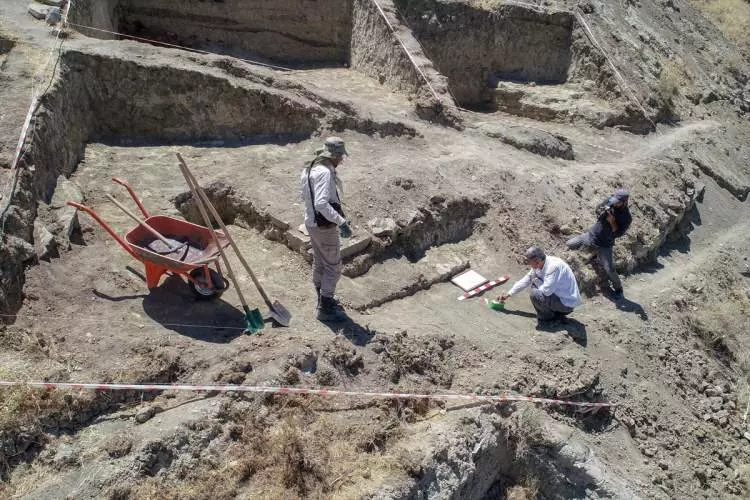
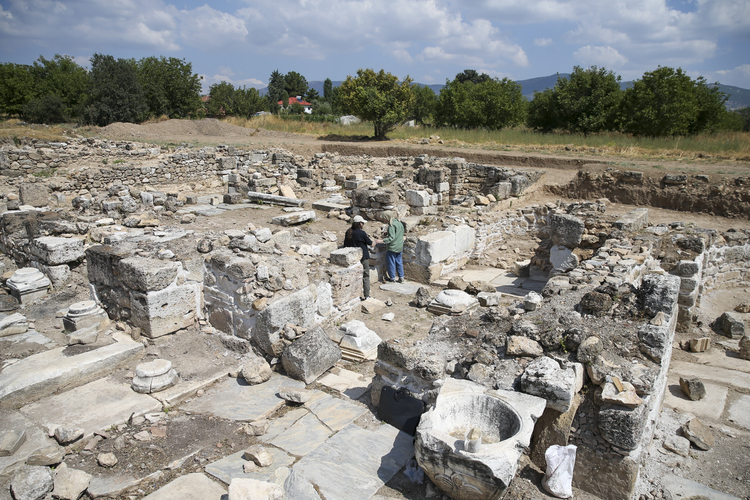
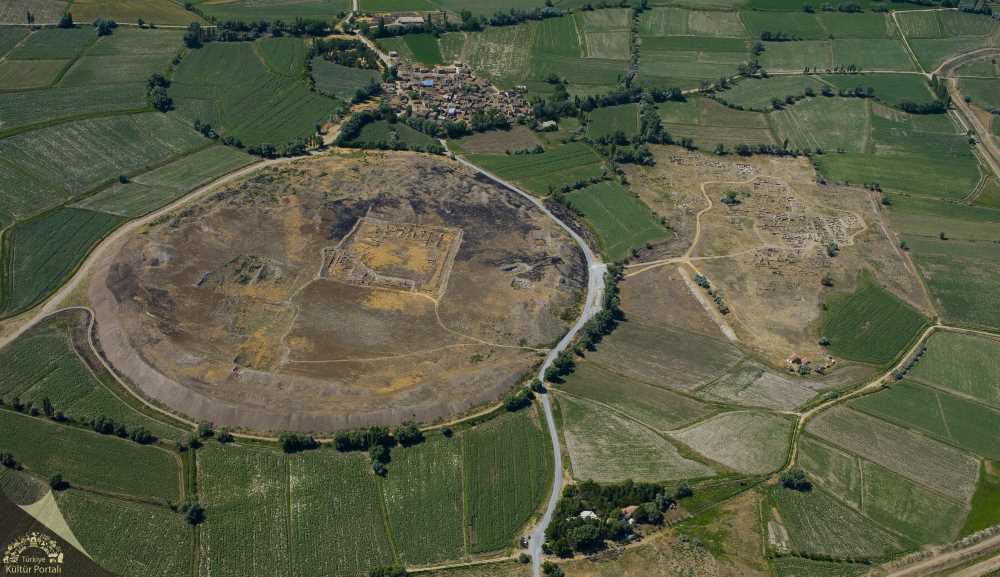
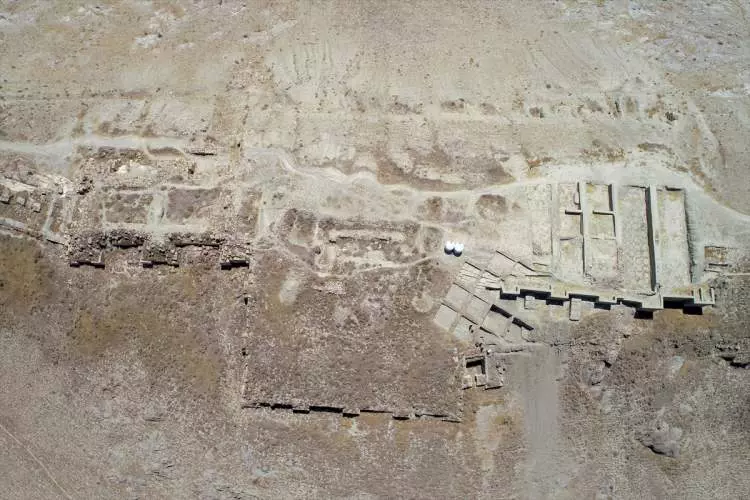
During the excavation works carried out at Çavuştepe Castle, which was built by King Sarduri II of Urartu in 750 BC, along with the necropolis area to the north, it was observed that the Urartians used terracing method to mitigate the destructive effects of earthquakes.
The Kingdom of Urartu ruled over a vast geographical area encompassing parts of present-day Eastern Turkey, Western Armenia, and northwestern Iran between 860 BC and 590 BC.

