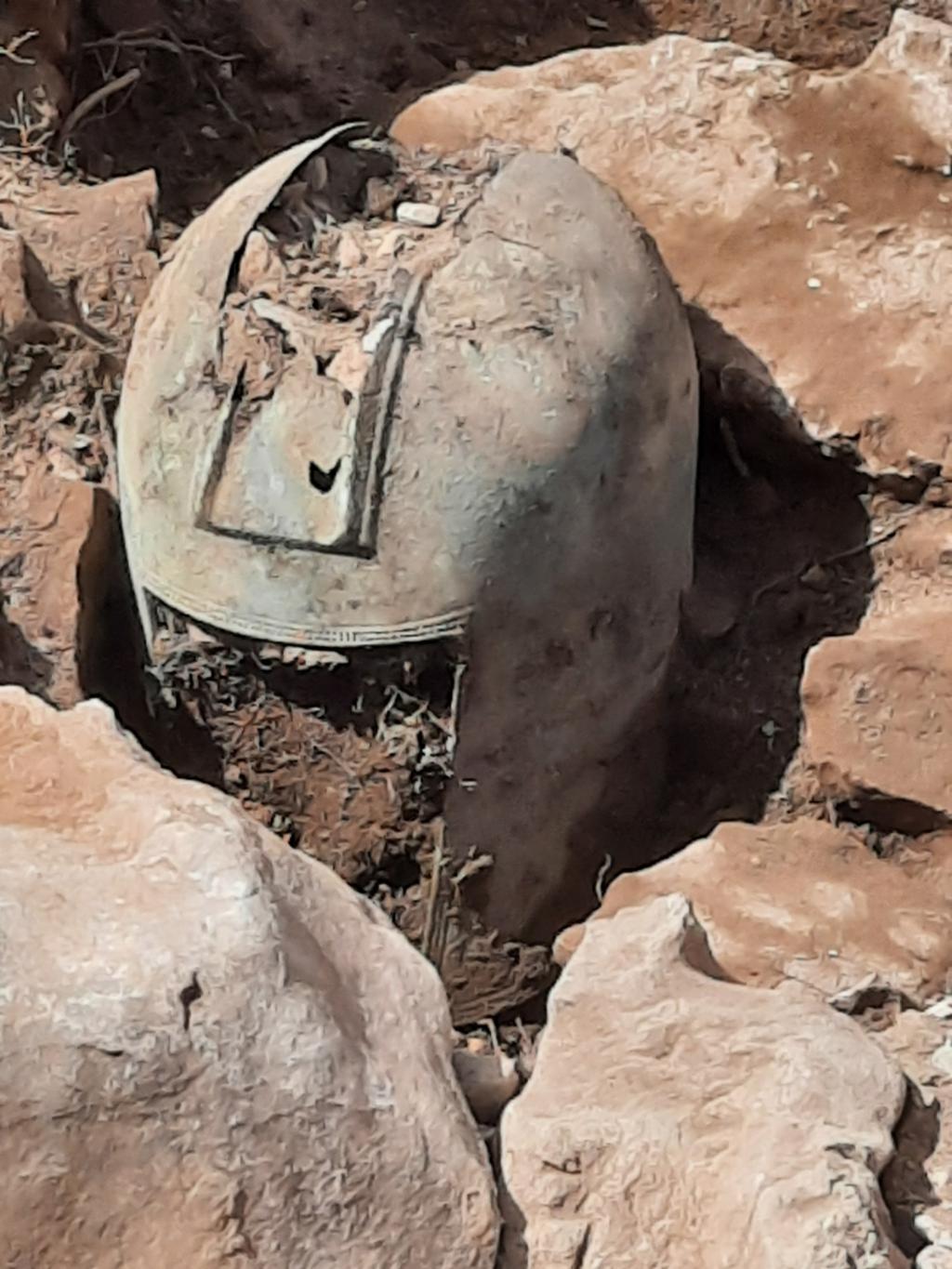
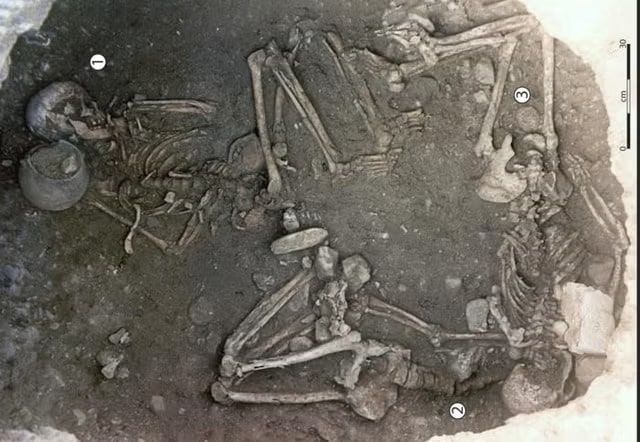
A Greek-Illyrian helmet more than 2,500 years old was discovered at the Gomile cave burial site in the village of Zakotorac on the Pelješac peninsula in Croatia, where rich graves from the second half of the 1st millennium BC were discovered.
