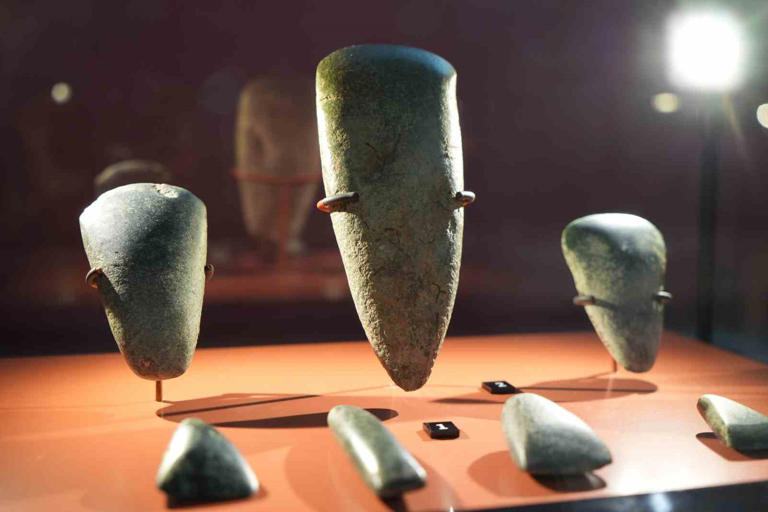
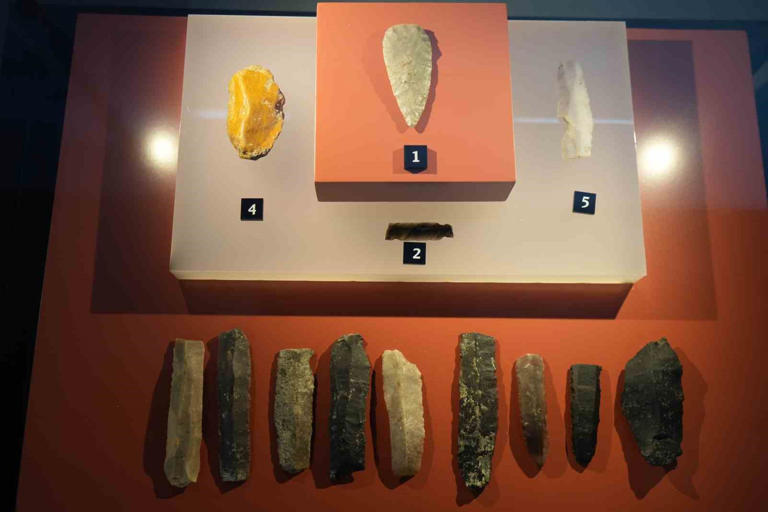
Obsidian (volcanic glass rock) blades and many tools belonging to the Chalcolithic Age between 5900-3200 BC, found during the excavations at Dündartepe mound, are on display at the Samsun Museum.
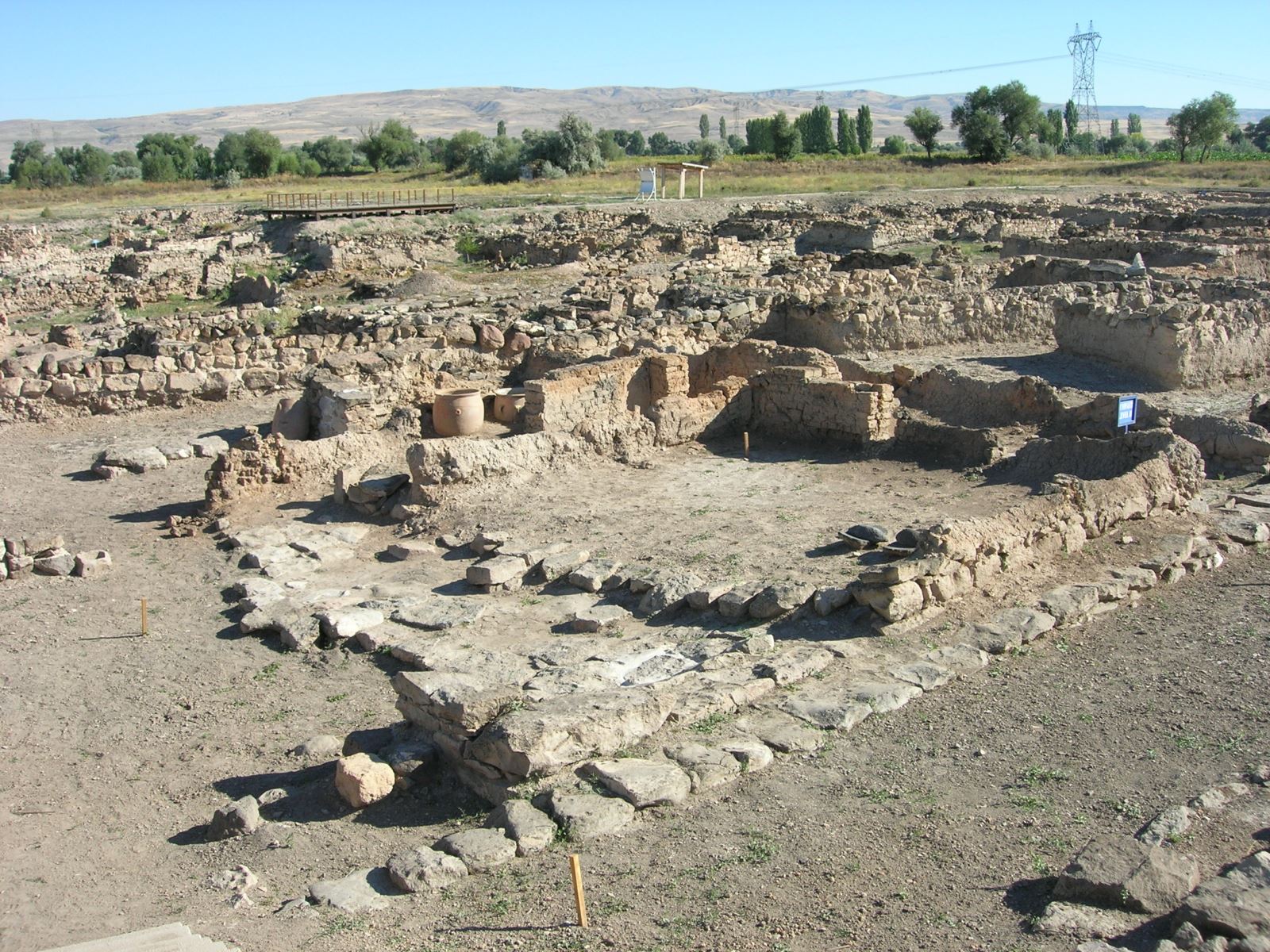
Dündartepe Mound is located in the İlkadım district of Samsun. Today the mound is located in the city center.
Dündartepe is also known as Öksürük Tepe. In the past, the people of the region gave this name to Dündartepe because treasure hunters constantly coughed while digging.