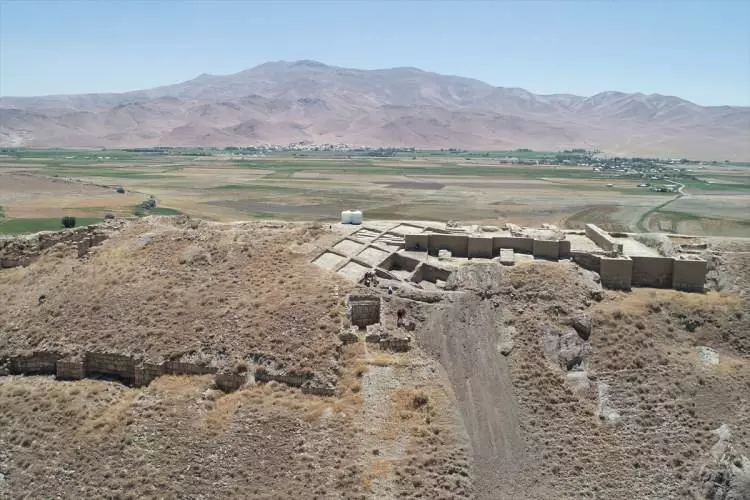
Çavuştepe Castle excavations are being conducted by a team of 24 experts, including an anthropologist, metal specialist, archaeologist, urban planner, art historian, architect, and restorers, under the leadership of Prof. Dr. Rafet Çavuşoğlu, who is the Dean of the Faculty of Literature at Van Yüzüncü Yıl University (YYÜ).
The excavations revealed that the inner and outer walls of the castle are connected to each other through structures that are 2 meters wide and 20 meters long, constructed using the terracing method to prevent collapse during potential earthquakes.
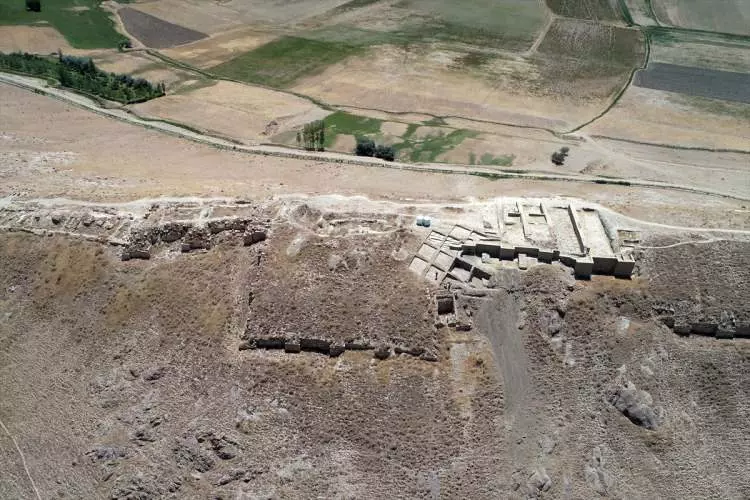

Çavuşoğlu stated, “We have evaluated that the castle experienced an earthquake in the 7th century BC. After this earthquake, we observed reconstruction activities. We determined that the section between the inner and outer walls was connected using the terracing method, approximately 2 meters wide and 20 meters long. Support walls were constructed between the walls. There are still many questions about the mystery of the castle, but we have almost solved the part related to the earthquake. It was granted to us in this year.”
Çavuşoğlu mentioned that during the excavations, they came across a hearth, indicating that the area had experienced a fire in the past. As a result of this fire incident, they determined that there was a reconstruction effort. In addition to this, in the necropolis area to the north of the castle, they have obtained significant data regarding Urartian burial customs.

He said, “Every year, we come across clues that surprise us in the necropolis. We have experienced many firsts here and acquired additional information. Especially, in the ‘cremation’ called urns, seals, and ornaments are found in the female skeletons.”
Çavuşoğlu stated, “This also indicates that this area belonged to the ruling class. It provides significant clues about the social and commercial life of women. So far, we have come across two types of burial techniques. One involves cremation, and the other involves burying the body. We have also encountered many different types of tombs.”
Cover Photo: AA