The discovery was made by archaeologists from the Dolenjski Museums.
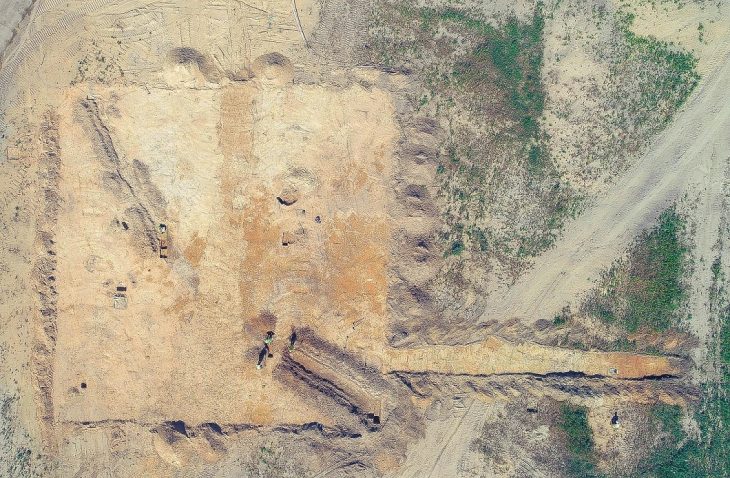
Excavations at the Gomile cave burial site have been ongoing since 2020.
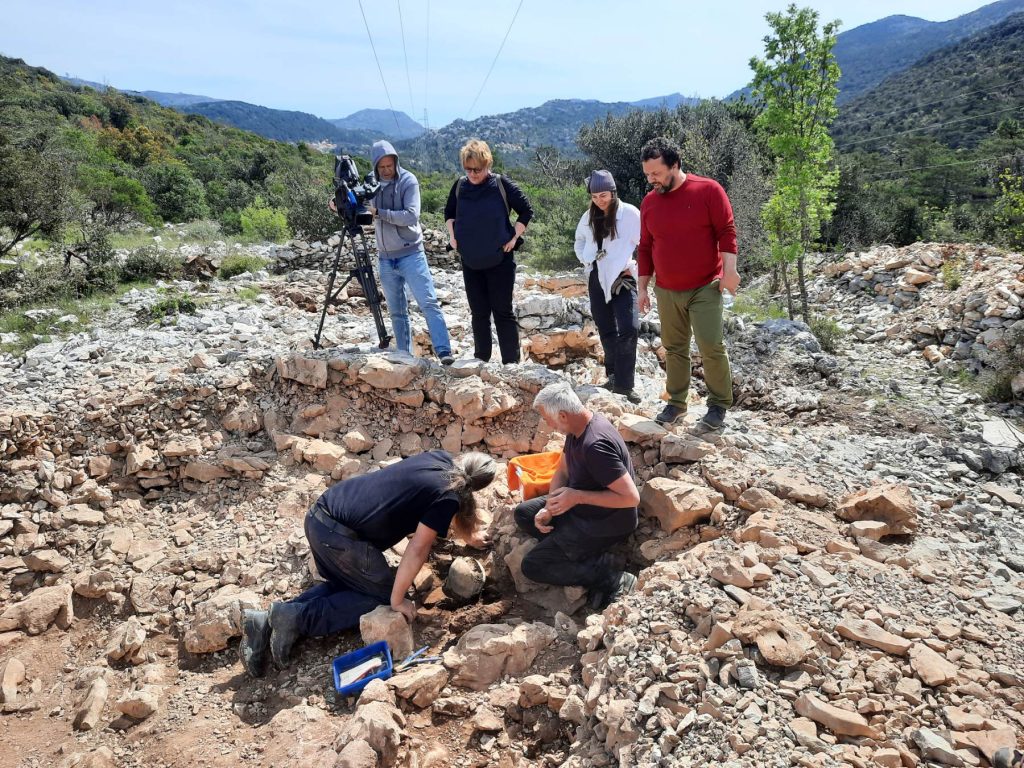

The helmet is the second Greco-Illyrian helmet found in the Gomile excavations. The previous example was found in a tomb with fragments of iron weapons and therefore probably belonged to a member of the warrior elite buried there. The recently discovered helmet was found in a dry-stone-walled annex to a tomb, so archaeologists believe it may have been a votive bed.
Greco-Ilyrian type helmets originated in the Peloponnese Peninsula of Ancient Greece, where they probably evolved from the Kegelhelm (or Kegel type) of the Archaic Period.
