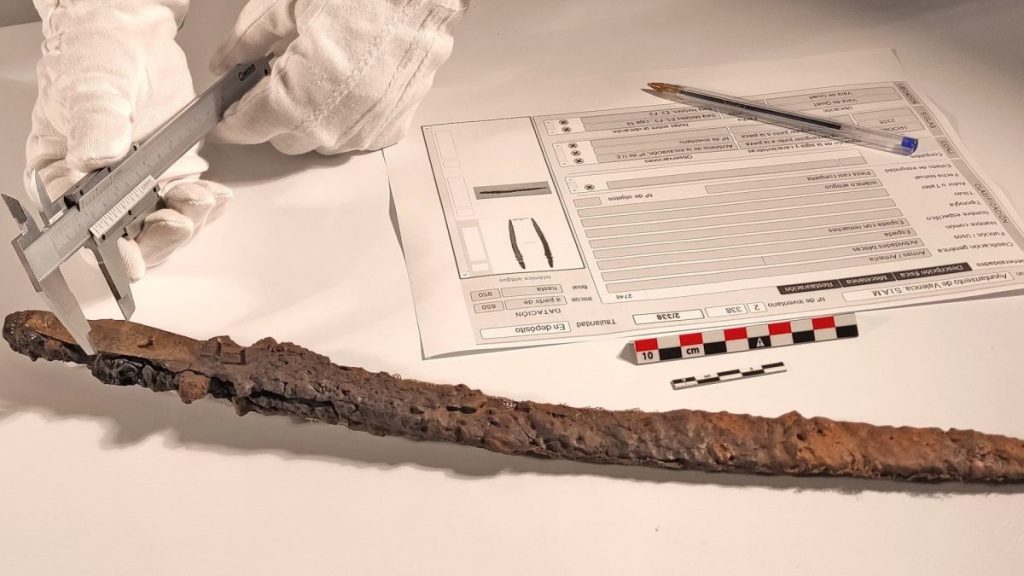

SIAM’s analysis shows that this sword represents the first discovery of its kind from the Islamic period in Valencia. Swords from this period are generally scarce in Spain, especially in Valencia, where the composition of the soil posed a challenge to conservation efforts.
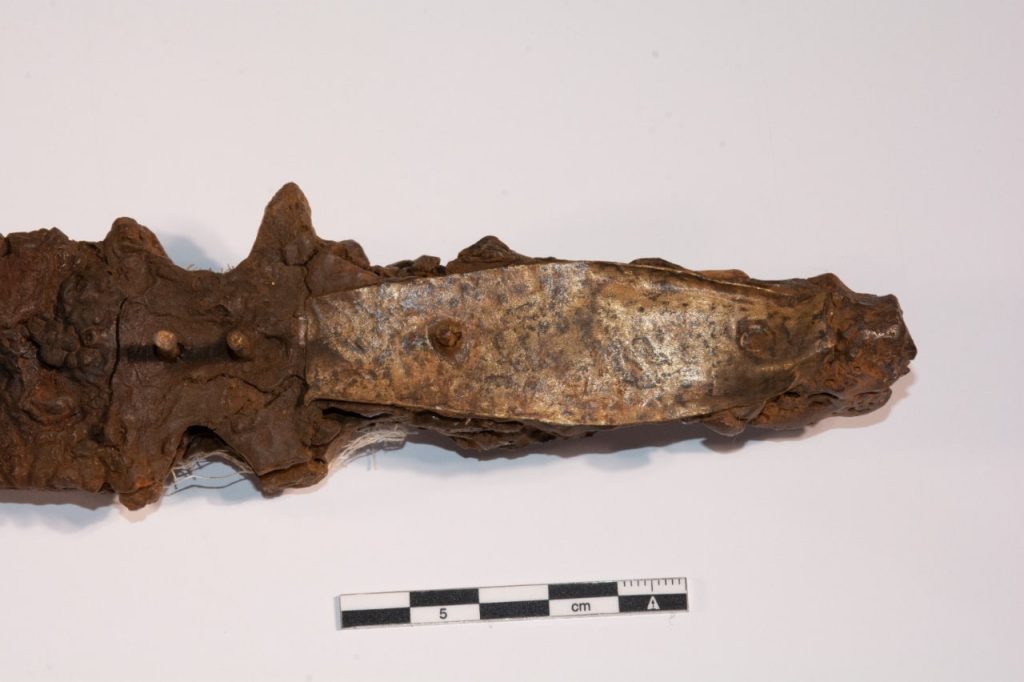
Archaeologist José Miguel Osuna, who led the research project on “Excalibur” earlier this year, found that the 18-inch blade belongs to the Islamic period because of its hilt, decorated with bronze plates and notches for handling. The sword’s curved metal tip caused confusion among researchers who thought it might have belonged to the Visigoths, but Osuna later debunked that idea.
The sword’s size and lack of a hand guard suggest that a mounted warrior may have wielded it during the Andalusian caliphate. Municipal technicians are clear that its origins date back to the Islamic period of Balansiya, although it may show evolutionary features from Visigoth models. So far, only one comparable example has emerged, unearthed during excavations of the Medina Azahara, the famous caliphate city built by Abderramán III in Córdoba.

The Islamic period in Spain began in 711 AD and ended in 1492 AD.
“Thanks to an archaeology scholarship raised by the Valencian City Council, archaeologist José Miguel Osuna is carrying out a detailed study of the analysis of metallic objects dating from the Roman period to the late medieval period, in which a new and exceptional find has come to light, which we call Excalibur de Roc Chabàs, very similar to the legendary sword of King Arthur.” José Luis Moreno, Valencia’s councillor for cultural action, heritage and cultural resources, said in a press release.
Cover photo: SERVICI D’ARQUEOLOGIA DE L’AJUNTAMENT DE VALÈNCIA SIAM