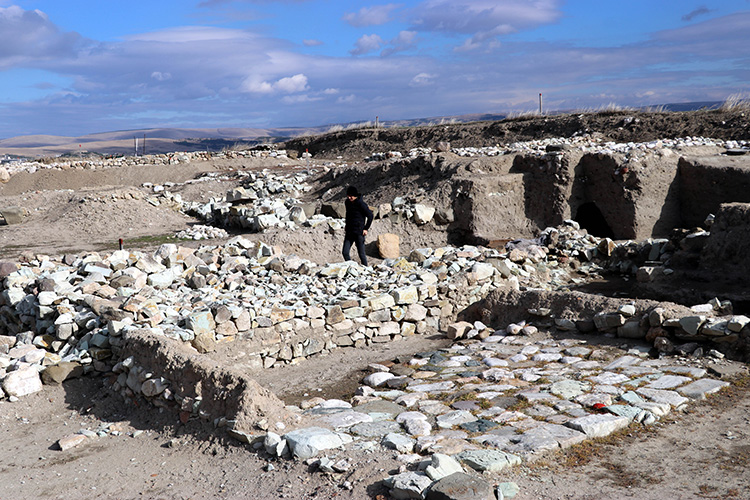
Stones inscribed with ‘Allah’ in Arabic were found among the ruins of a Byzantine church in the 1001 churches region of Karaman.
The 1001 churches were frequented by Christian pilgrims on their way from Europe to Jerusalem and one of the three most important Christian centers of late antiquity.
Located in the north of Karaman province, on the northern slopes of Karadağ, 1001 churches is about 50 kilometers from Karaman city center.
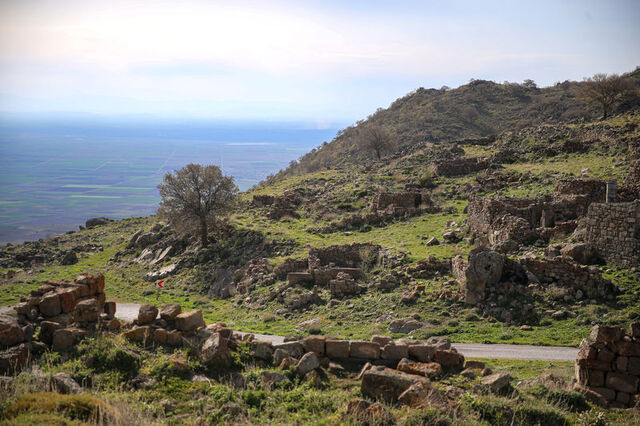

The region is known to be a sacred area since the Hittite period. During the Byzantine period, it became the most important religious center of the region.
There are approximately 50 Byzantine church ruins in the region. Although the name of 1001 churches in the ancient period is not known exactly, it is associated with the ancient city of Barata in some sources.