The mound is located on the banks of the Mert Stream, among fertile soils. The hill is 220 x 200 meters in size and 15 meters high.
Excavations began in 1940-41 under the direction of Prof. Dr. İsmail Kılıç Kökten and Prof. Dr. Nimet Özgüç.
During the simultaneous excavations that have been going on for seventy years, 3 cultural levels were identified in the settlement with 2 sections defined as the lower and upper city.

The oldest settlement layers (Level 1) are dated to the Early Chalcolithic Age. The 2nd layer of Dündartepe, which was inhabited at the same time as Alisar 2 and Alacahöyük 4th layer, is dated to the Early Bronze Age.
In the publications where the first researches and their results are shared, the dating of the 3rd layer, which is dated to the Hittite period, is discussed with current findings.
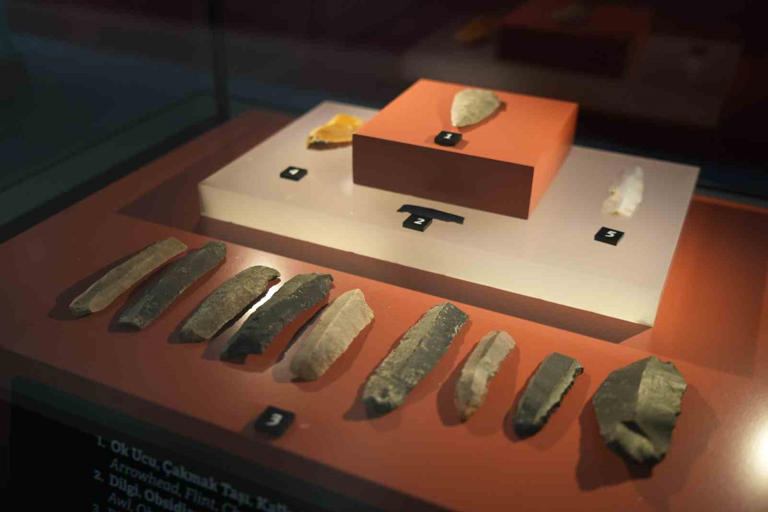

The volcanic glass rock slice from the Chalcolithic Age between 5900-3200 BC, discovered during excavations, is on display at the recently opened Samsun Museum.
Among the finds from Dündartepe, which are exhibited in a special area in Samsun Museum, there are also stone, serpentine axe, flint arrowhead, obsidian (volcanic glass rock) blade, flint blade, radiolarid blade and chalcedony blades from the Chalcolithic Age.
Cover Photo: IHA