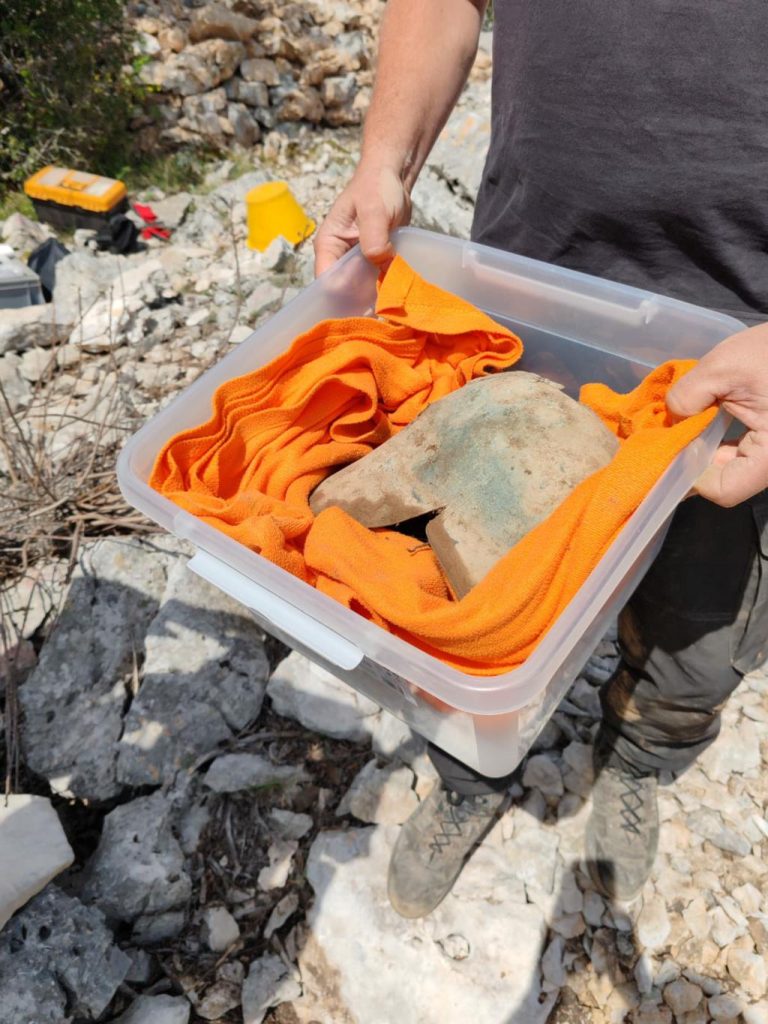

Helmets are of different types and dates. Discovered in 2020 is an open-faced helmet with a rectangular cutout on the face, edged with a decorative border, a variant actively used in Greece and Illyria in the 4th century BC.
It is the latest helmet dating to the 6th century BC. Few examples of the 4th century BC type have survived, only about 40 are known in Europe, and 6th century BC helmets are even rarer. It is unprecedented to find two different Greek-Ilyrian helmets in one area.
What is very interesting is that two different types appear here in the same place, which actually speaks about the continuity of the power of the community concerned. Dr. sc. Hrvoje Potrebica from the Department of Archaeology at the Faculty of Philosophy in Zagreb said that these helmets were always a symbol of some kind of status and power.
It was used by the Ancient Greeks, Etruscans, Scythians and Illyrians between 700 and 500 BC.