In the historical area located on the foothills of extinct volcanic Karadağ, Necmettin Erbakan University Faculty of Social Sciences and Humanities, Department of Art History, Early Christian and Byzantine Arts Department Head of the Department of Early Christian and Byzantine Arts Dr. Lecturer İlker Mete Mimiroğlu is conducting a study under the presidency.
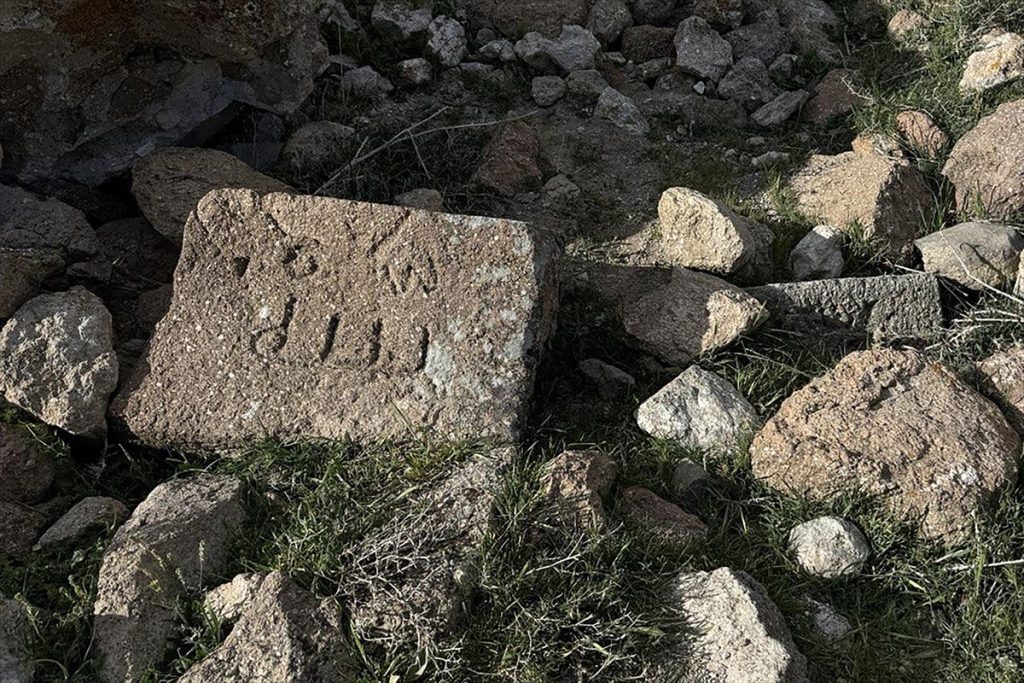

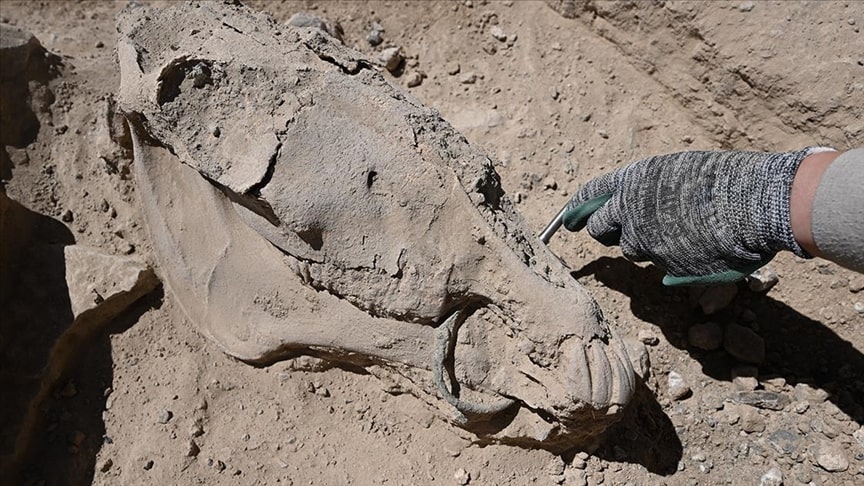
New findings were found in the Archaeological Survey of the Eastern Roman Period Religious Architecture of Karadağ 1001 churches, which was initiated last year with the permission of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism.
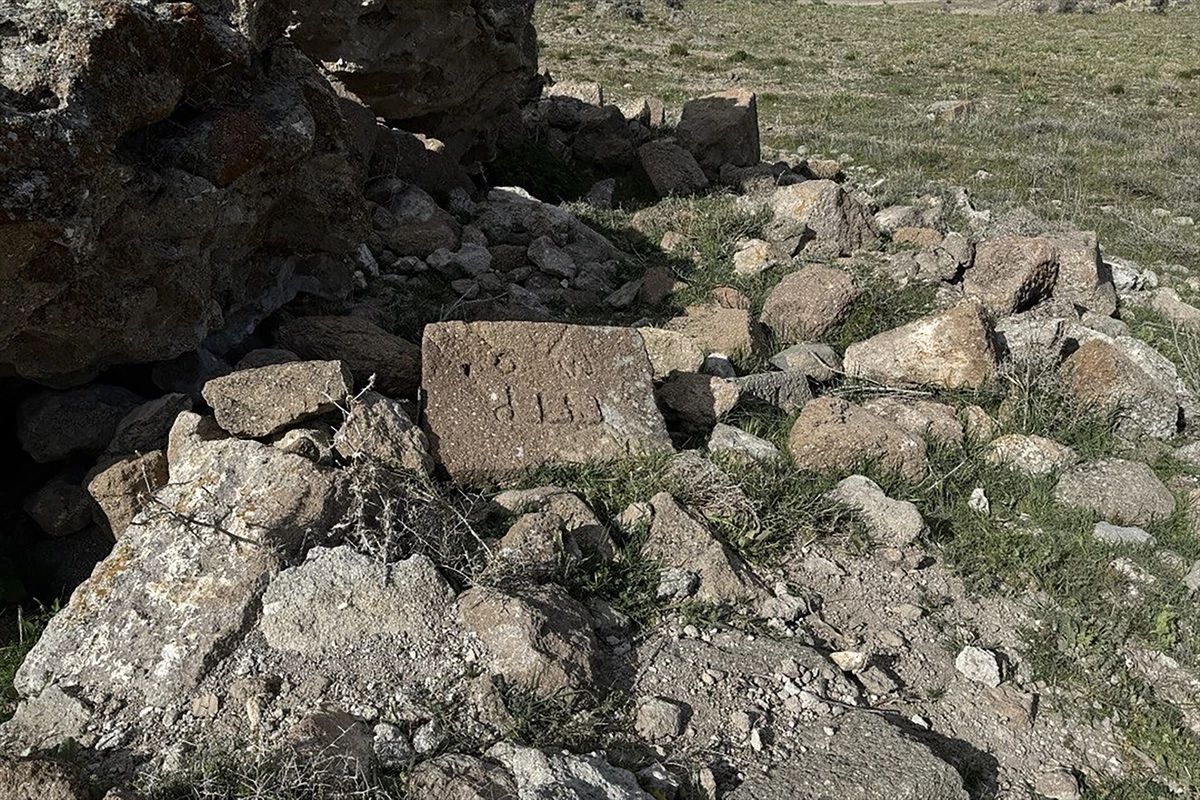
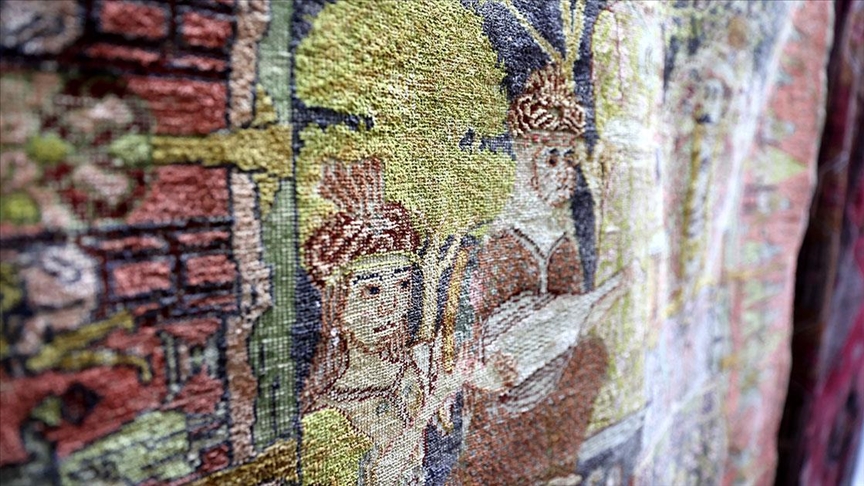
Among the ruins of a Byzantine church destroyed by a massive earthquake in 1900, the research team found the Arabic inscription “Allah” on 4 stones.
İlker Mete Mimiroğlu stated that conquest raids were organized to ancient cities and settlements in Central Anatolia during the early Islamic period (700-800s) and shared the following information.
“These finds should also be found in Central Anatolia because we think that there should be traces of different cultural assets such as masjids and tombstones in many places, not just writings. In this context, we also look at the studies from that point of view. The discovery of the inscription ‘Allah’ made us doubt whether it is a trace of this period. The interpretation of this requires specialization because there is no specific date. Therefore, we get this information from our professors in different disciplines. We have professors from different disciplines in our team. With the contributions of these professors, we will be able to reach clear conclusions by analyzing the documents and information we have.”
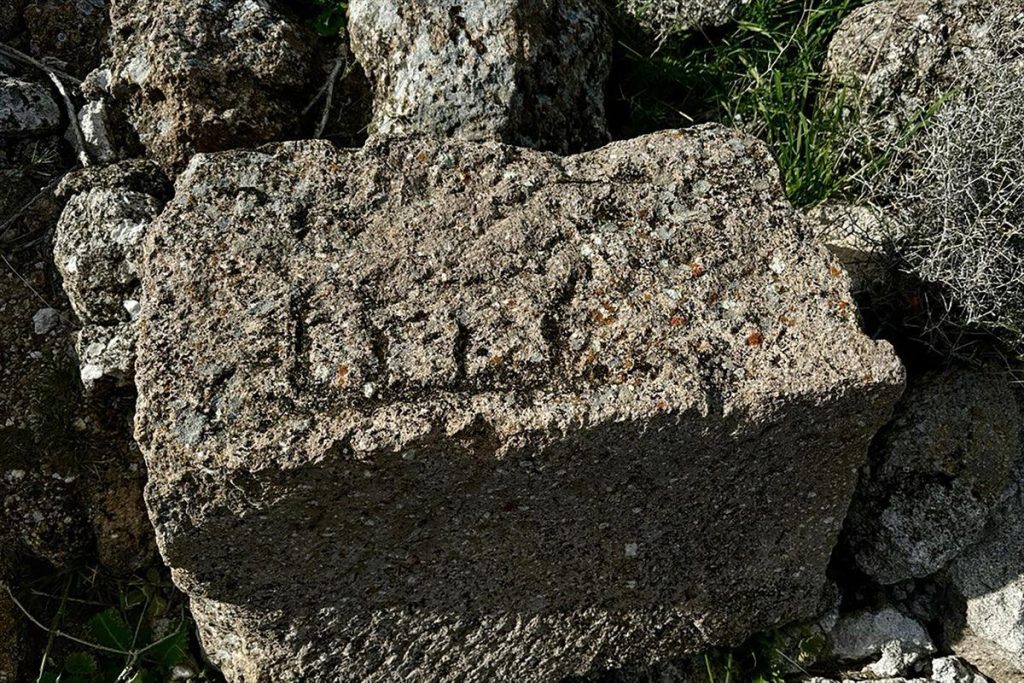
Mimiroğlu stated that 4 different words “Allah” engraved in Arabic script on the stones of the church structure were recorded in the inventory and said: “It is a large church in terms of its structure, it has been destroyed. Although it was a little more intact in the early 1900s, today it has been largely destroyed. So ancient period inscriptions, shapes… It was quite exciting to see such an Islamic form. It made us think that it was old not only in terms of form and typeface but also in terms of processing and trace. In this context, and the fact that it was found in a very rural area and that there were more than one example, brought to mind the possibility that these artifacts may belong to the early Islamic period. We further clarified our studies and examinations in the region and made the determinations. Now we are in the process of evaluating the data with our expert professors.”
