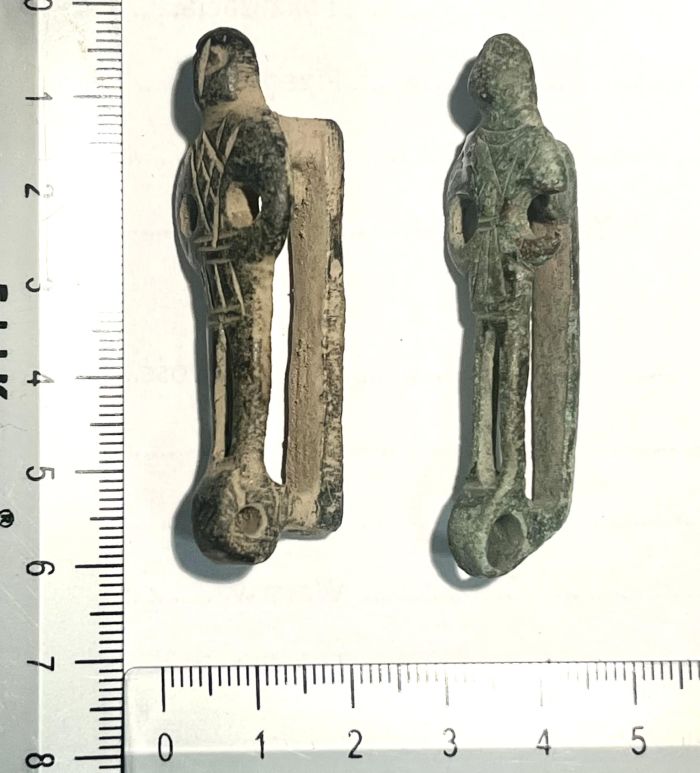
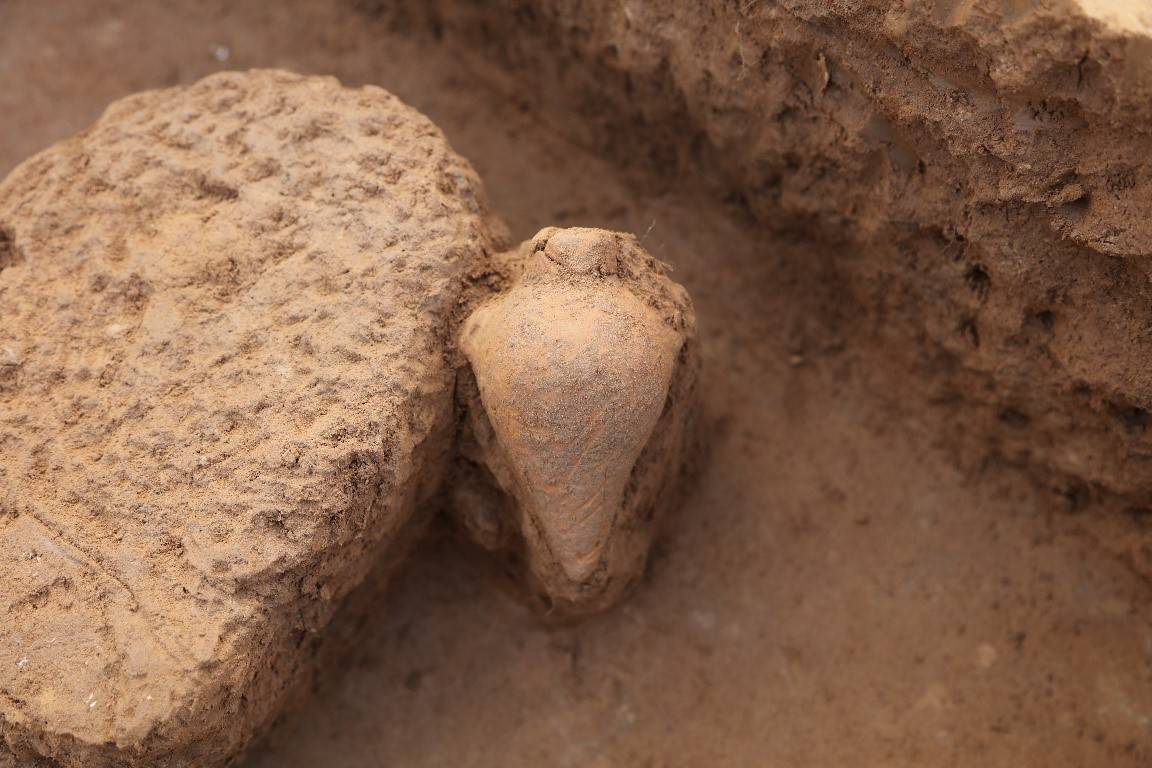
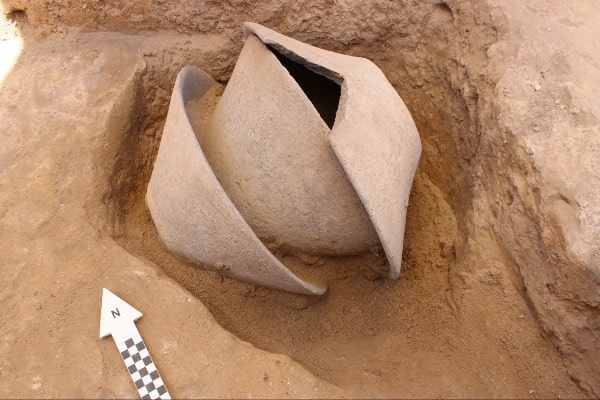
The extremely valuable and rare helmets accompany other exceptional grave goods, including 15 bronze and silver fibulae, 12 pins, spiral bronze jewelry, bronze tweezers, hundreds of glass and amber beads, a bronze diadem and more than three dozen vessels of Greek origin, most of them made in Attica and Italic workshops.
These were the most valuable pieces of pottery of the time. Had they been obtained through trade, the cost would have been very high. It is also possible that they were obtained through piracy, a pursuit for which Illyrian warriors on the Adriatic coast were famous.
Cover photo: Dolenjski Museum